(Peer-Reviewed) Lymphangiogenesis contributes to exercise-induced physiological cardiac growth
Yihua Bei 贝毅桦 ¹ ², Zhenzhen Huang ¹ ², Xing Feng ¹ ², Lin Li ¹ ², Meng Wei ¹ ², Yujiao Zhu ¹ ², Shuqin Liu 刘书琴 ¹ ², Chen Chen ¹ ², Mingming Yin ¹ ², Huimin Jiang 姜惠敏 ³, Junjie Xiao 肖俊杰 ¹ ²
¹ Cardiac Regeneration and Ageing Lab, Institute of Geriatrics (Shanghai University), Affiliated Nantong Hospital of Shanghai University (The Sixth People's Hospital of Nantong), School of Medicine, Shanghai University, Nantong 226011, China
上海大学医学院 上海大学附属南通医院(南通市第六人民医院)上海大学老年医学研究院 再生与衰老实验室 南通 中国
² Shanghai Engineering Research Center of Organ Repair, School of Life Science, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China
中国 上海 上海大学生命科学学院上海器官修复工程技术研究中心
³ Clinical Laboratory Center, Beijing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing, 100010, China
中国 北京 北京中医医院 临床检验中心
Abstract
Background
Promoting cardiac lymphangiogenesis exerts beneficial effects for the heart. Exercise can induce physiological cardiac growth with cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and increased proliferation markers in cardiomyocytes. However, it remains unclear whether and how lymphangiogenesis contributes to exercise-induced physiological cardiac growth. We aimed to investigate the role and mechanism of lymphangiogenesis in exercise-induced physiological cardiac growth.
Methods
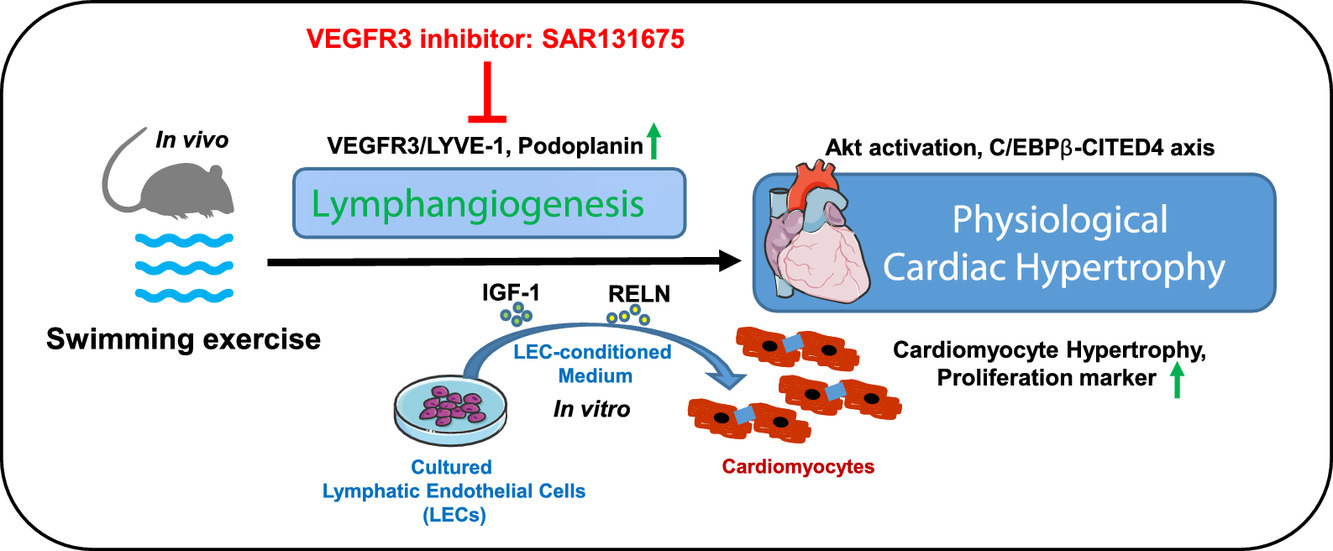
Adult C57BL6/J mice were subjected to 3 weeks of swimming exercise to induce physiological cardiac growth. Oral treatment with vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 (VEGFR3) inhibitor SAR131675 was used to investigate whether cardiac lymphangiogenesis was required for exercise-induced physiological cardiac growth by VEGFR3 activation. Furthermore, human dermal lymphatic endothelial cell (LEC)-conditioned medium was collected to culture isolated neonatal rat cardiomyocytes to determine whether and how LECs could influence cardiomyocyte proliferation and hypertrophy.
Results
Swimming exercise induced physiological cardiac growth accompanied by a remarkable increase of cardiac lymphangiogenesis as evidenced by increased density of lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronic acid receptor 1–positive lymphatic vessels in the heart and upregulated lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronic acid receptor 1 and Podoplanin expressions. VEGFR3 was upregulated in the exercised heart, while VEGFR3 inhibitor SAR131675 attenuated exercise-induced physiological cardiac growth as evidenced by blunted myocardial hypertrophy and reduced proliferation marker Ki67 in cardiomyocytes, which was correlated with reduced lymphatic vessel density and downregulated lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronic acid receptor 1 and Podoplanin in the heart upon exercise. Furthermore, LEC-conditioned medium promoted both hypertrophy and proliferation of cardiomyocytes and contained higher levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 and the extracellular protein Reelin, while LEC-conditioned medium from LECs treated with SAR131675 blocked these effects. Functional rescue assays further demonstrated that protein kinase B activation, as well as reduced CCAAT enhancer-binding protein beta and increased CBP/p300-interacting transactivators with E (glutamic acid)/D (aspartic acid)–rich-carboxylterminal domain 4, contributed to the promotive effect of LEC-conditioned medium on cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and proliferation.
Conclusion
Our findings reveal that cardiac lymphangiogenesis is required for exercise-induced physiological cardiac growth by VEGFR3 activation, and they indicate that LEC-conditioned medium promotes both physiological hypertrophy and proliferation of cardiomyocytes through protein kinase B activation and the CCAAT enhancer-binding protein beta–rich-carboxylterminal domain 4 axis. These results highlight the essential roles of cardiac lymphangiogenesis in exercise-induced physiological cardiac growth.
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25