(Peer-Reviewed) Prediction of pandemic risk for animal-origin coronavirus using a deep learning method
Zheng Kou 寇铮 ¹, Yi-Fan Huang ¹, Ao Shen ¹, Saeed Kosari ¹, Xiang-Rong Liu 刘向荣 ², Xiao-Li Qiang 强小利 ¹
¹ Institute of Computing Science and Technology, Guangzhou University, Guangzhou, 510006, China
中国 广州 广州大学计算科技研究院
² Department of Computer Science, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005, China
中国 厦门 厦门大学计算机科学系
Background
Coronaviruses can be isolated from bats, civets, pangolins, birds and other wild animals. As an animal-origin pathogen, coronavirus can cross species barrier and cause pandemic in humans. In this study, a deep learning model for early prediction of pandemic risk was proposed based on the sequences of viral genomes.
Methods
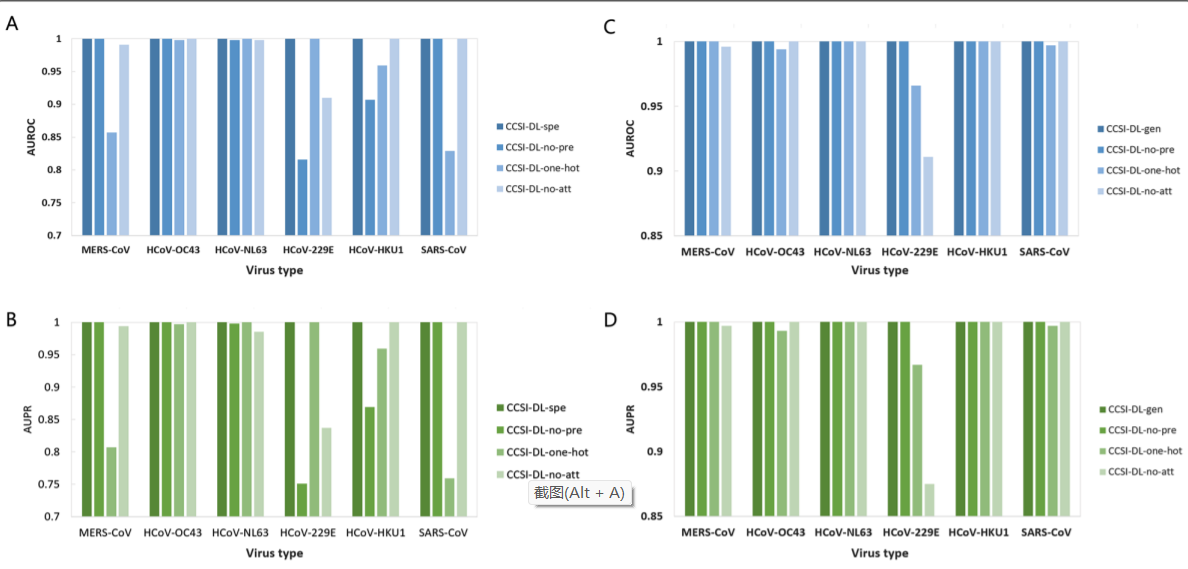
A total of 3257 genomes were downloaded from the Coronavirus Genome Resource Library. We present a deep learning model of cross-species coronavirus infection that combines a bidirectional gated recurrent unit network with a one-dimensional convolution. The genome sequence of animal-origin coronavirus was directly input to extract features and predict pandemic risk. The best performances were explored with the use of pre-trained DNA vector and attention mechanism. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) and the area under precision-recall curve (AUPR) were used to evaluate the predictive models.
Results
The six specific models achieved good performances for the corresponding virus groups (1 for AUROC and 1 for AUPR). The general model with pre-training vector and attention mechanism provided excellent predictions for all virus groups (1 for AUROC and 1 for AUPR) while those without pre-training vector or attention mechanism had obviously reduction of performance (about 5–25%). Re-training experiments showed that the general model has good capabilities of transfer learning (average for six groups: 0.968 for AUROC and 0.942 for AUPR) and should give reasonable prediction for potential pathogen of next pandemic. The artificial negative data with the replacement of the coding region of the spike protein were also predicted correctly (100% accuracy). With the application of the Python programming language, an easy-to-use tool was created to implements our predictor.
Conclusions
Robust deep learning model with pre-training vector and attention mechanism mastered the features from the whole genomes of animal-origin coronaviruses and could predict the risk of cross-species infection for early warning of next pandemic.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25