(Peer-Reviewed) Electric-field-induced second-harmonic generation
Hangkai Fan ¹ ² ³ ⁴, Alexey Proskurin ⁴, Mingzhao Song ¹ ² ⁵, Andrey Bogdanov ¹ ⁴
¹ Qingdao Innovation and Development Center, Harbin Engineering University, Qingdao 266000, China
中国 青岛 哈尔滨工程大学青岛创新发展基地
² Key Laboratory of Photonic Materials and Device Physics for Oceanic Applications, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of China, Harbin 150001, China
中国 哈尔滨 海洋光子材料与器件物理工业和信息化部重点实验室
³ College of Information and Communication Engineering, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
中国 哈尔滨 哈尔滨工程大学信息与通信工程学院
⁴ School of Physics and Engineering, ITMO University, St. Petersburg 191002, Russia
⁵ College of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
中国 哈尔滨 哈尔滨工程大学物理与光电工程学院
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2026-01-27
Abstract
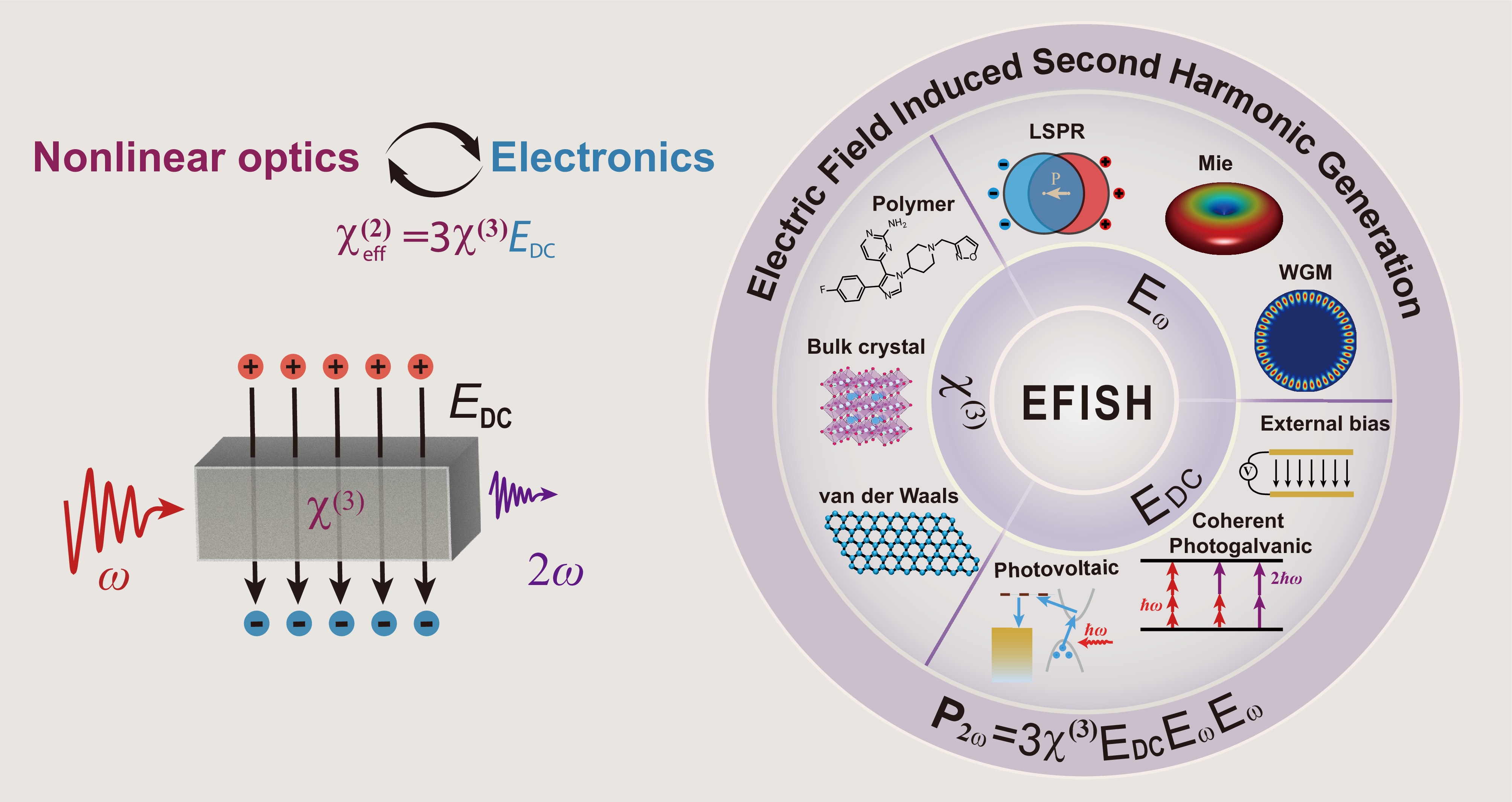
Second-harmonic generation (SHG) is a fundamental nonlinear optical process widely used in photonics; however, it is strictly forbidden in the bulk of centrosymmetric materials due to their inversion symmetry. Nevertheless, applying an external electric field breaks this inversion symmetry. It induces an effective second-order nonlinear response known as the electric-field-induced second-harmonic generation (EFISH) effect.
This mechanism enables SHG in centrosymmetric media and provides a effective mechanism for electrically tunable nonlinear nanophotonics. Here, we present a comprehensive overview of the EFISH effect, covering the fundamentals, various material platforms (including bulk semiconductor crystals, ferroelectrics, van der Waals materials, and polymers), as well as diverse strategies for electric field engineering.
We distinguish EFISH from related effects including current-induced SHG and the quantum-confined Stark effect, and highlight emerging applications of EFISH in tunable photonic devices, carrier dynamics probing, and nonlinear optical modulation across optical, electronic, and THz regimes. Finally, we outline key challenges and prospects for the future development of electrically controlled nonlinear optical systems.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25