(Peer-Reviewed) CW laser damage of ceramics induced by air filament
Chuan Guo 郭川 ¹ ², Kai Li 李凯 ³, †, Zelin Liu 刘泽琳 ¹, Yuyang Chen 陈宇杨 ³, Junyang Xu 徐俊洋 ³, Zhou Li 李洲 ³, Wenda Cui 崔文达 ¹ ², Changqing Song 宋长青 ¹ ², Cong Wang 王聪 ³, Xianshi Jia 贾贤石 ³, Ji'an Duan 段吉安 ³, Kai Han 韩凯 ¹ ²
¹ College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 400073, China
中国 长沙 国防科技大学前沿交叉学科学院
² Nanhu Laser Laboratory, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 400073, China
中国 长沙 国防科技大学南湖之光实验室
³ State Key Laboratory of Precision Manufacturing for Extreme Service Performance, College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
中国 长沙 中南大学极端服役性能精准制造全国重点实验室
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2025-06-27
Abstract
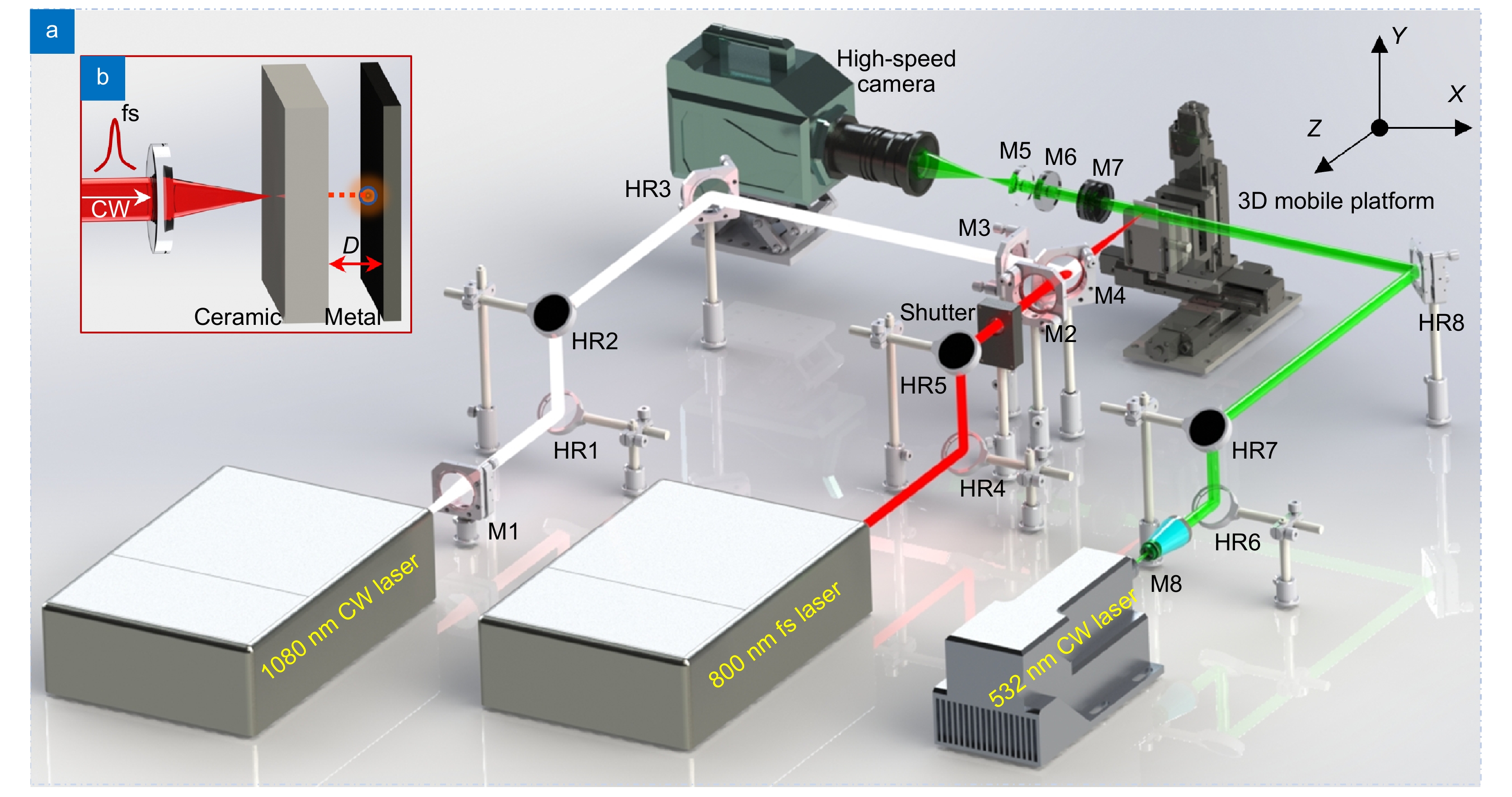
Combined pulsed laser (CPL), introduced in 1975 for target damage, integrates different lasers to achieve high peak power and pulse energy. However, despite decades of research, CPL remains unused for long-range target damage due to the challenge of maintaining high peak power density over long distances.
We note that a potential solution lies in leveraging the air filament generated by femtosecond laser, which can transmit peak power densities higher than 1014 W/cm2 under the power clamping effect. To address this, a concept of a femtosecond laser induced air filament-CW CPL for surface damage of ceramics was introduced. We found no surface changes in ceramic targets when irradiated with a CW laser alone.
By way of contrast, the target can be penetrated in a very short time (20 ms) with the assistance of the femtosecond laser induced air filament. In this context, we employ high-speed shadow imaging, cross-timescale simulation models and macro-microscopic characterization, to elucidate the CPL damage mechanism. The optimal CPL, combining a 1 mJ femtosecond laser and a 500 W CW laser, yields a damage rate of 1.51×107 μm3/J, representing an improvement of approximately 175% compared to single femtosecond laser ablation and around 59% enhancement compared to coating-assisted CW laser ablation.
Furthermore, the efficacy of the proposed femtosecond-CW CPL method is demonstrated in causing penetration damage of ceramic/metal composite material or direct damage of sapphire, showcasing its versatility in damaging applications. Consequently, the femtosecond-CW CPL ablation method presented in this paper holds great promise as a new type of damage method for transparent hard and brittle materials.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25