(Peer-Reviewed) p62/SQSTM1 Participates in the Innate Immune Response of Macrophages Against Candida albicans Infection
He Yan-Zhi ¹, Duan Zhi-Min 段志敏 ², Chen Xu 陈旭 ¹ ³, Li Min 李岷 ¹ ³
¹ Center for Global Health, School of Public Health, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu 211166, China
中国 南京 南京医科大学 公共卫生学院 全球健康中心
² Department of Dermatology, Hospital for Skin Diseases (Institute of Dermatology), Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Nanjing, Jiangsu 210042, China
中国 江苏 南京 中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院 皮肤病医院(皮肤病研究所)皮肤科
³ Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology for Skin Diseases and STIs, Hospital for Skin Diseases (Institute of Dermatology), Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Nanjing, Jiangsu 210042, China
中国 江苏 南京 中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院 皮肤病医院(皮肤病研究所)江苏省皮肤病与性病分子生物学重点实验室
Abstract
Objective
This study was designed to evaluate whether p62/SQSTM1 (hereafter referred to as p62) is involved in the immune response of macrophages against challenge by Candida albicans (C. albicans).
Methods
We cultured bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) to investigate the immune response to challenge by C. albicans. The p62 gene was knocked down by transfection with p62 small interfering RNA (siRNA) in the p62 siRNA group. BMDMs transfected with nonsense siRNA served as the negative control (NC) group. These two groups of BMDMs were challenged with C. albicans in vitro. We detected p62 expression through quantitative reverse transcription PCR and western blotting. The phagocytosis ability of BMDMs was evaluated by flow cytometry and microscopic examination using an Olympus FV1000 laser scanning confocal microscope. Moreover, we determined the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in BMDMs. The mRNA levels of proinflammatory cytokines were determined by quantitative reverse transcription PCR.
