(Peer-Reviewed) A combined multiscale modeling and experimental study on surface modification of high-volume micro-nanoparticles with atomic accuracy
Zoushuang Li 李邹霜 ¹, Junren Xiang 向俊任 ¹ ⁵, Xiao Liu 刘潇 ¹, Xiaobo Li 李小波 ², Lijie Li ³, Bin Shan 单斌 ⁴, Rong Chen 陈蓉 ¹
¹ State Key Laboratory of Digital Manufacturing Equipment and Technology, School of Mechanical Science and Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 1037 Luoyu Road, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, People's Republic of China
中国 湖北 武汉 华中科技大学机械科学与工程学院 数字制造装备与技术国家重点实验室
² School of Energy and Power Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, People's Republic of China
中国 湖北 武汉 华中科技大学能源与动力工程学院
³ College of Engineering, Swansea University, SA18 EN Swansea, United Kingdom
⁴ State Key Laboratory of Material Processing and Die and Mould Technology, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, People's Republic of China
中国 湖北 武汉 华中科技大学材料科学与工程学院 材料成形与模具技术国家重点实验室
⁵ Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, Hubei 430063, People's Rep
中国 湖北 武汉 武汉理工大学
Abstract
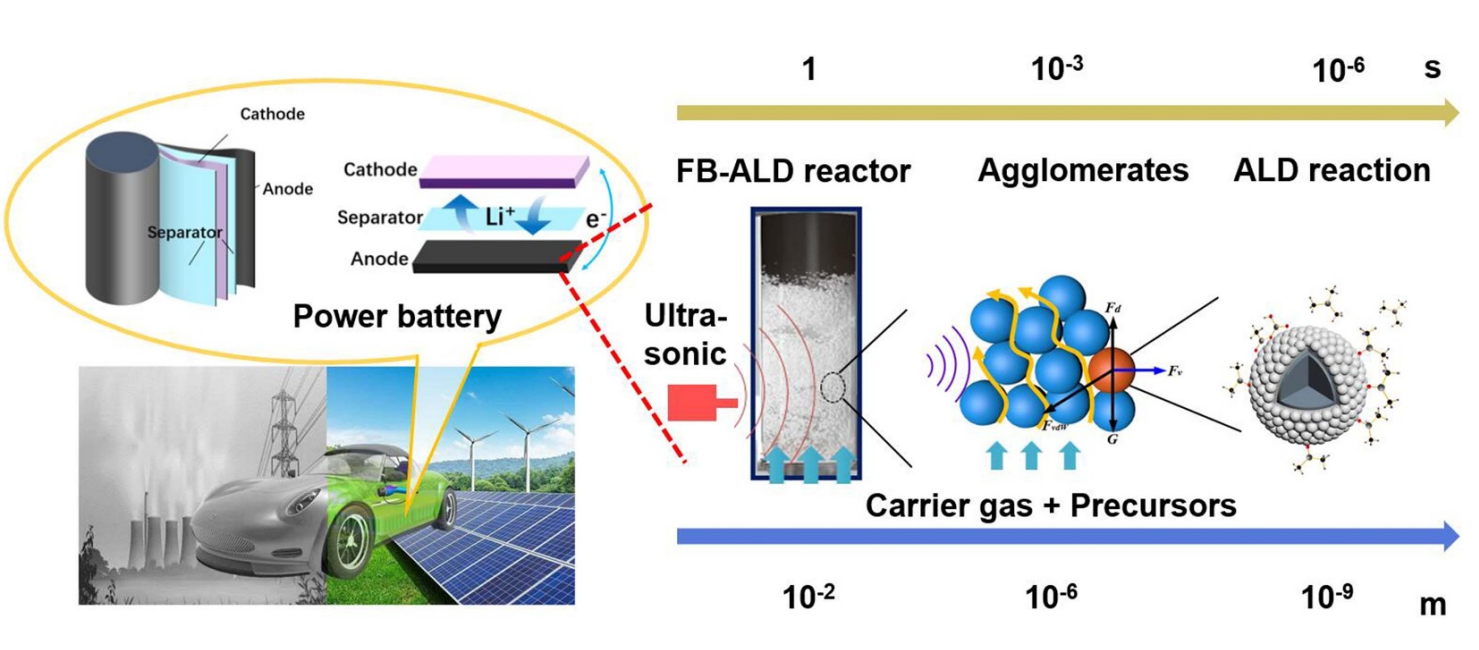
Surface modification for micro-nanoparticles at the atomic and close-to-atomic scales is of great importance to enhance their performance in various applications, including high-volume battery, persistent luminescence, etc. Fluidized bed atomic layer deposition (FB-ALD) is a promising atomic-scale manufacturing technology that offers ultrathin films on large amounts of particulate materials. Nevertheless, nanoparticles tend to agglomerate due to the strong cohesive forces, which is much unfavorable to the film conformality and also hinders their real applications.
In this paper, the particle fluidization process in an ultrasonic vibration-assisted FB-ALD reactor is numerically investigated from micro-scale to macro-scale through the multiscale computational fluid dynamics and discrete element method (CFD-DEM) modeling with experimental verification. Various vibration amplitudes and frequencies are investigated in terms of their effects on the fluid dynamics, distribution of particle velocity and solid volume fraction, as well as the size of agglomerates. Results show that the fluid turbulent kinetic energy, which is the key power source for the particles to obtain the kinetic energy for overcoming the interparticle agglomeration forces, can be strengthened obviously by the ultrasonic vibration.
Besides, the application of ultrasonic vibration is found to reduce the mean agglomerate size in the FB. This is bound to facilitate the heat transfer and precursor diffusion in the entire FB-ALD reactor and the agglomerates, which can largely shorten the coating time and improve the film conformality as well as precursor utilization. The simulation results also agree well with our battery experimental results, verifying the validity of the multiscale CFD-DEM model. This work has provided momentous guidance to the mass manufacturing of atomic-scale particle coating from lab-scale to industrial applications.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25