(Peer-Reviewed) Extracts of Portulaca oleracea promote wound healing by enhancing angiology regeneration and inhibiting iron accumulation in mice
Jinglin Guo 郭景琳 ¹, Juan Peng 彭娟 ², Jing Han 韩晶 ¹, Ke Wang 王珂 ³, Ruijuan Si 司瑞娟 ¹, Hui Shan 山慧 ¹, Xiaoying Wang 王晓莹 ¹, Ju Zhang 张菊 ¹
¹ School of Nursing, Qingdao University, Qingdao 266071, China
中国 青岛 青岛大学护理学院
² Surgery of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Second Affiliated Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 300150, China
中国 天津 天津中医药大学第二附属医院中医外科
³ School of Pharmacy, Qingdao University, Qingdao 266071, China
中国 青岛 青岛大学药学院
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the role of Portulaca oleracea (POL) in promoting revascularization and re-epithelization as well as inhibiting iron aggregation and inflammation of deep tissue pressure injury (DTPI).
Methods
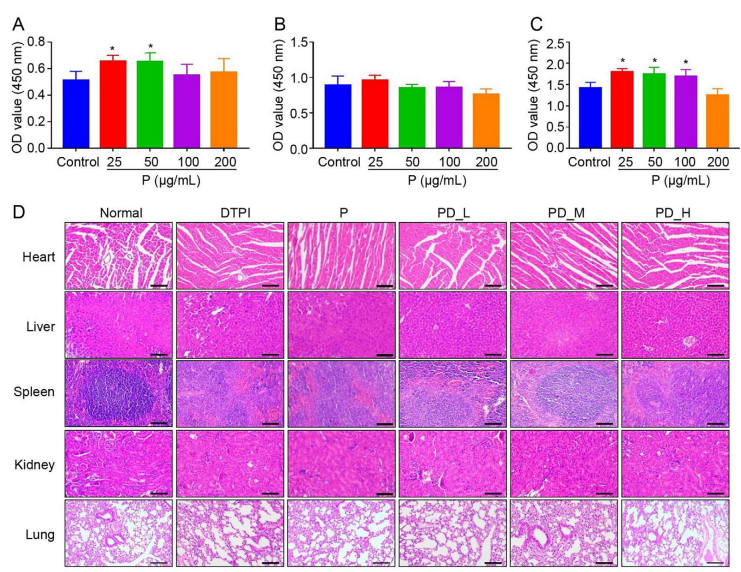
The hydroalcoholic extract of POL (P) and aqueous phase fraction of POL (PD) were prepared based on maceration and liquid–liquid extraction. The number of new blood vessels and VEGF-A expression level were assessed using H&E stain and Western blot on injured muscle to examine the role of POL different extracts in vascularization. The iron distribution and total elemental iron of injured muscle were detected using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and Perls’ staining to determine whether POL extracts can inhibit the iron accumulation. Besides, the ability of POL extracts to promote wound healing by combining re-epithelization time, inflammation degree and collagen deposition area were comprehensively evaluated.
Results
In vitro, we observed a significant increase in HUVEC cell viability, migration rate and the number of the tube after P and PD treatment (P < 0.05). In vivo, administration of P and PD impacted vascularization and iron accumulation on injured tissue, evident from more new blood vessels, higher expression of VEGF-A and decreased muscle iron concentration of treatment groups compared with no-treatment groups (P < 0.05). Besides, shorter re-epithelization time, reduced inflammatory infiltration and distinct collagen deposition were associated with administration of P and PD (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
POL extract administration groups have high-quality wound healing, which is associated with increased new blood vessels, collagen deposition and re-epithelization, along with decreased iron accumulation and inflammatory infiltration. Our results suggest that that POL extract is beneficial to repair injured muscle after ischemia–reperfusion, highlighting the potential of POL in the DTPI treatment.
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25