(Peer-Reviewed) Implementation of Abstract MAC Layer Under Jamming
Yifei Zou 邹逸飞 ¹, Minghui Xu 徐明辉 ¹, Dongxiao Yu 于东晓 ¹, Liandong Chen 陈连栋 ², Shaoyong Guo 郭少勇 ³, Xiaoshuang Xing 邢晓双 ⁴
¹ School of Computer Science and Technology, Shandong University, Qingdao 266237, China
中国 青岛 山东大学计算机科学与技术学院
² Information and Telecommunication Branch, State Grid Hebei Electric Power Company Ltd., Shijiazhuang 050022, China
中国 石家庄 国网河北省电力有限公司信息通信分公司
³ State Key Laboratory of Networking and Switching Technology, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
中国 北京 北京邮电大学 网络与交换技术国家重点实验室
⁴ School of Computer Science and Engineering, Changshu Institute of Technology, Changshu 215500, China
中国 常熟 常熟理工学院 计算机科学与工程学院
Abstract
In the past decades, with the widespread implementation of wireless networks, such as the Internet of Things, an enormous demand for designing relative algorithms for various realistic scenarios has arisen. However, with the widening of scales and deepening of network layers, it has become increasingly challenging to design such algorithms when the issues of message dissemination at high levels and the contention management at the physical layer are considered.
Accordingly, the abstract medium access control (absMAC) layer, which was proposed in 2009, is designed to solve this problem. Specifically, the absMAC layer consists of two basic operations for network agents: the acknowledgement operation to broadcast messages to all neighbors and the progress operation to receive messages from neighbors. The absMAC layer divides the wireless algorithm design into two independent and manageable components, i.e., to implement the absMAC layer over a physical network and to solve higher-level problems based on the acknowledgement and progress operations provided by the absMAC layer, which makes the algorithm design easier and simpler.
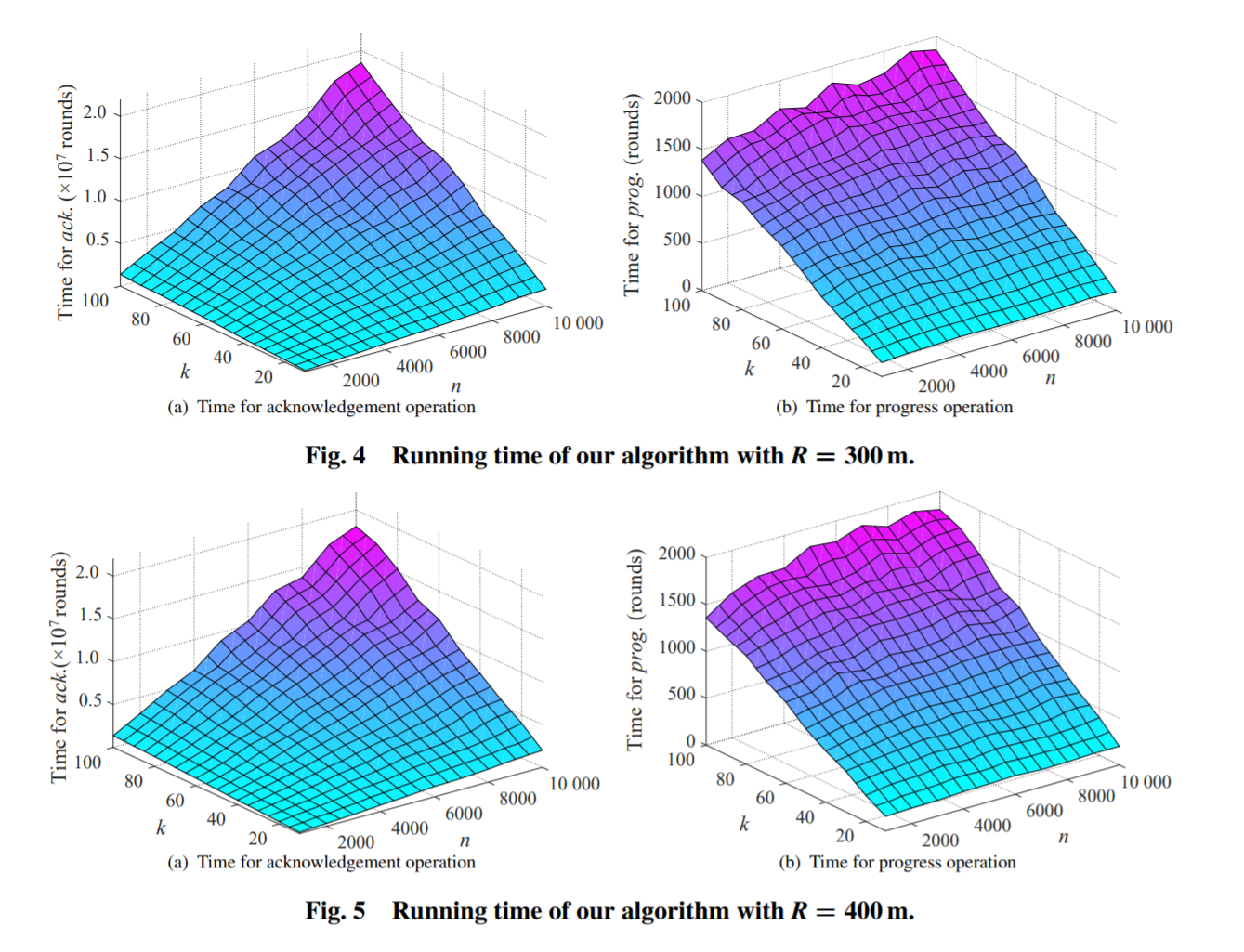
In this study, we consider the implementation of the absMAC layer under jamming. An efficient algorithm is proposed to implement the absMAC layer, attached with rigorous theoretical analyses and extensive simulation results. Based on the implemented absMAC layer, many high-level algorithms in non-jamming cases can be executed in a jamming network.
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25