(Peer-Reviewed) Filament based ionizing radiation sensing
Pengfei Qi 齐鹏飞 ¹ ², Haiyi Liu 刘海毅 ¹ ³, Jiewei Guo 郭杰伟 ¹ ², Nan Zhang 张楠 ¹ ², Lu Sun 孙陆 ¹ ², Shishi Tao 陶诗诗 ¹ ², Binpeng Shang 尚滨鹏 ¹ ³, Lie Lin 林列 ¹ ³, Weiwei Liu 刘伟伟 ¹ ²
¹ Institute of Modern Optics, Eye Institute, Nankai University, Tianjin 300350, China
中国 天津 南开大学现代光学研究所 眼科学研究院
² Tianjin Key Laboratory of Micro-scale Optical Information Science and Technology, Tianjin 300350, China
中国 天津 天津市微尺度光学信息技术科学重点实验室
³ Tianjin Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Sensor and Sensing Network Technology, Tianjin 300350, China
中国 天津 天津市光电传感器与传感网络技术重点实验室
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2025-12-25
Abstract
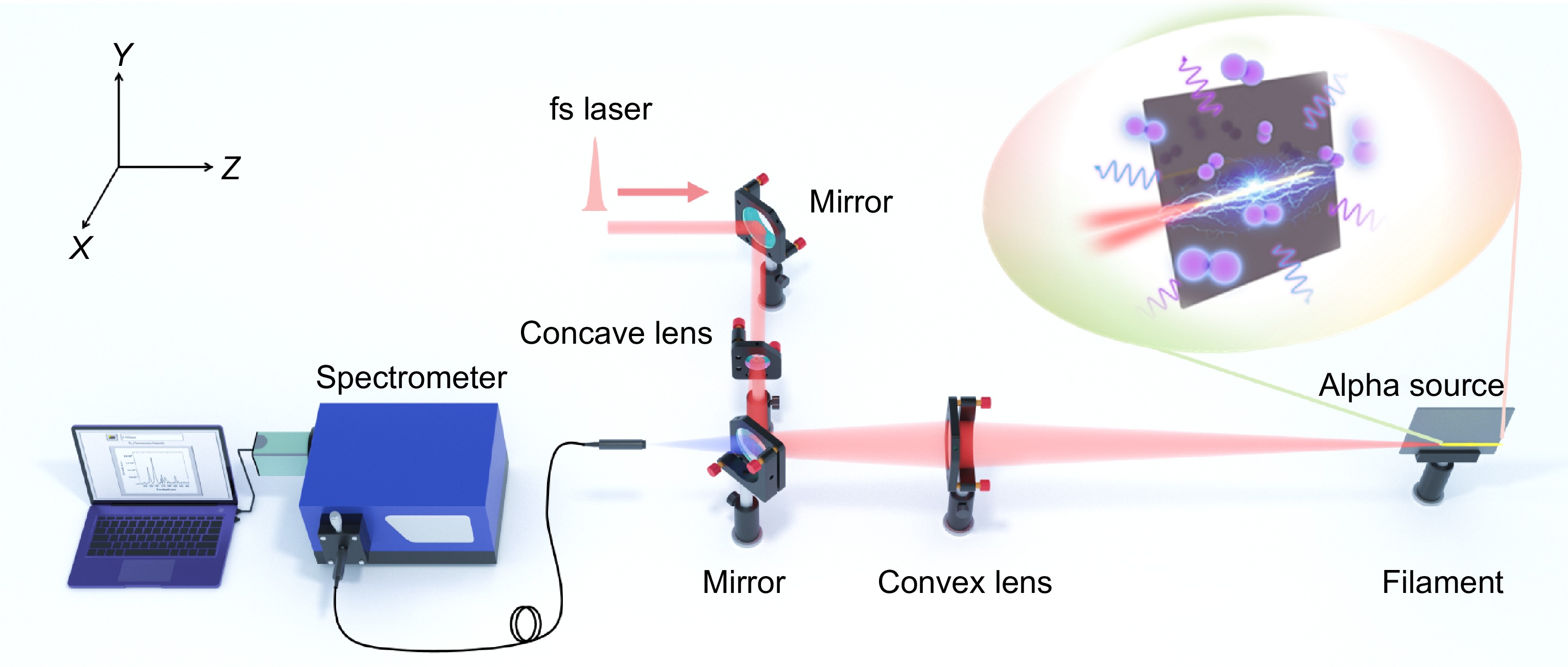
Accidental exposure to overdose ionizing radiation will inevitably lead to severe biological damage, thus detecting and localizing radiation is essential. Traditional measurement techniques are generally restricted to the detection range of few centimeters, posing a great risk to operators. The prospect in remote sensing makes femtosecond laser filament technology a great candidate for constructively addressing this challenge.
Here we propose a novel filament-based ionizing radiation sensing method, and clarify the interaction mechanism between filaments and ionizing radiation from systematic experiment to microscopic theory. Specifically, it is demonstrated that the energetic electrons produced by α radiation in air can be effectively accelerated within the filament, serving as seed electrons, which will enhance nitrogen fluorescence. The extended nitrogen fluorescence lifetime of ~1 ns is also observed.
Lastly, the combined microscopic model was elaborately established to quantitatively explain the modulation of nitrogen fluorescence emission from filament by ionizing radiation. These findings provide insights into the intricate interaction among ultra-strong light field, plasma and energetic particle beam, potentially suggesting a promising novel avenue for remote sensing of ionizing radiation.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25