Results
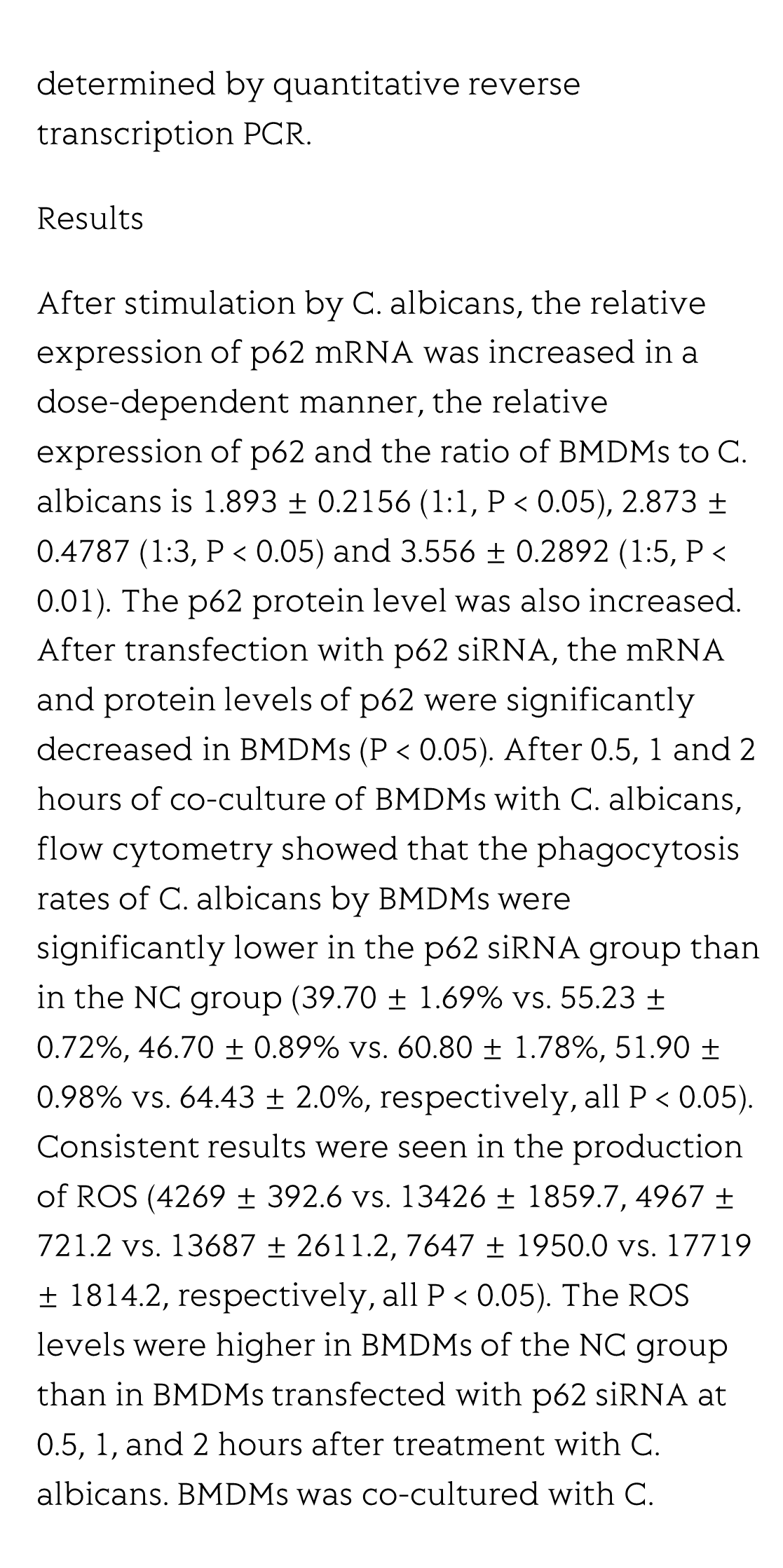
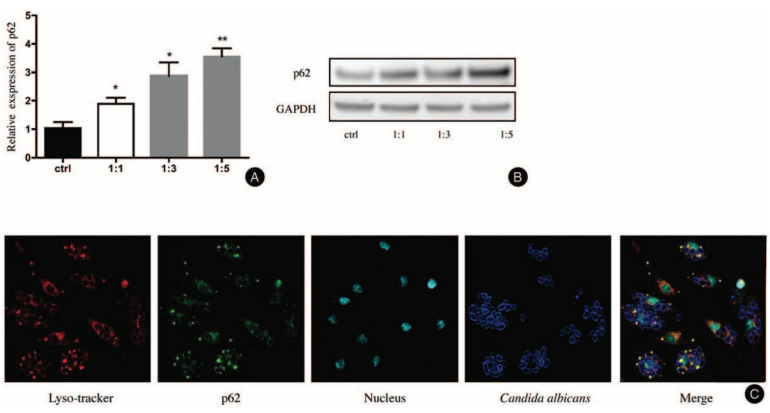
After stimulation by C. albicans, the relative expression of p62 mRNA was increased in a dose-dependent manner, the relative expression of p62 and the ratio of BMDMs to C. albicans is 1.893 ± 0.2156 (1:1, P < 0.05), 2.873 ± 0.4787 (1:3, P < 0.05) and 3.556 ± 0.2892 (1:5, P < 0.01). The p62 protein level was also increased. After transfection with p62 siRNA, the mRNA and protein levels of p62 were significantly decreased in BMDMs (P < 0.05). After 0.5, 1 and 2 hours of co-culture of BMDMs with C. albicans, flow cytometry showed that the phagocytosis rates of C. albicans by BMDMs were significantly lower in the p62 siRNA group than in the NC group (39.70 ± 1.69% vs. 55.23 ± 0.72%, 46.70 ± 0.89% vs. 60.80 ± 1.78%, 51.90 ± 0.98% vs. 64.43 ± 2.0%, respectively, all P < 0.05). Consistent results were seen in the production of ROS (4269 ± 392.6 vs. 13426 ± 1859.7, 4967 ± 721.2 vs. 13687 ± 2611.2, 7647 ± 1950.0 vs. 17719 ± 1814.2, respectively, all P < 0.05). The ROS levels were higher in BMDMs of the NC group than in BMDMs transfected with p62 siRNA at 0.5, 1, and 2 hours after treatment with C. albicans. BMDMs was co-cultured with C. albicans for 4 and 12 hours, the mRNA levels of interleukin-1β and interleukin-18 in NCs were also higher than p62 siRNA group, interleukin-1β: (6.14 ± 1.63 vs. 12.12 ± 0.54, 8.81 ± 0.86 vs. 26.2 ± 4.67, respectively, all P < 0.05), IL-18: (0.38 ± 0.02 vs. 0.97 ± 0.06, 0.44 ± 0.02 vs. 2.23 ± 0.46, respectively, all P < 0.05).
Conclusion
p62 plays an important role in the process of phagocytosis in BMDMs challenged by C. albicans through ROS production and expression of proinflammatory cytokines.
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25