(Peer-Reviewed) Highly sensitive laser spectroscopy sensing based on a novel four-prong quartz tuning fork
Runqiu Wang 王润秋 ¹ ², Shunda Qiao 乔顺达 ¹ ², Ying He 何英 ¹ ², Yufei Ma 马欲飞 ¹ ²
¹ National Key Laboratory of Laser Spatial Information, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150000, China
中国 哈尔滨 哈尔滨工业大学 激光空间信息全国重点实验室
² Zhengzhou Research Institute, Harbin Institute of Technology, Zhengzhou 450000, China
中国 哈尔滨 哈尔滨工业大学郑州研究院
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2025-01-22
Abstract
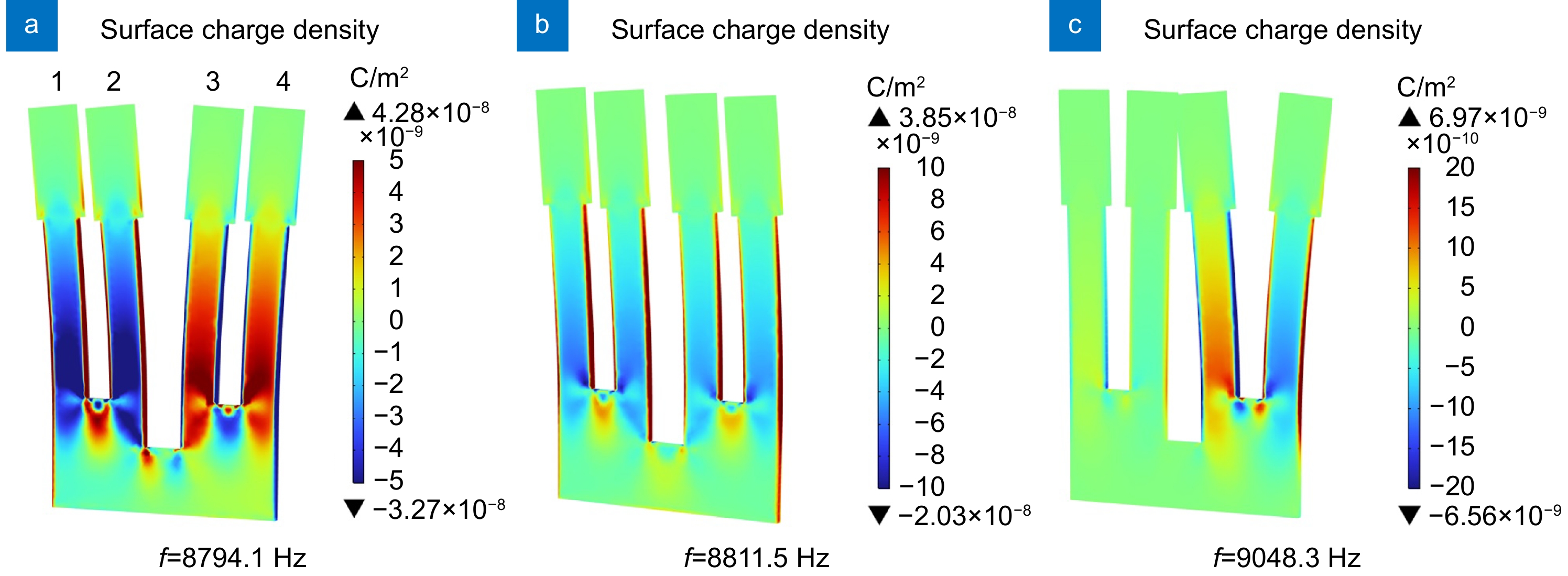
In this paper, a novel four-prong quartz tuning fork (QTF) was designed with enlarged deformation area, large prong gap, and low resonant frequency to improve its performance in laser spectroscopy sensing. A theoretical simulation model was established to optimize the design of the QTF structure.
In the simulation of quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy (QEPAS) technology, the maximum stress and the surface charge density of the four-prong QTF demonstrated increases of 11.1-fold and 15.9-fold, respectively, compared to that of the standard two-prong QTF. In the simulation of light-induced thermoelastic spectroscopy (LITES) technology, the surface temperature difference of the four-prong QTF was found to be 11.4 times greater than that of the standard QTF.
Experimental results indicated that the C₂H₂-QEPAS system based on this innovative design improved the signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) by 4.67 times compared with the standard QTF-based system, and the SNR could increase up to 147.72 times when the four-prong QTF was equipped with its optimal acoustic micro-resonator (AmR).
When the average time of the system reached 370 s, the system achieved a MDL as low as 21 ppb. The four-prong QTF-based C₂H₂-LITES system exhibited a SNR improvement by a factor of 4.52, and a MDL of 96 ppb was obtained when the average time of the system reached 100 s. The theoretical and experimental results effectively demonstrated the superiority of the four-prong QTF in the field of laser spectroscopy sensing.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25