(Peer-Reviewed) Partially coherent optical chip enables physical-layer public-key encryption
Bo Wu 吴波 ¹, Wenkai Zhang 张文凯 ¹, Hailong Zhou 周海龙 ¹, Jianji Dong 董建绩 ¹, Yilun Wang 王逸伦 ², Xinliang Zhang 张新亮 ¹
¹ Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, School of Optical and Electronic Information, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
中国 武汉 华中科技大学光学与电子信息学院 武汉光电国家研究中心
² College of Science, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
中国 长沙 中国人民解放军国防科技大学理学院
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2025-11-25
Abstract
Public-key encryption is essential for secure communications, eliminating the need for pre-shared keys. However, traditional schemes such as RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) and elliptic curve cryptography rely on computational complexity, making them increasingly susceptible to advances in computing power and algorithms. Physical-layer encryption, which leverages the intrinsic properties of physical systems, offers a promising alternative with security rooted in physics. Despite progress in this field, public-key encryption at the optical layer remains largely unexplored.
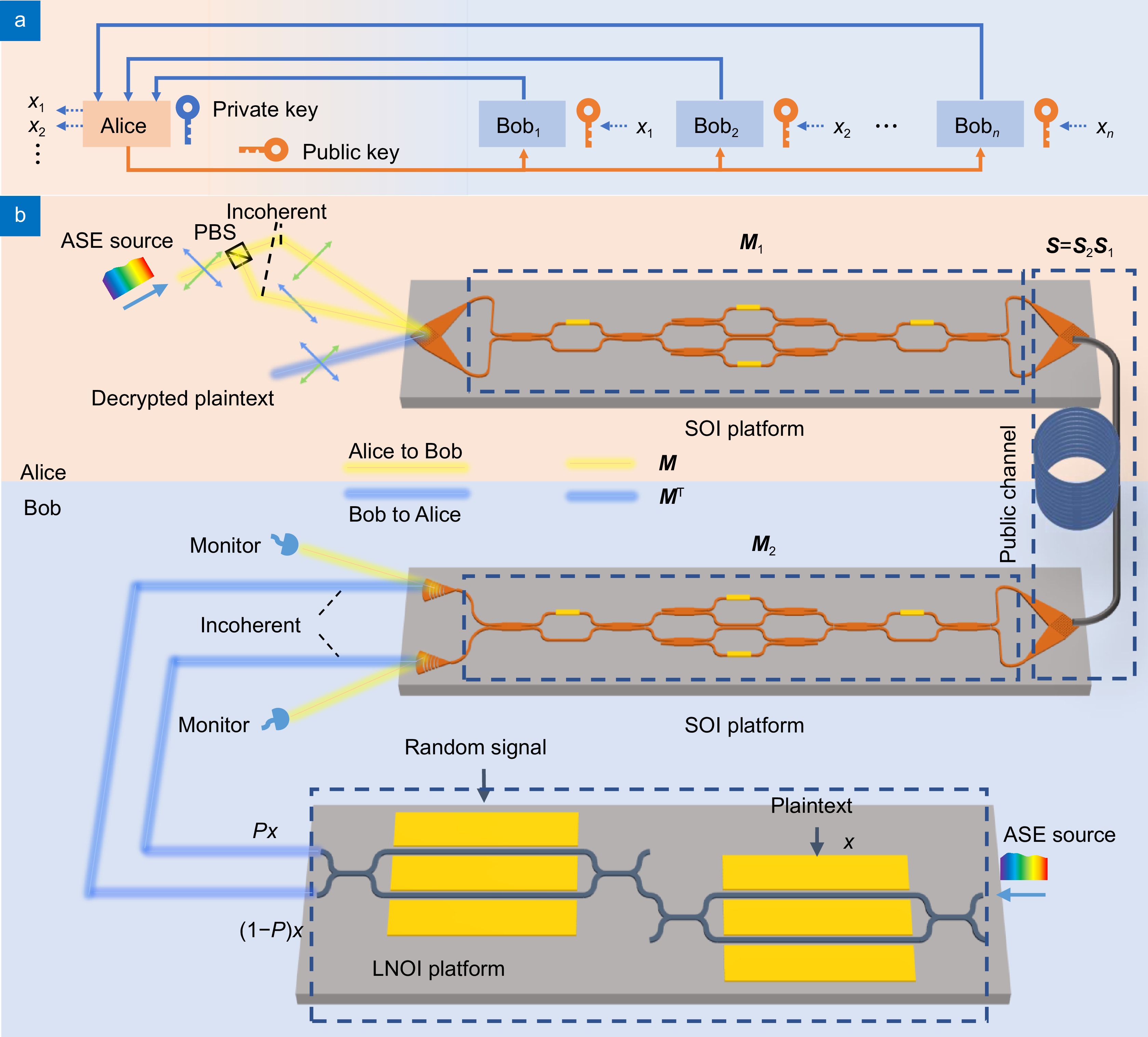
Here, we propose a novel optical public-key encryption scheme based on partially coherent light sources. The cryptographic keys are encoded in the incoherent optical transmission matrix of an on-chip Mach-Zehnder interferometer mesh, providing high complexity and resilience to computational attacks. We experimentally demonstrate encrypted image transmission over 40 km of optical fiber with high decryption fidelity and achieve a 10 Gbit/s optical encryption rate using a lithium niobate photonic chip.
This represents the first implementation of public-key encryption at the physical optical layer. The approach offers key advantages in security, cost, energy efficiency, and compatibility with commercial optical communication systems. By integrating public-key encryption into photonic hardware, this work opens a new direction for secure and high-speed optical communications in next-generation networks.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25