(Peer-Reviewed) Non-volatile tunable multispectral compatible infrared camouflage based on the infrared radiation characteristics of Rosaceae plants
Xin Li 李鑫 ¹, Xinye Liao 廖欣叶 ¹, Junxiang Zeng 曾俊翔 ¹, Zao Yi 易早 ², Xin He 何新 ¹, Jiagui Wu 吴加贵 ³, Huan Chen 陈欢 ¹, Zhaojian Zhang 张兆健 ¹, Yang Yu 于洋 ¹, Zhengfu Zhang 张振福 ¹, Sha Huang 黄沙 ¹, Junbo Yang 杨俊波 ¹
¹ College of Science, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
中国 长沙 国防科技大学理学院
² Joint Laboratory for Extreme Conditions Matter Properties, Southwest University of Science and Technology, Mianyang 621010, China
中国 绵阳 西南科技大学 极端条件物质特性联合实验室
³ School of Physical Science and Technology, Southwest University, Chongqing 400715, China
中国 重庆 西南大学物理科学与技术学院
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2025-07-09
Abstract
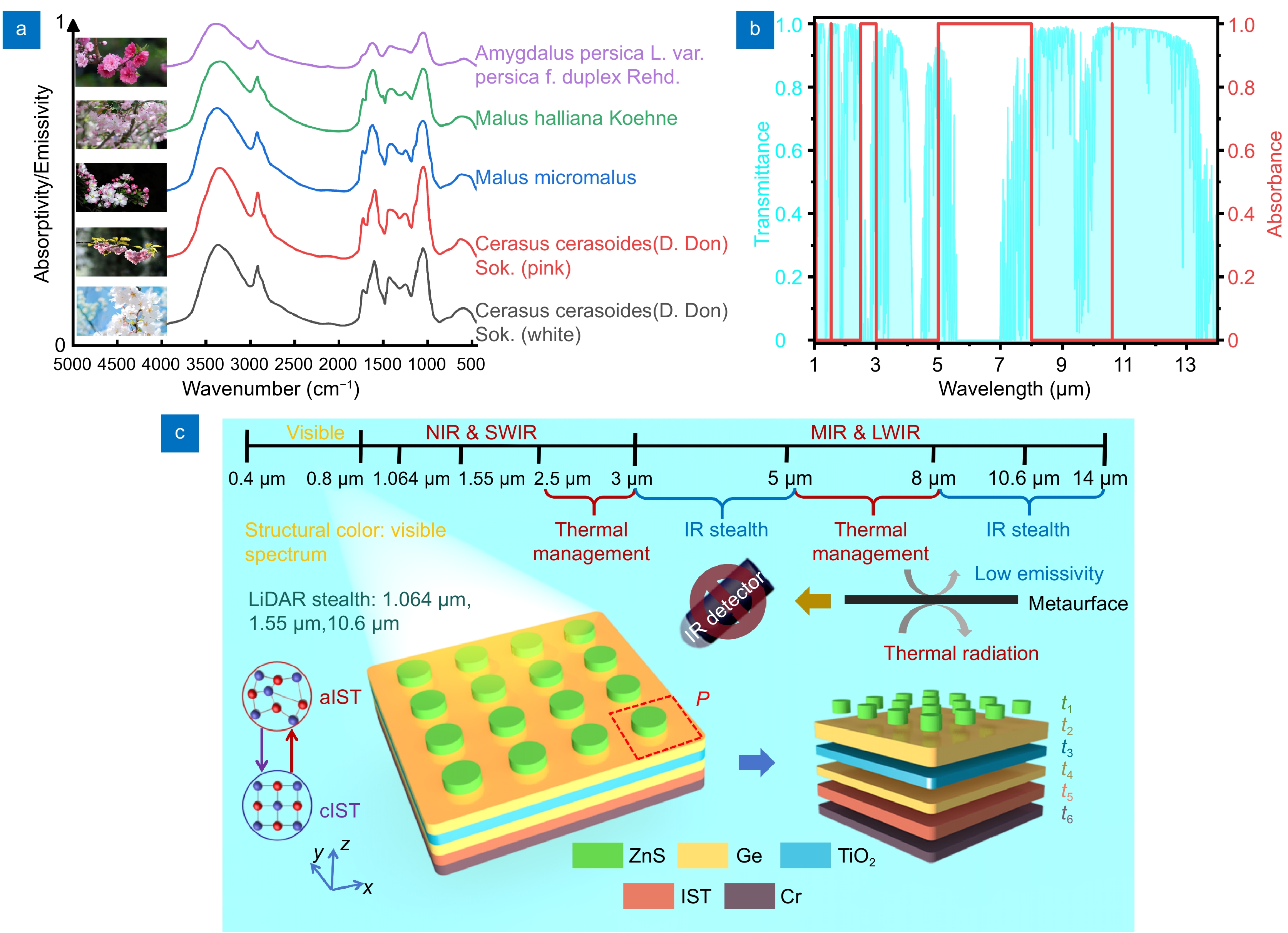
Most multispectral compatible infrared camouflage devices primarily focus on achieving low emissivity but neglect environmental emissivity matching when environmental emissivity exceeds that of the devices, this creates a "low-emissivity exposure" risk. To address this issue, we develop a tunable multispectral compatible infrared camouflage device using phase change material In3SbTe2 (IST).
Simulation and experimental results demonstrate that in both the amorphous (aIST) and crystalline (cIST) states, the device achieves simulated plant infrared camouflage and ultra-low emissivity infrared camouflage within the atmospheric window bands (3–5 µm and 8–14 µm). To address thermal management, it utilizes two non-atmospheric window bands (2.5–3 µm and 5–8 µm) for heat dissipation. Additionally, laser stealth is realized at three specific wavelengths (1.064 µm, 1.55 µm, and 10.6 µm).
In the visible spectrum, high absorptivity enables effective visible light camouflage. Adjusting the geometric parameters of top layer structure enables color variation. This work not only highlights potential applications in reversible switching, reconfigurable imaging, and dynamic coding using IST but also offers an effective strategy to counter multispectral detection technology.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25