(Peer-Reviewed) Holocene dust storm variations over northern china: transition from a natural forcing to an anthropogenic forcing
Shengqian Chen 陈圣乾 ¹, Jianbao Liu 刘建宝 ¹ ² ³, Xin Wang 王鑫 ¹, Shuang Zhao 赵爽 ¹ ⁴, Jianhui Chen 陈建徽 ¹, Mingrui Qiang 强明瑞 ¹ ⁵, Bing Liu 刘冰 ⁶, Qinghai Xu 许清海 ⁷, Dunsheng Xia 夏敦胜 ¹, Fahu Chen 陈发虎 ¹ ² ³
¹ Key Laboratory of Western China's Environmental Systems (Ministry of Education), College of Earth and Environmental Science, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, China. 兰州大学 地球与环境科学学院 西部环境教育部重点实验室
² Group of Alpine Paleoecology and Human Adaptation, State Key Laboratory of Tibetan Plateau Earth System, Resources and Environment, Institute of Tibetan Plateau Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China. 中国科学院 青藏高原研究所
³ Center for Excellence in Tibetan Plateau Earth Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China. 中国科学院 青藏高原地球科学卓越创新中心
⁴ College of Geography and Tourism, Qufu Normal University, Rizhao 276826, China 曲阜师范大学 地理与旅游学院
⁵ School of Geography, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510631, China. 华南师范大学地理科学学院
⁶ Key Laboratory of Desert and Desertification, Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou 730000, China. 中国科学院 西北生态环境资源研究院 沙漠与沙漠化重点实验室
⁷ College of Resources and Environment, Hebei Normal University, Shijiazhuang 050024, China. 河北师范大学 资源与环境科学学院
Science Bulletin, 2021-08-11
Abstract
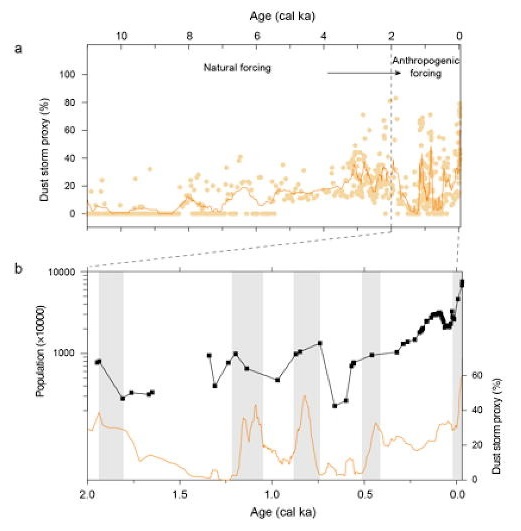
Asian dust storms have long been a major environmental concern in China, affecting the lives of about one billion people. However, it is unclear whether the mechanisms responsible for Asian dust storms during the Holocene varied on different timescales, and thus it is unclear whether there was a shift from a natural forcing to an anthropogenic forcing of dust storms.
We reconstructed a high-resolution Holocene record of dust storms from the sediments of an undisturbed alpine lake on the Chinese Loess Plateau. We found that Asian dust storm activity generally increased during the Holocene, with the largest fluctuations occurring during the past 2000 years. The increase in dust storm activity was in contrast to the decrease in East Asian winter monsoon (EAWM) intensity during the Holocene, indicating that the EAWM played a limited role in modulating dust storms.
By contrast, the increase in dust storms corresponded to a decrease in East Asian summer monsoon (EASM) precipitation. This demonstrates that EASM precipitation was the dominant control of dust storm activity on a millennial timescale, because decreased EASM precipitation expanded the desert area and thus increased the dust storm activity.
The increasing intensity of human activity in the region since the Bronze Age resulted in an acceleration of dust storm activity against the background of decreased EASM precipitation. As human disturbance continued to intensify, beginning at least at ∼2 cal ka BP, increased dust storms were closely linked to increasing human populations in the dust source regions, and there is a strong temporal coherence between increased dust storms and higher EASM precipitation.
This was completely different from when natural processes are dominant. During that period, fewer dust storms occurred during periods of a strengthened EASM. Therefore, there was a shift from a natural forcing to an anthropogenic forcing of dust storms on a multi-decadal to centennial timescale, and was a mode in which "human activity overtook the EASM as the dominant control of the Earth surface system".
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25