(Peer-Reviewed) Ferroelectric domain engineering of lithium niobate
Jackson J. Chakkoria ¹ ², Aditya Dubey ¹ ², Arnan Mitchell ¹ ², Andreas Boes ² ³ ⁴
¹ Integrated Photonics and Applications Centre, School of Engineering, RMIT University, Melbourne, VIC 3001, Australia
² ARC Centre of Excellence in Optical Microcombs for Breakthrough Science (COMBS)
³ School of Electrical and Mechanical Engineering, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, SA 5005, Australia
⁴ Institute for Photonics and Advanced Sensing, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, SA 5005, Australia
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2025-01-03
Abstract
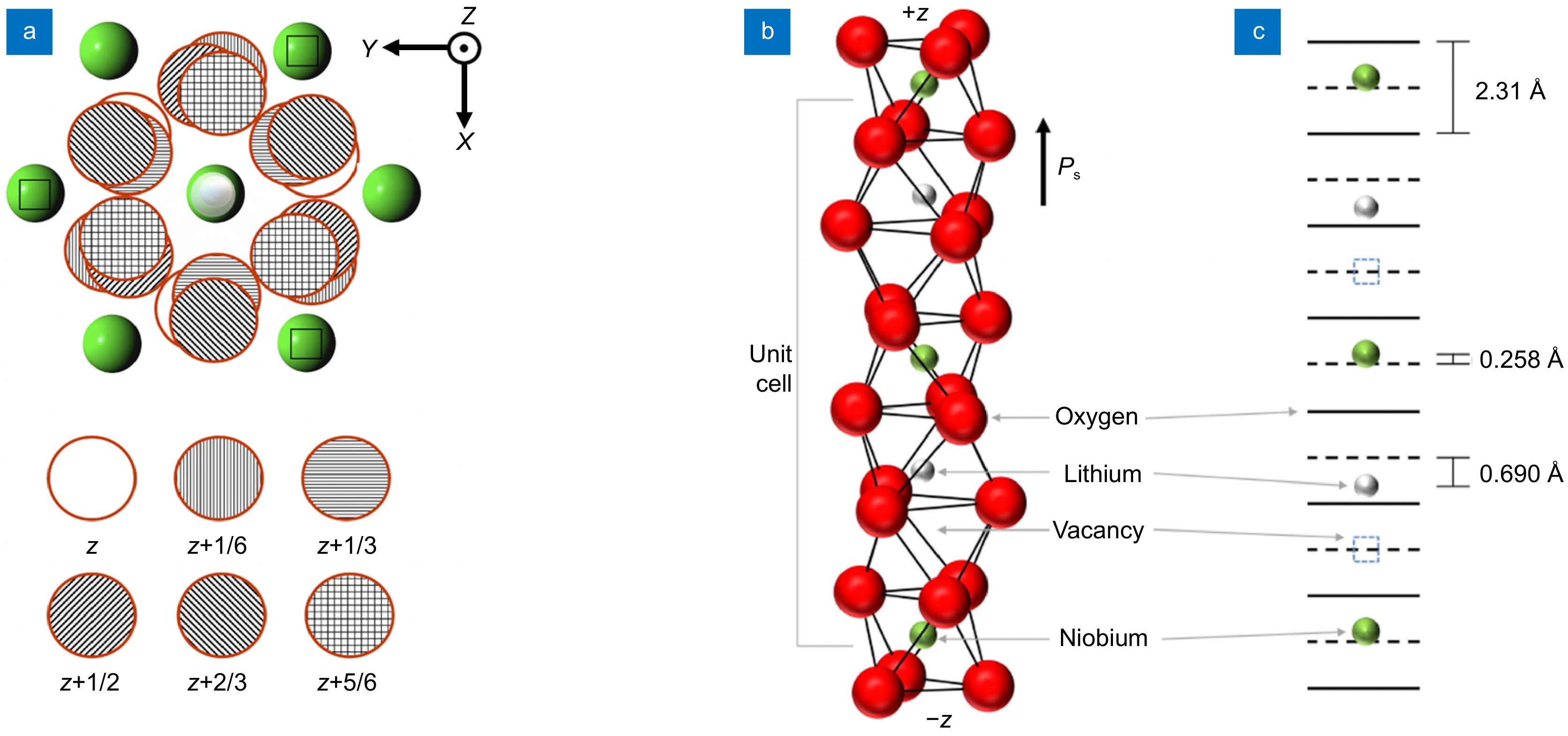
Lithium niobate (LN) has remained at the forefront of academic research and industrial applications due to its rich material properties, which include second-order nonlinear optic, electro-optic, and piezoelectric properties. A further aspect of LN’s versatility stems from the ability to engineer ferroelectric domains with micro and even nano-scale precision in LN, which provides an additional degree of freedom to design acoustic and optical devices with improved performance and is only possible in a handful of other materials.
In this review paper, we provide an overview of the domain engineering techniques developed for LN, their principles, and the typical domain size and pattern uniformity they provide, which is important for devices that require high-resolution domain patterns with good reproducibility. It also highlights each technique's benefits, limitations, and adaptability for an application, along with possible improvements and future advancement prospects.
Further, the review provides a brief overview of domain visualization methods, which is crucial to gain insights into domain quality/shape and explores the adaptability of the proposed domain engineering methodologies for the emerging thin-film lithium niobate on an insulator platform, which creates opportunities for developing the next generation of compact and scalable photonic integrated circuits and high frequency acoustic devices.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25