(Peer-Reviewed) Integrated photonic synapses, neurons, memristors, and neural networks for photonic neuromorphic computing
Shufei Han 韩书菲 ¹ ², Weihong Shen 沈微宏 ¹ ², Min Gu 顾敏 ¹ ², Qiming Zhang 张启明 ¹ ²
¹ School of Artificial Intelligence Science and Technology, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
中国 上海 上海理工大学智能科技学院
² Institute of Photonic Chips, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
中国 上海 上海理工大学光子芯片研究院
Opto-Electronic Technology, 2025-12-25
Abstract
Rising demands for bandwidth, speed, and energy efficiency are reshaping the landscape of computing beyond the limits of von Neumann electronics. Neuromorphic photonics—using light to emulate neural computation—offers ultrafast, massively parallel, and low-energy information processing, positioning integrated photonic neural networks (IPNNs) as promising hardware for next-generation artificial intelligence (AI).
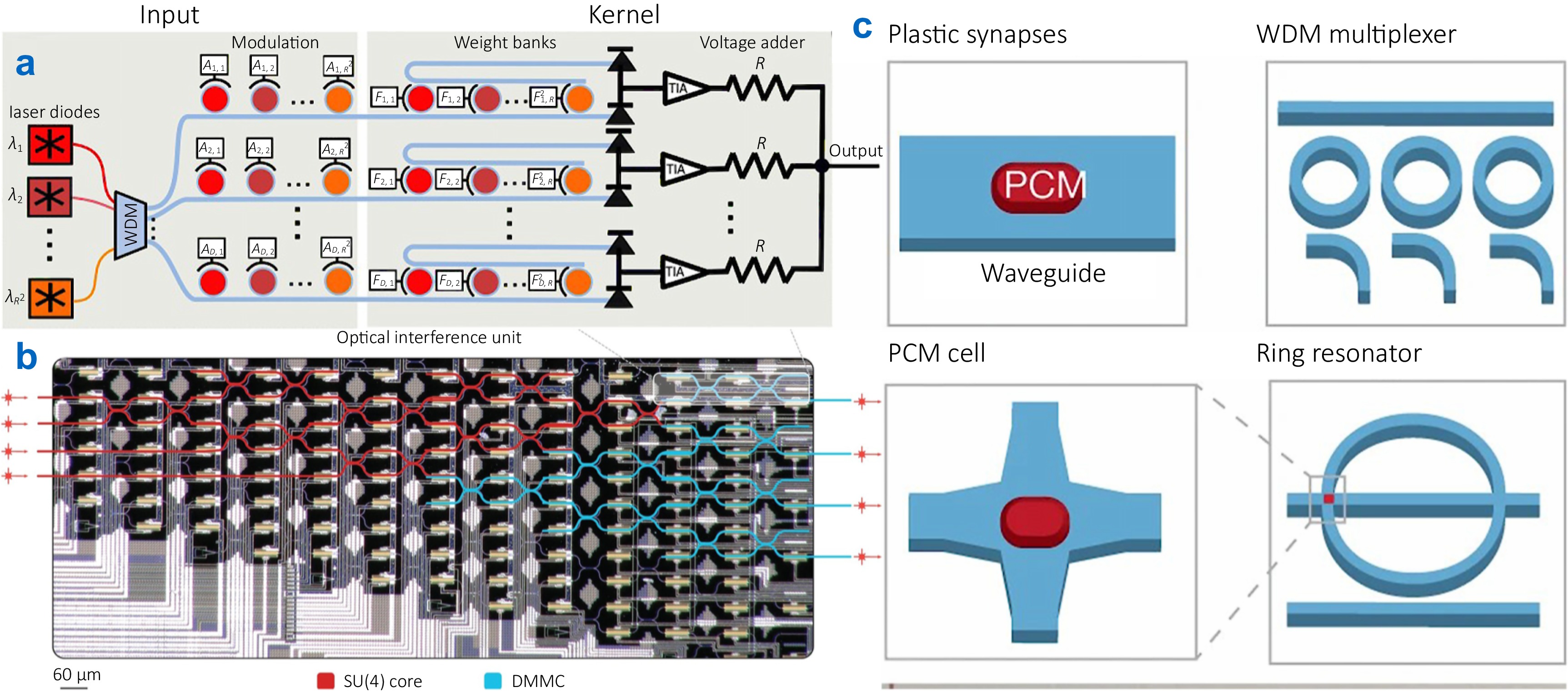
By combining the architectural efficiency of neuromorphic models with the physical advantages of integrated photonics, IPNNs enable high-speed and programmable linear operations during the in-plane optical transmission, while leaving room for compact and reconfigurable on-chip optical nonlinearities and memory functions. Firstly, we review the concepts and principles of key building blocks in IPNN, that are photonic synapses, neurons, and photonic memristors which offer optical memory and storage capabilities.
And then, we summarize the representative IPNN architectures and their recent advances, including coherent, parallel, diffractive, and reservoir computing, for photonic neuromorphic computing with high throughput and high efficiency. Finally, we outline practical considerations—calibration and stability of large-scale networks, routes toward co-integration with electronics, diffractive–interferometric hybrid architectures, and programmable photonic architectures for general AI purposes.
We highlight a forward outlook on enabling IPNN with low energy consumption, robust photonic operations, and efficient training strategies, aiming to guide the maturation of general-purpose, low-power photonic AI.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25