(Peer-Reviewed) Orthogonal matrix of polarization combinations: concept and application to multichannel holographic recording
Shujun Zheng 郑淑君 ¹, Jiaren Tan ², Hongjie Liu 刘宏杰 ¹, Xiao Lin 林枭 ³, Yusuke Saita 最田裕介 ⁴, Takanori Nomura 野村孝徳 ⁴, Xiaodi Tan 谭小地 ³
¹ Information Photonics Research Center, College of Photonic and Electronic Engineering, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350117, China
中国 福州 福建师范大学光电与信息工程学院 信息光子学研究中心
² Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Duke University, Durham, NC 27708, USA
³ College of Photonic and Electronic Engineering, Key Laboratory of Opto-Electronic Science and for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Photonics Technology, Fujian Provincial Engineering Technology Research Center of Photoelectric Sensing Application, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350117, China
中国 福州 福建师范大学光电与信息工程学院 医学光电科学与技术教育部重点实验室 福建省光子技术重点实验室 福建省光电传感应用工程技术研究中心
⁴ Faculty of Systems Engineering, Wakayama University, 930 Sakaedani, Wakayama, 640-8510, Japan
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2024-10-23
Abstract
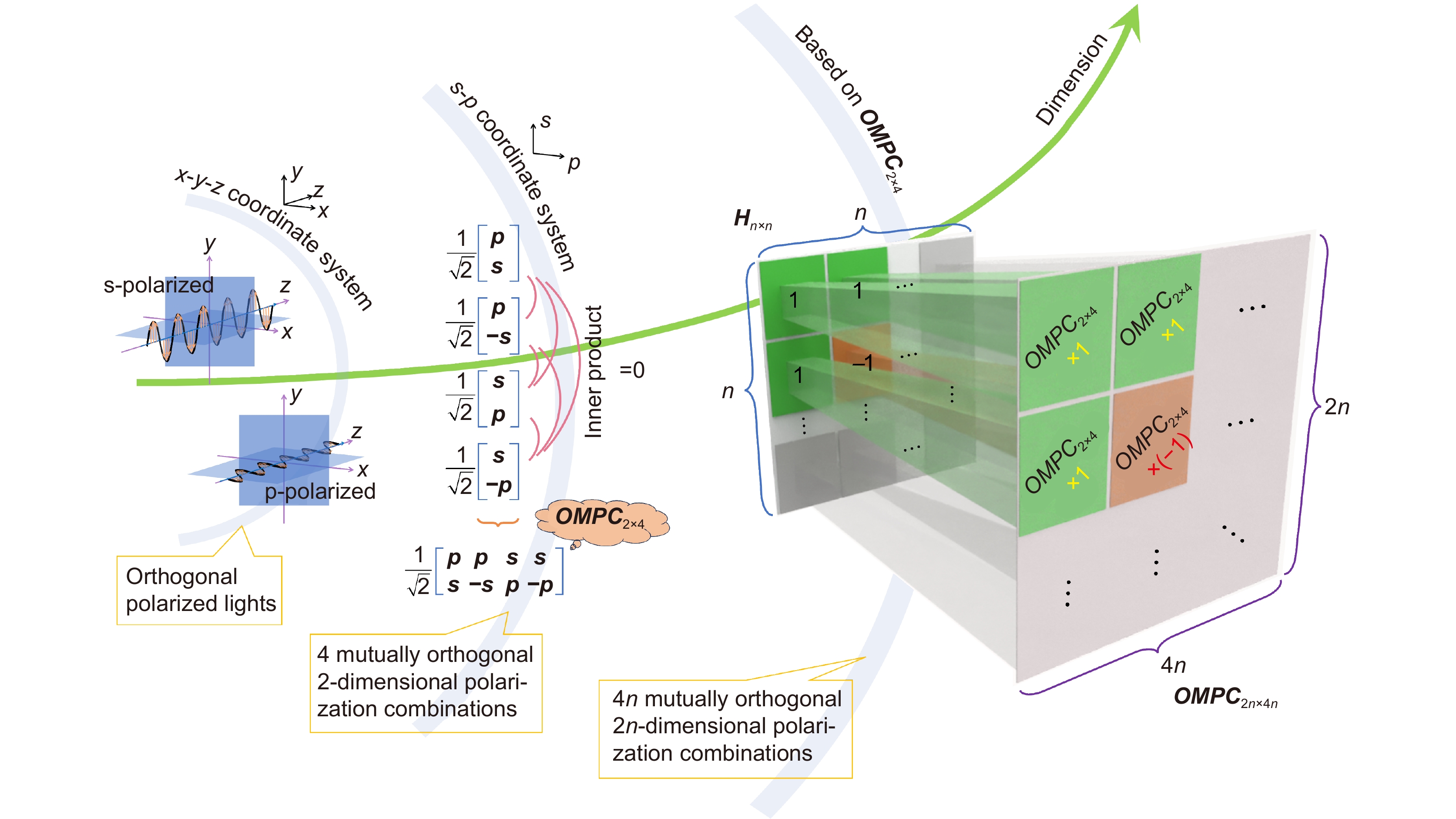
Orthogonal matrices have become a vital means for coding and signal processing owing to their unique distributional properties. Although orthogonal matrices based on amplitude or phase combinations have been extensively explored, the orthogonal matrix of polarization combinations (OMPC) is a novel, relatively unexplored concept.
Herein, we propose a method for constructing OMPCs of any dimension encompassing 4n (where n is 1, 2, 4, 8, …) mutually orthogonal 2n-component polarization combinations. In the field of holography, the integration of polarization multiplexing techniques with polarization-sensitive materials is expected to emerge as a groundbreaking approach for multichannel hologram multiplexing, offering considerable enhancements in data storage capacity and security.
A multidimensional OMPC enables the realization of multichannel multiplexing and dynamical modulation of information in polarization holographic recording. Despite consolidating all information into a single position within the material, we effectively avoided extraneous crosstalk during the reconstruction process.
Our results show that achieving four distinct holographic images individually and simultaneously depends on the polarization combination represented by the incident wave. This discovery opens up a new avenue for achieving highly holographic information storage and dynamically displayed information, harnessing the potential of OMPC to expand the heretofore limited dimensionality of orthogonal polarization.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25