(Peer-Reviewed) Identification of proteins associated with Fusarium crown rot resistance in wheat using label-free quantification analysis
JIN Jing-jing 金京京 ¹ ², DUAN Shuo-nan 段硕楠 ³, QI Yong-zhi 齐永志 ¹ ², ZHEN Wen-chao 甄文超 ² ⁴, MA Jun 马骏 ³
¹ College of Plant Protection, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding 071001, P.R.China
中国 保定 河北农业大学植物保护学院
² State Key Laboratory of North China Crop Improvement and Regulation, Baoding 071001, P.R.China
中国 保定 华北作物改良与调控国家重点实验室
³ College of Agronomy and Biotechnology, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100193, P.R.China
中国 北京 中国农业大学农学与生物技术学院
⁴ College of Agronomy, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding 071001, P.R.China
中国 保定 河北农业大学农学院
Abstract
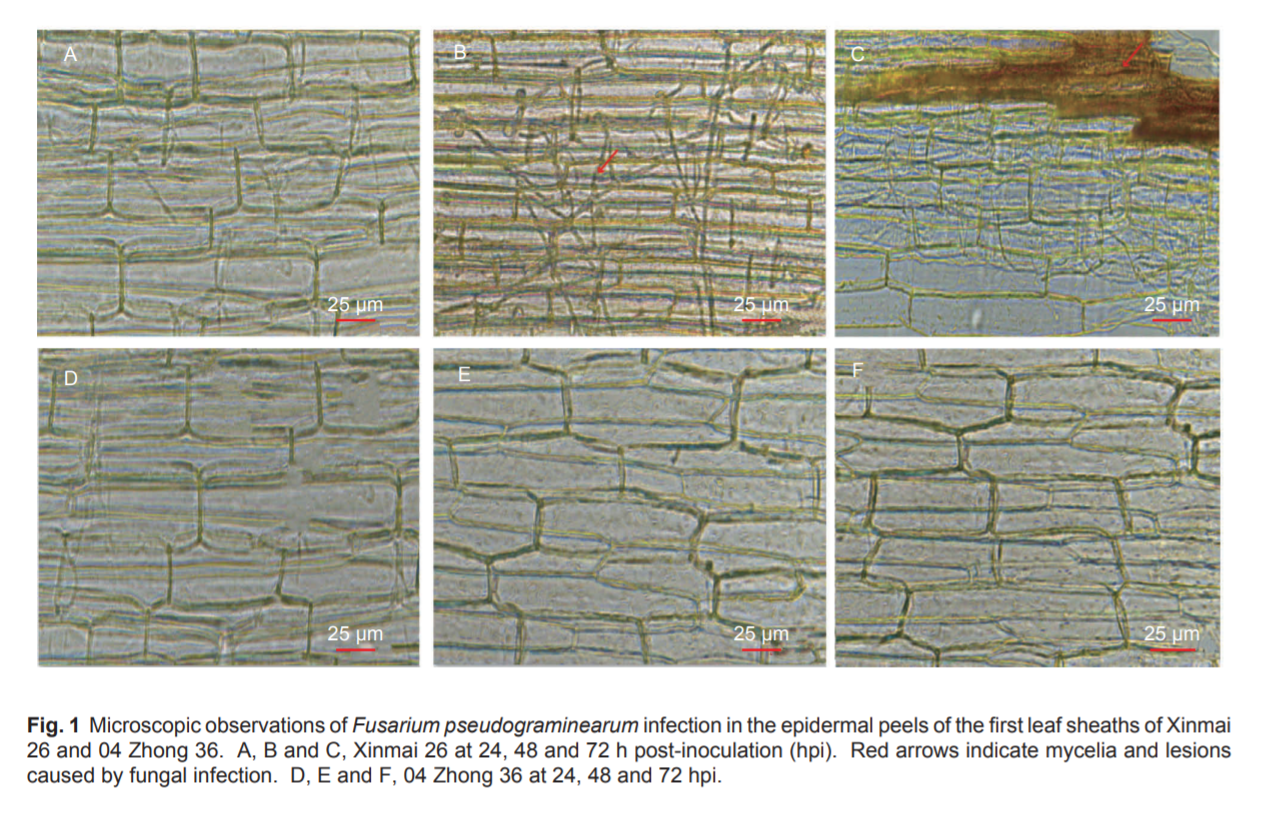
Fusarium crown rot (FCR), typically caused by Fusarium pseudograminearum, is a severe soil-borne disease that, in recent years, has become an emerging threat to Chinese wheat crops. For the first time in this study, we investigated and compared the proteomic characteristics of two Chinese wheat varieties (04 Zhong 36 and Xinmai 26) at 24, 48, and 72 h post-inoculation using label-free quantitative proteomic analysis.
A total of 9 234 proteins were successfully quantified, of which 783 were differentially expressed after inoculation. These proteins were mainly involved in metabolic, single-organism, and cellular processes. Thirty-three proteins associated with defense, cell wall formation, photosynthesis, etc., showed consistently different expression between the two genotypes at multiple time points. In particular, chitinase, which degrades chitin in the fungal cell wall and limits fungal growth, was exclusively and consistently upregulated in 04 Zhong 36 across the three time points. Other proteins such as flavonoid O-methyltransferase, glycosyltransferase, and peroxidase were only upregulated in 04 Zhong 36, and proteins, including the berberine bridge enzyme and rubisco large subunit-binding protein, were specifically downregulated in Xinmai 26.
The expression of transcripts encoding eight selected proteins through qRT-PCR analysis supported the proteomic profiles. Overall, the results of this study allow us to understand FCR resistance in wheat at the protein level. Some proteins and their corresponding genes may be useful resources for the genetic improvement of FCR resistance in wheat.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25