(Peer-Reviewed) Enhanced amplified spontaneous emission via splitted strong coupling mode in large-area plasmonic cone lattices
Jiazhi Yuan 袁佳智 ¹, Jiang Hu 胡江 ¹, Yan Zheng 郑燕 ¹ ³ ⁴, Hao Wei 魏浩 ¹ ³, Jiamin Xiao 肖佳敏 ¹, Yi Wang 王祎 ¹ ², Xuchao Zhao 赵绪超 ¹, Ye Xiang 向冶 ¹, Yong Lei 雷勇 ⁴, Wenxin Wang 王文鑫 ¹ ² ⁵
¹ Qingdao Innovation and Development Center of Harbin Engineering University, Harbin Engineering University, Qingdao 266500, China
中国 青岛 哈尔滨工程大学青岛创新发展基地
² College of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
中国 哈尔滨 哈尔滨工程大学物理与光电工程学院
³ College of Material Sciences and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
中国 哈尔滨 哈尔滨工程大学材料科学与化学工程学院
⁴ Institute of Physics, Department of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, TU Ilmenau, Ilmenau 98693, Germany
⁵ College for Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
中国 长沙 国防科技大学前沿交叉学科学院
Opto-Electronic Science, 2024-12-19
Abstract
Periodic metal nanoarrays serving as cavities can support directional-tunable amplified spontaneous emission that goes beyond the diffraction limit due to the hybrid states of surface plasmons and Bloch surface waves. Most of these modes' interactions remain within the weak coupling regime, yet strong coupling is also anticipated to occur.
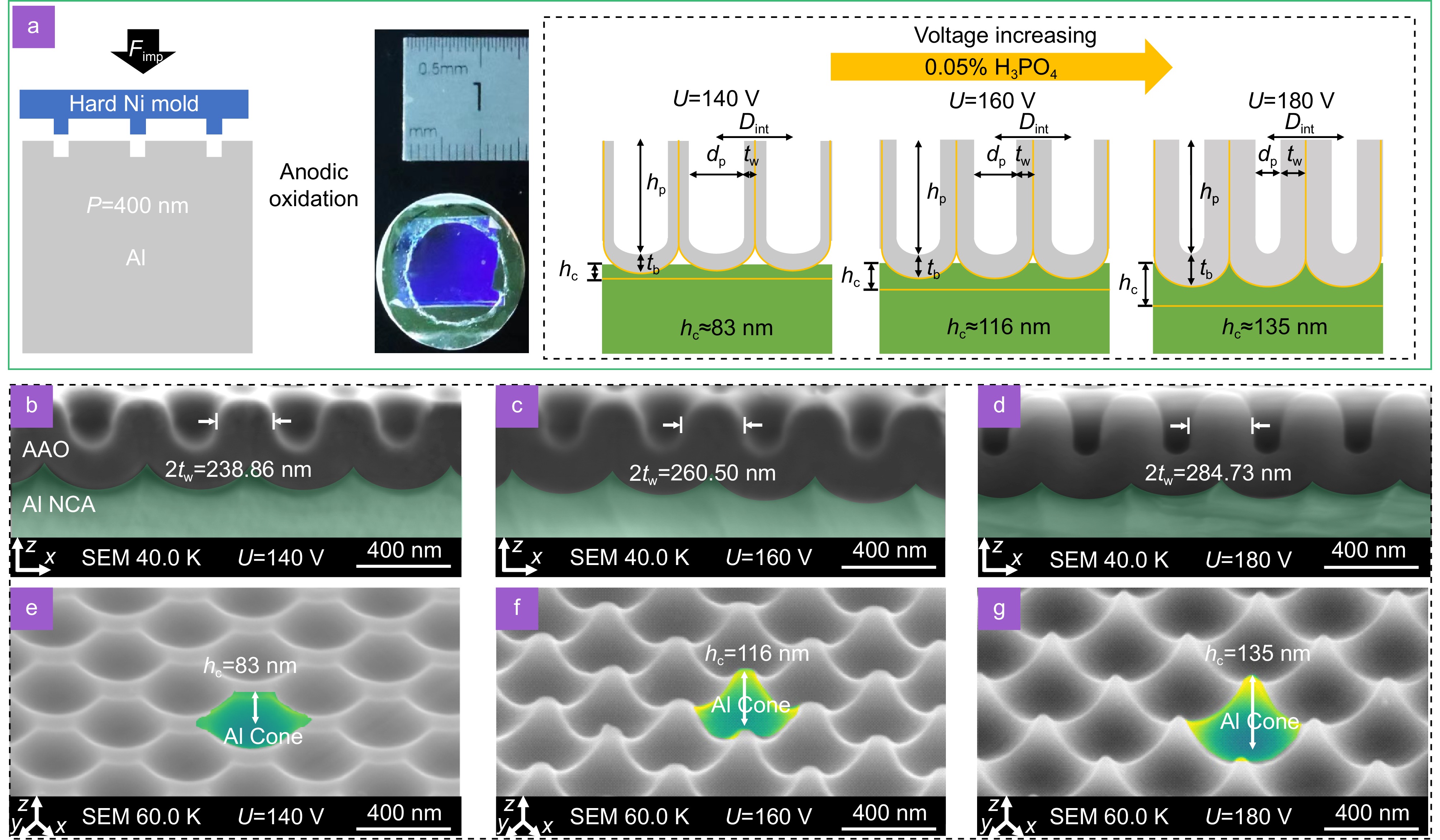
In this work, we present an intriguing case of amplified spontaneous emission (ASE), amplified by the splitting upper polariton mode within a strong coupling system, stemming from a square lattice of plasmonic cone lattices (PCLs). The PCLs are fabricated using an anodized aluminum oxide membrane (AAO), which facilitates strong coupling between surface plasmons and Bloch surface wave modes, with the maximum Rabi splitting observed at 0.258 eV for the sample with an aspect ratio of 0.33.
A 13.5-fold increase in amplified spontaneous emission is recorded when the emission from Nile Red coincides with this flat energy branch of upper polariton, which exhibits a high photon density of states. Reduced group velocity can prolong photon lifetime and boost the probability of light-matter interaction. The observed ASE phenomenon in this strong coupling plasmonic system widens the scope for applications in nanolasing and polariton lasing.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25