(Peer-Reviewed) Inter-annual variations of 6.5-day planetary waves and their relations with QBO
Ying-Ying Huang 黄莹莹 ¹ ² ³, Jun Cui 崔峻 ⁴ ⁵, Hui-Jun Li 李汇军 ⁶, Chongyin Li 李崇银 ⁷
¹ National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
中国 北京 中国科学院国家天文台
² State Key Laboratory of Space Weather, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
中国 北京 中国科学院空间天气学国家重点实验室
³ CAS Key Laboratory of Lunar and Deep Space Exploration, National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
中国 北京 中国科学院国家天文台 中国科学院月球与深空探测重点实验室
⁴ Planetary Environmental and Astrobiological Research Laboratory (PEARL), School of Atmospheric Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University, Zhuhai, Guangdong, China
中国 广东 珠海 中山大学大气科学学院 行星环境与宜居性研究实验室
⁵ School of Atmospheric Sciences, Sun Yat-Sen University, Zhuhai, Guangdong, China
中国 广东 珠海 中山大学大气科学学院
⁶ College of Astronautics, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, China
中国 南京 南京航空航天大学航天学院
⁷ LASG, Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
中国 北京 中国科学院大气物理研究所 大气科学和地球流体力学数值模拟国家重点实验室
Abstract
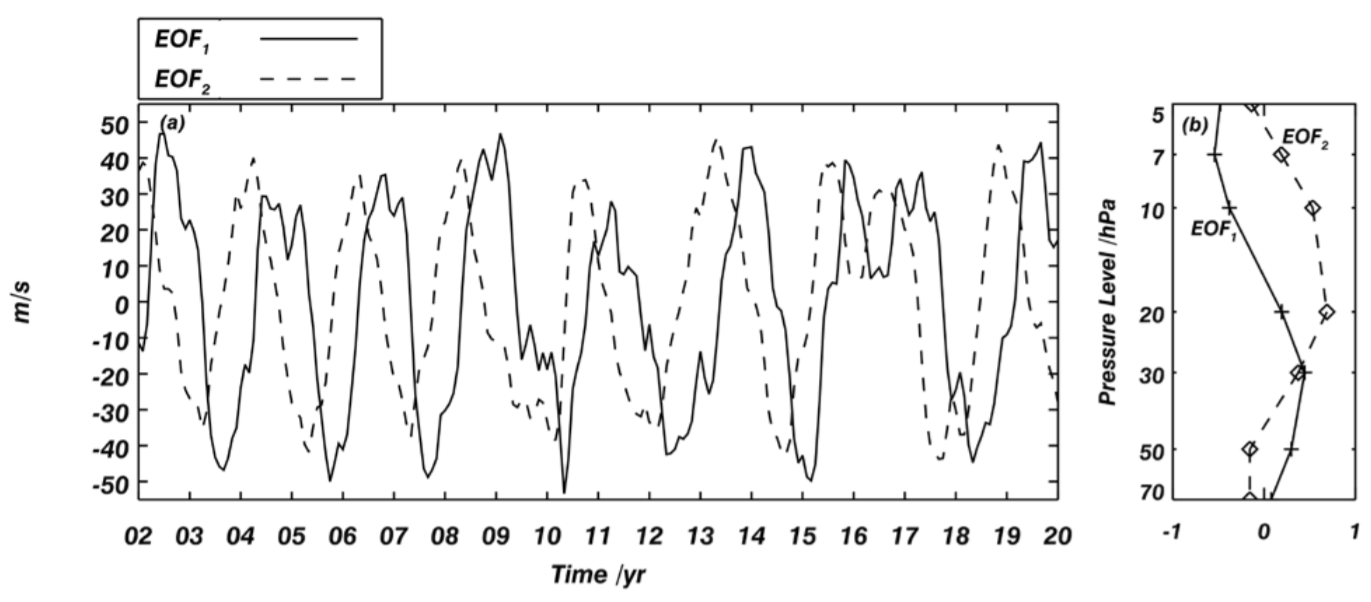
This paper studies inter-annual variations of 6.5-Day Waves (6.5DWs) in 20-110 km between 52°S-52°N during March 2002-January 2021 and their relations with equatorial stratospheric Quasi-Biennial Oscillation (QBO). 6.5DWs' amplitudes in temperature are calculated based on SABER/TIMED observations. QBO zonal winds are obtained from ERA5 reanalysis dataset. QBO phases are derived from Empirical Orthogonal Functions (EOF) method. Wavelet analysis of 6.5DW variations demonstrates obvious spectral maximums around 28-38 months in 32°-52°N and 26-30 months in 32°-52°S.
In the Northern Hemisphere, peak periods get longer poleward, while they remain unchanged with latitude in the Southern Hemisphere. Residual 6.5DWs' amplitudes are calculated by removing composite amplitudes from 6.5DWs' amplitudes. Comparisons between QBO and the monthly maximum residual 6.5DWs' amplitudes (A_Mmax) show clear relations between QBO and 6.5DWs in both hemispheres, especially in the NH. When A_Mmax is large in the NH, mean QBO profile is easterly at all levels from 70 to 5 hPa. When it's weak, mean QBO wind is weak westerly below 30 hPa. Linear Pearson correlation coefficients between QBO phases and A_Mmax show large positive values in 60-110 km between 20°-52°N in April and around 64 km at 24°S in February, and large negative values from 80 to 110 km between 20°N-50°N in August and at 96-106 km between 20°S-44°S in February.
These results indicate quantitative relations between QBO and 6.5DWs and provide credible evidences for further studies of QBO modulations on long-term variations of 6.5DWs.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25