(Peer-Reviewed) Better prognostic determination of cT3 rectal cancer through measurement of distance to mesorectal fascia: A multicenter study
Xiaoyan Zhang 张晓燕 ¹, Qiaoyuan Lu 卢巧媛 ¹, Xiangjie Guo 郭相杰 ², Wuteng Cao 曹务腾 ³, Hongmei Zhang 张红梅 ⁴, Tao Yu 于韬 ⁵, Xiaoting Li 李晓婷 ¹, Zhen Guan 管真 ¹, Xueping Li ¹, Ruijia Sun ¹, Yingshi Sun 孙应实 ¹
¹ Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and Translational Research (Ministry of Education/Beijing), Department of Radiology, Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing 100142, China
中国 北京 北京大学肿瘤医院 放疗科 恶性肿瘤发病机制及转化研究教育部/北京市重点实验室
² Department of Forensic Medicine, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, China
中国 太原 山西医科大学法医学院
³ Department of Radiology, the Sixth Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510655, China
中国 广州 中山大学附属第六医院 放疗科
⁴ Department of Radiology, National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100021, China
中国 北京 国家癌症中心/ 国家肿瘤临床医学研究中心/ 中国医学科学院北京协和医学院肿瘤医院
⁵ Department of Medical Imaging, Cancer Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110042, China
中国 沈阳 中国医科大学肿瘤医院 医学影像科
Objective
To forward the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) based distance between the deepest tumor invasion and mesorectal fascia (DMRF), and to explore its prognosis differentiation value in cT3 stage rectal cancer with comparison of cT3 substage.
Methods
This was a retrospective, multicenter cohort study including cT3 rectal cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy followed by radical surgery from January 2013 to September 2014. DMRF and cT3 substage were evaluated from baseline MRI. The cutoff of DMRF was determined by disease progression. Multivariate cox regression was used to test the prognostic values of baseline variables.
Results
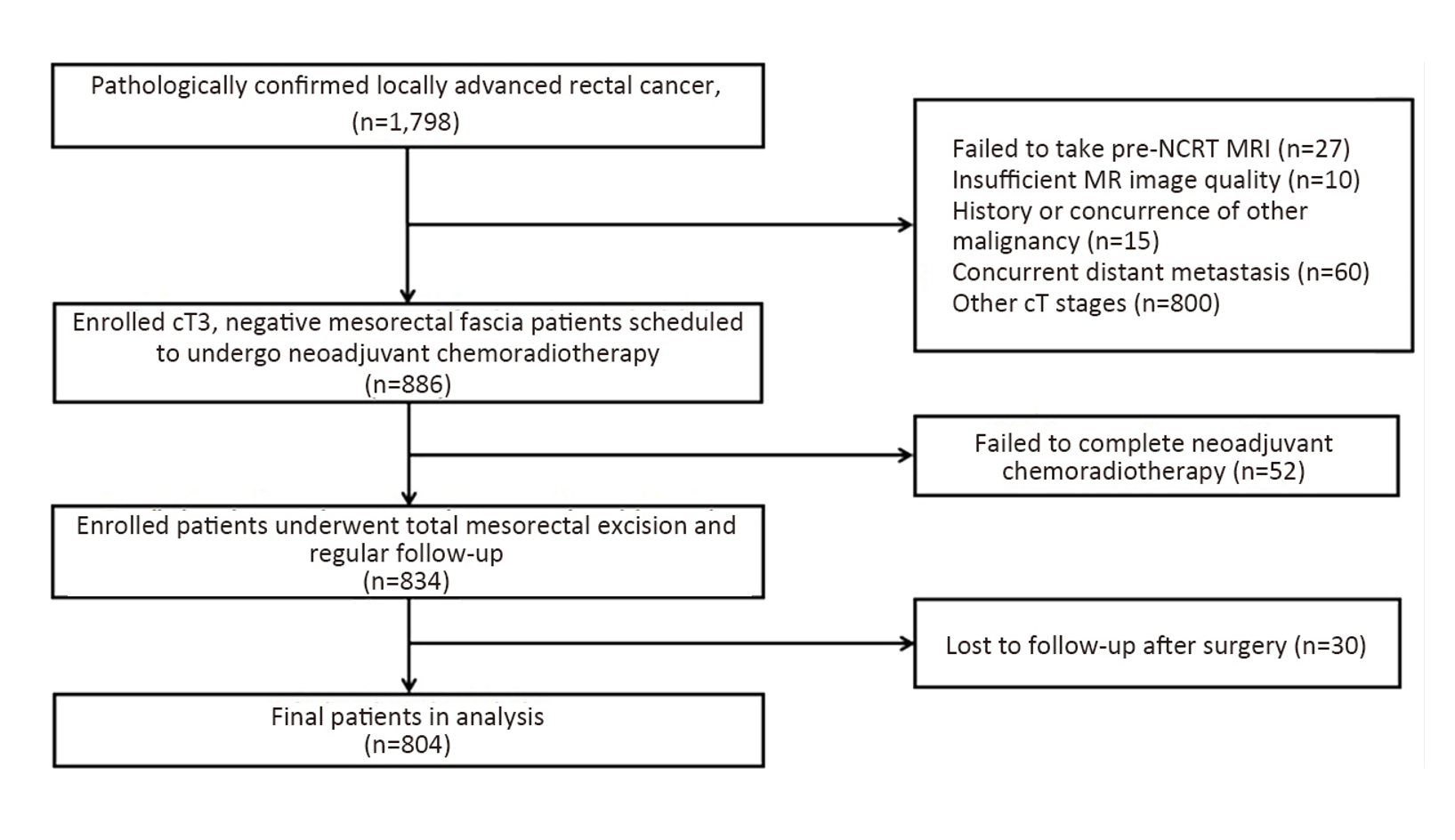
A total of 804 patients were included, of which 226 (28.1%) developed progression. A DMRF cutoff of 7 mm was chosen. DMRF category, the clock position of the deepest position of tumor invasion (CDTI) and extramural venous invasion (EMVI) were independent predictors for disease progression, and hazard ratios (HRs) were 0.26 [95% confidence interval (95% CI), 0.13−0.56], 1.88 (95% CI, 1.33−2.65) and 1.57 (95% CI, 1.13−2.18), respectively. cT3 substage was not a predictor for disease progression.
Conclusions
The measurement of DMRF value on baseline MRI can better distinguish cT3 rectal cancer prognosis rather than cT3 substage, and was recommended in clinical evaluation.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25