(Peer-Reviewed) Aberration-corrected differential phase contrast microscopy with annular illuminations
Yao Fan 范瑶 ¹ ² ³, Chenyue Zheng 郑辰越 ¹ ² ³, Yefeng Shu 束业峰 ¹ ² ³, Qingyang Fu 符庆杨 ¹ ² ³, Lixiang Xiong 熊立翔 ¹ ² ³, Guifeng Lu 卢桂锋 ¹ ² ³, Jiasong Sun 孙佳嵩 ¹ ² ³, Chao Zuo 左超 ¹ ² ³, Qian Chen 陈钱 ¹ ² ³
¹ Smart Computational Imaging Laboratory (SCILab), School of Electronic and Optical Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China
中国 南京 南京理工大学智能计算成像实验室
² Smart Computational Imaging Research Institute (SCIRI) of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210019, China
中国 南京 南京理工大学智能计算成像研究院
³ Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Visual Sensing & Intelligent Perception, Nanjing 210094, China
中国 南京 江苏省光谱成像与智能感知重点实验室
Opto-Electronic Science, 2025-08-25
Abstract
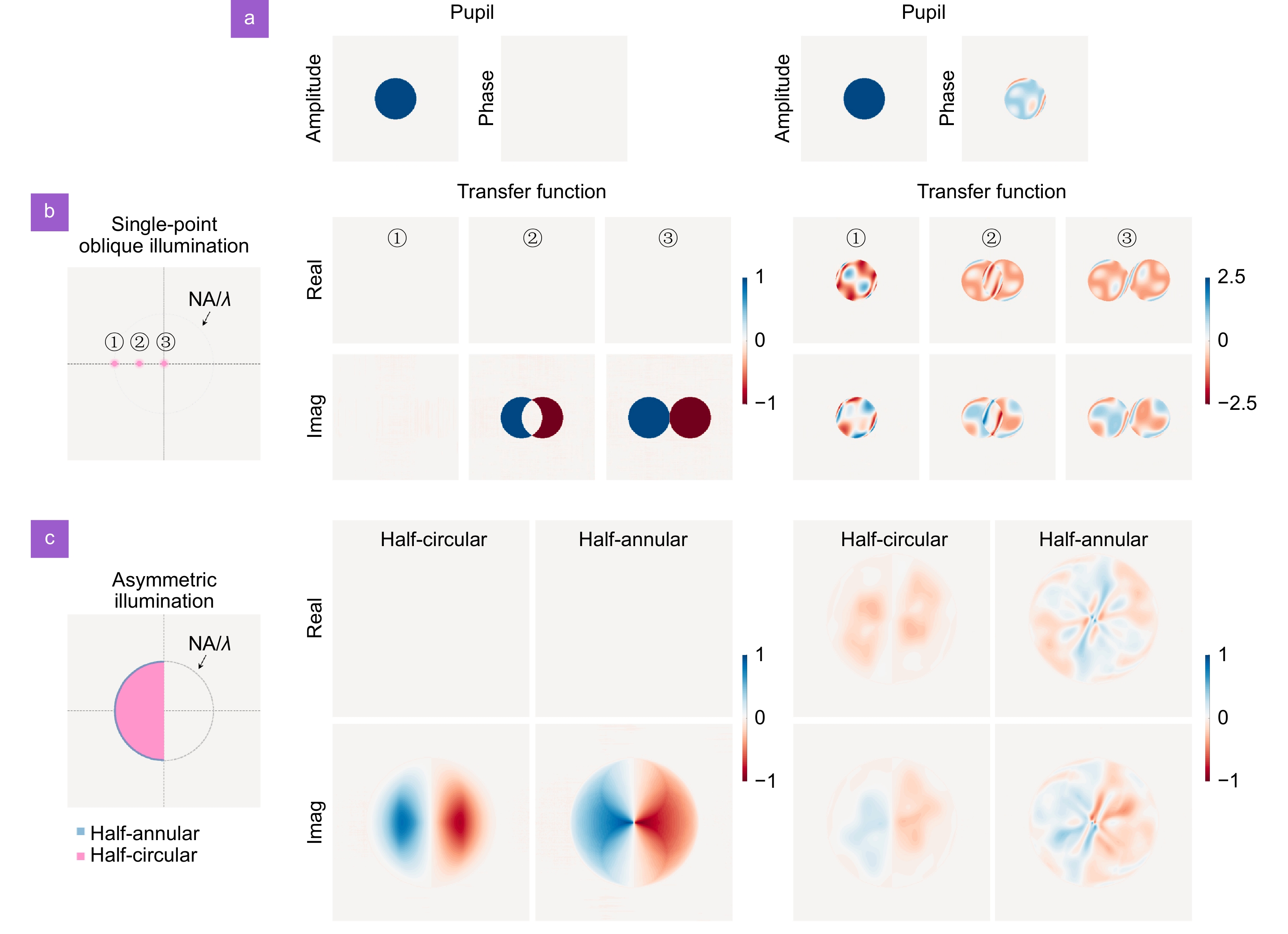
Quantitative phase imaging (QPI) enables non-invasive cellular analysis by utilizing cell thickness and refractive index as intrinsic probes, revolutionizing label-free microscopy in cellular research. Differential phase contrast (DPC), a non-interferometric QPI technique, requires only four intensity images under asymmetric illumination to recover the phase of a sample, offering the advantages of being label-free, non-coherent and highly robust. Its phase reconstruction result relies on precise modeling of the phase transfer function (PTF).
However, in real optical systems, the PTF will deviate from its theoretical ideal due to the unknown wavefront aberrations, which will lead to significant artifacts and distortions in the reconstructed phase. We propose an aberration-corrected DPC (ACDPC) method that utilizes three intensity images under annular illumination to jointly retrieve the aberration and the phase, achieving high-quality QPI with minimal raw data.
By employing three annular illuminations precisely matched to the numerical aperture of the objective lens, the object information is transmitted into the acquired intensity with a high signal-to-noise ratio. Phase retrieval is achieved by an iterative deconvolution algorithm that uses simulated annealing to estimate the aberration and further employs regularized deconvolution to reconstruct the phase, ultimately obtaining a refined complex pupil function and an aberration-corrected quantitative phase.
We demonstrate that ACDPC is robust to multi-order aberrations without any priori knowledge, and can effectively retrieve and correct system aberrations to obtain high-quality quantitative phase. Experimental results show that ACDPC can clearly reproduce subcellular structures such as vesicles and lipid droplets with higher resolution than conventional DPC, which opens up new possibilities for more accurate subcellular structure analysis in cell biology.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25