(Peer-Reviewed) Photonic synapses with ultralow energy consumption for artificial visual perception and brain storage
Caihong Li 李彩虹 ¹, Wen Du 杜文 ¹, Yixuan Huang 黄一轩 ¹, Jihua Zou 邹吉华 ¹, Lingzhi Luo 罗凌志 ¹, Song Sun 孙松 ² ³, Alexander O. Govorov ⁴, Jiang Wu 巫江 ¹ ⁵, Hongxing Xu 徐红星 ¹ ⁶, Zhiming Wang 王志明 ¹
¹ Institute of Fundamental and Frontier Sciences, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
中国 成都 电子科技大学 基础与前沿研究院
² Microsystem and Terahertz Research Center, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Chengdu 610200, China
中国 成都 中国工程物理研究院 微系统与太赫兹研究中心
³ Institute of Electronic Engineering, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621999, China
中国 绵阳 中国工程物理研究院 电子工程研究所
⁴ Department of Physics and Astronomy, Ohio University, Athens, Ohio 45701, United States
⁵ State Key Laboratory of Electronic Thin Films and Integrated Devices, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610065, China
中国 成都 电子科技大学 电子薄膜与集成器件国家重点实验室
⁶ School of Physics and Technology, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430072, China
中国 武汉 武汉大学物理科学与技术学院
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2022-06-24
Abstract
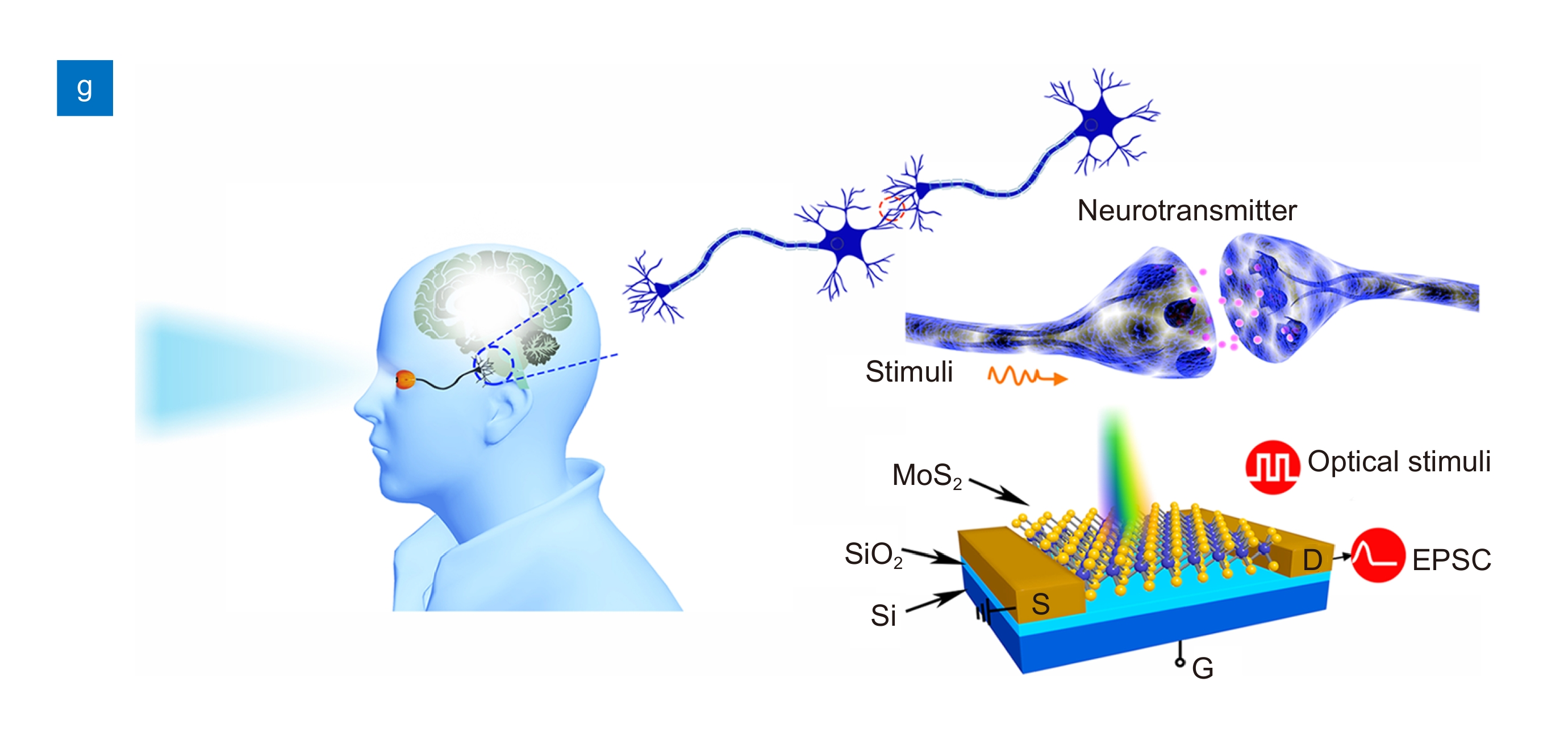
The human visual system, dependent on retinal cells, can be regarded as a complex combination of optical system and nervous system. Artificial retinal system could mimic the sensing and processing function of human eyes. Optically stimulated synaptic devices could serve as the building blocks for artificial retinas and subsequent information transmission system to brain.
Herein, photonic synaptic transistors based on polycrystalline MoS2, which could simulate human visual perception and brain storage, are presented. Moreover, the photodetection range from visible light to near-infrared light of MoS2 multilayer could extend human eyes’ vision limitation to near-infrared light. Additionally, the photonic synaptic transistor shows an ultrafast speed within 5 μs and ultralow power consumption under optical stimuli about 40 aJ, several orders of magnitude lower than biological synapses (50 ms and 10 fJ).
Furthermore, the backgate control could act as emotional modulation of the artificial brain to enhance or suppress memory function, i.e. the intensity of photoresponse. The proposed carrier trapping/detrapping as the main working mechanism is presented for the device. In addition, synaptic functionalities including short synaptic plasticity, long synaptic plasticity and paired-pulse facilitation could be successfully simulated based on the prepared device. Furthermore, the large difference between short synaptic plasticity and long synaptic plasticity reveals the better image pre-processing function of the prepared photonic synapses.
The classical Pavlovian conditioning associated with the associative learning is successfully implemented as well. Therefore, the efficient and rich functionalities demonstrate the potential of the MoS2 synaptic device that integrates sensing-memory-preprocessing capabilities for realizing artificial neural networks with different emotions that mimic human retina and brain.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25