(Peer-Reviewed) 100 Hertz frame-rate switching three-dimensional orbital angular momentum multiplexing holography via cross convolution
Weijia Meng 孟维佳 ¹ ², Yilin Hua 华怡林 ¹ ², Ke Cheng 成科 ¹ ², Baoli Li 李保莉 ¹ ², Tingting Liu 刘婷婷 ¹ ², Qinyu Chen 陈沁雨 ¹ ², Haitao Luan 栾海涛 ¹ ², Min Gu 顾敏 ¹ ², Xinyuan Fang 方心远 ¹ ²
¹ Institute of Photonic Chips, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
中国 上海 上海理工大学光子芯片研究院
² Centre for Artificial-Intelligence Nanophotonics, School of Optical-Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
中国 上海 上海理工大学光电信息与计算机工程学院 人工智能纳米光子学中心
Opto-Electronic Science, 2022-09-07
Abstract
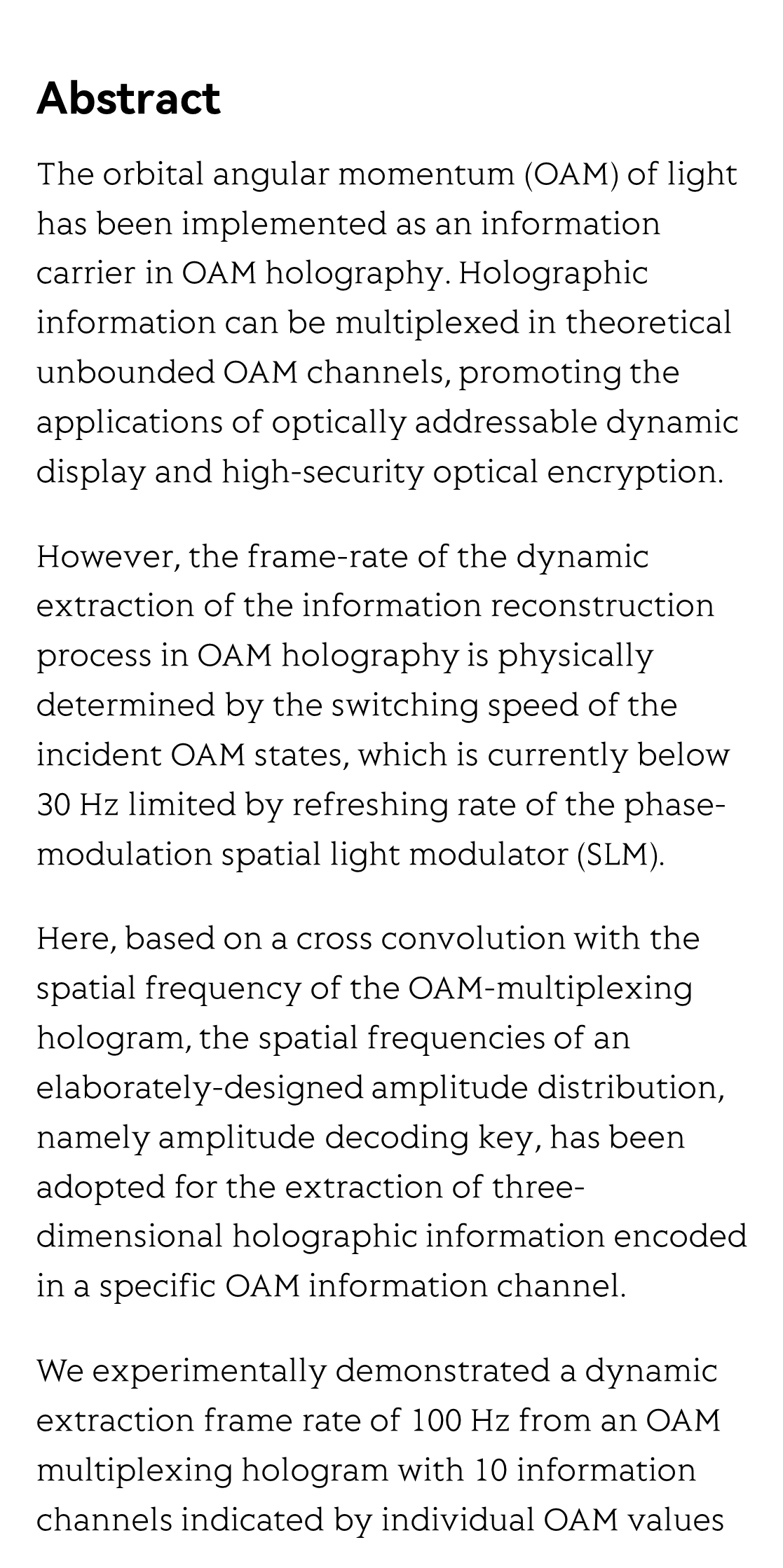
The orbital angular momentum (OAM) of light has been implemented as an information carrier in OAM holography. Holographic information can be multiplexed in theoretical unbounded OAM channels, promoting the applications of optically addressable dynamic display and high-security optical encryption.
However, the frame-rate of the dynamic extraction of the information reconstruction process in OAM holography is physically determined by the switching speed of the incident OAM states, which is currently below 30 Hz limited by refreshing rate of the phase-modulation spatial light modulator (SLM).
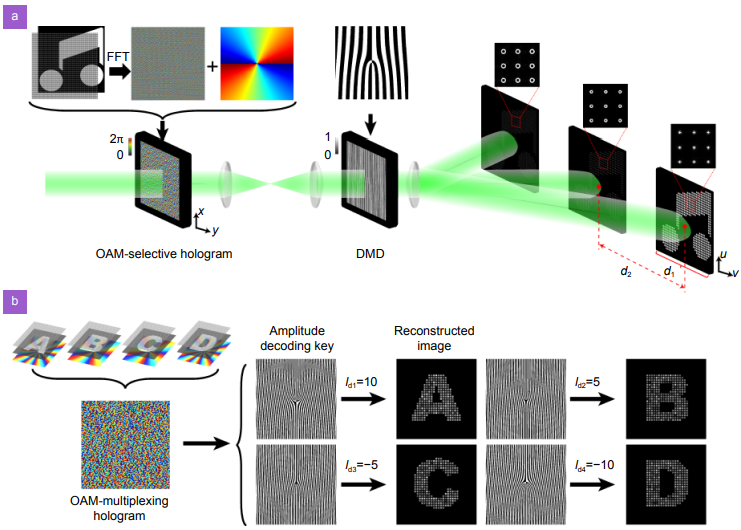
Here, based on a cross convolution with the spatial frequency of the OAM-multiplexing hologram, the spatial frequencies of an elaborately-designed amplitude distribution, namely amplitude decoding key, has been adopted for the extraction of three-dimensional holographic information encoded in a specific OAM information channel.
We experimentally demonstrated a dynamic extraction frame rate of 100 Hz from an OAM multiplexing hologram with 10 information channels indicated by individual OAM values from –50 to 50. The new concept of cross convolution theorem can even provide the potential of parallel reproduction and distribution of information encoded in many OAM channels at various positions which boosts the capacity of information processing far beyond the traditional decoding methods.
Thus, our results provide a holographic paradigm for high-speed 3D information processing, paving an unprecedented way to achieve the high-capacity short-range optical communication system.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25