(Peer-Reviewed) Epigenetic integrity of paternal imprints enhances the developmental potential of androgenetic haploid embryonic stem cells
Hongling Zhang 张红玲 ¹, Yuanyuan Li 李元元 ¹, Yongjian Ma 马永健 ¹, Chongping Lai ², Qian Yu ³, Guangyong Shi ¹, Jinsong Li 李劲松 ¹ ² ⁴
¹ State Key Laboratory of Cell Biology, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Andrology, CAS Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science, Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 200031, China
中国 上海 中国科学院大学生物化学与细胞生物学研究所 中国科学院分子细胞科学卓越创新中心 细胞生物学国家重点实验室 上海市分子男科学重点实验室
² School of Life Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, 201210, China
中国 上海 上海科技大学生命科学与技术学院
³ Animal Core Facility, Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Center for Excellence in Molecular Cell Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 200031, China
中国 上海 中国科学院分子细胞科学卓越创新中心 上海生物化学与细胞生物学研究所 动物实验技术平台
⁴ School of Life Science, Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, 310024, China
中国 杭州 中国科学院大学杭州高等研究院 生命与健康科学学院
Abstract
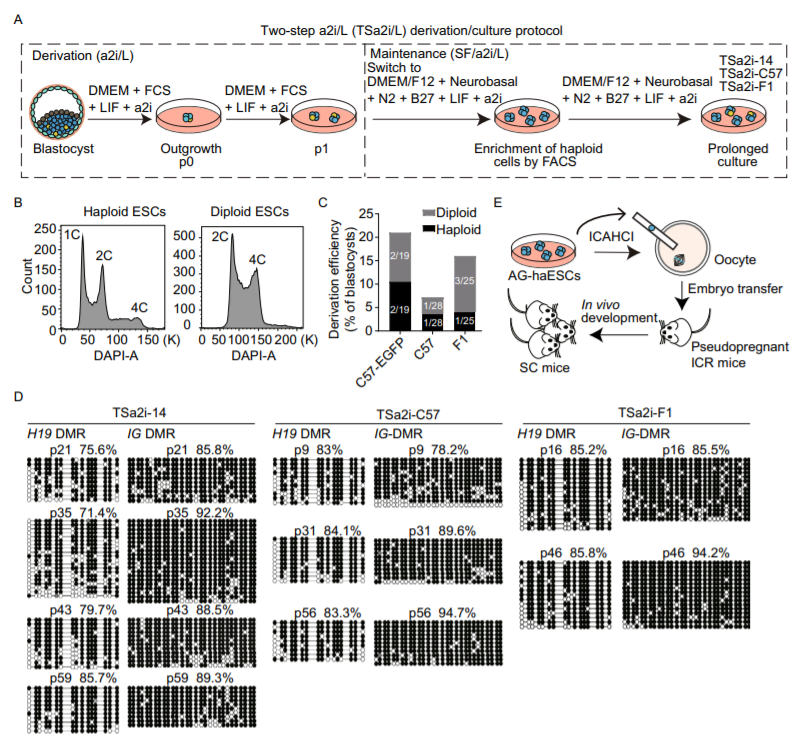
The use of two inhibitors of Mek1/2 and Gsk3β (2i) promotes the generation of mouse diploid and haploid embryonic stem cells (ESCs) from the inner cell mass of biparental and uniparental blastocysts, respectively. However, a system enabling long-term maintenance of imprints in ESCs has proven challenging.
Here, we report that the use of a two-step a2i (alternative two inhibitors of Src and Gsk3β, TSa2i) derivation/culture protocol results in the establishment of androgenetic haploid ESCs (AG-haESCs) with stable DNA methylation at paternal DMRs (differentially DNA methylated regions) up to passage 60 that can efficiently support generating mice upon oocyte injection. We also show coexistence of H3K9me3 marks and ZFP57 bindings with intact DMR methylations. Furthermore, we demonstrate that TSa2i-treated AG-haESCs are a heterogeneous cell population regarding paternal DMR methylation.
Strikingly, AG-haESCs with late passages display increased paternal-DMR methylations and improved developmental potential compared to early-passage cells, in part through the enhanced proliferation of H19-DMR hypermethylated cells. Together, we establish AG-haESCs that can long-term maintain paternal imprints.
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25