(Peer-Reviewed) Decay rate of Larix gmelinii coarse woody debris on burned patches in the Greater Khingan Mountains
Shubo Huang 黄书博 ¹, Lixiang Wen 温理想 ¹, Shuai Yin ², Meng Guo 郭蒙 ¹, Fangbing Yu 于方冰 ¹
¹ Key Laboratory of Geographical Processes and Ecological Security in Changbai Mountains, School of Geographical Sciences, Northeast Normal University, Ministry of Education, Changchun, 130024, People's Republic of China
中国 长春 东北师范大学地理科学学院 长白山地理过程与生态安全教育部重点实验室
² Center for Global Environmental Research, National Institute for Environmental Studies, Tsukuba, 3058506, Japan
Abstract
The decomposition of coarse woody debris (CWD) affects the energy flow and nutrient cycling in forest ecosystems. Previous studies on CWD have focused on the input, decomposition, reserve dynamics, and CWD functions, but coarse woody debris decomposition is complex and the results from different regions vary considerably. It is not clear which factors affect decay rate (k), especially at different decomposition stages.
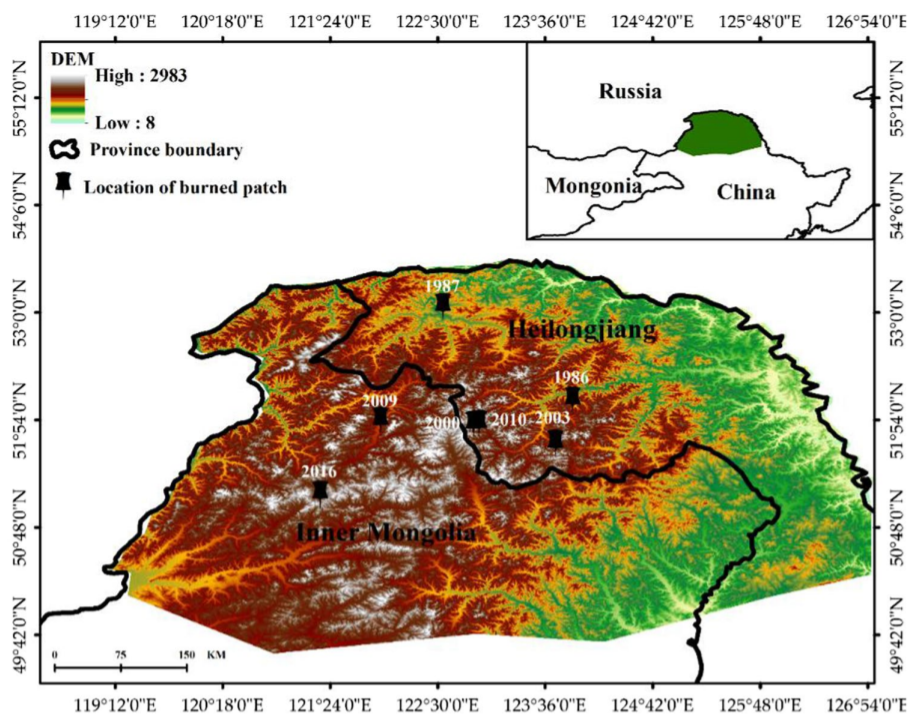
In this study, a single-exponential decay model was used to analyze the characteristics of CWD decomposition in Larix gmelinii forests over the 33 years following a fire in the Greater Khingan Mountains. The results show that the decay rate of coarse woody debris was positively correlated to decay class. The average decomposition rate was 0.019, and 41 years and 176 years are needed for a 50% and 95% mass loss, respectively. CWD nutrient content, density, and water content could explain the variance in the decay rate (~ 42%) of the decay factors such as amount of leaching, degree of fragmentation, respiration of the debris, and biotransformation, and varied significantly between different decay classes.
Using the space–time substitution method, this study arranged the coarse woody debris of different mortality times to form a 33 year chronosequence which revealed the decomposition process. It was concluded that the decay rate was mainly explained by structural component of the debris and its nitrogen and water contents. This paper quantifies the indicators affecting CWD decay to explain the decomposition process.
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25