(Peer-Reviewed) Multi-prior physics-enhanced neural network enables pixel super-resolution and twin-image-free phase retrieval from single-shot hologram
Xuan Tian 田璇 ¹ ², Runze Li 李润泽 ¹, Tong Peng 彭彤 ¹, Yuge Xue 薛雨阁 ¹ ², Junwei Min 闵俊伟 ¹, Xing Li 栗星 ¹, Chen Bai 柏晨 ¹ ², Baoli Yao 姚保利 ¹ ²
¹ State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics, Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi'an 710119, China
中国 西安 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所 瞬态光学与光子技术国家重点实验室
² University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
中国 北京 中国科学院大学
Opto-Electronic Advances
, 2024-08-28
Abstract
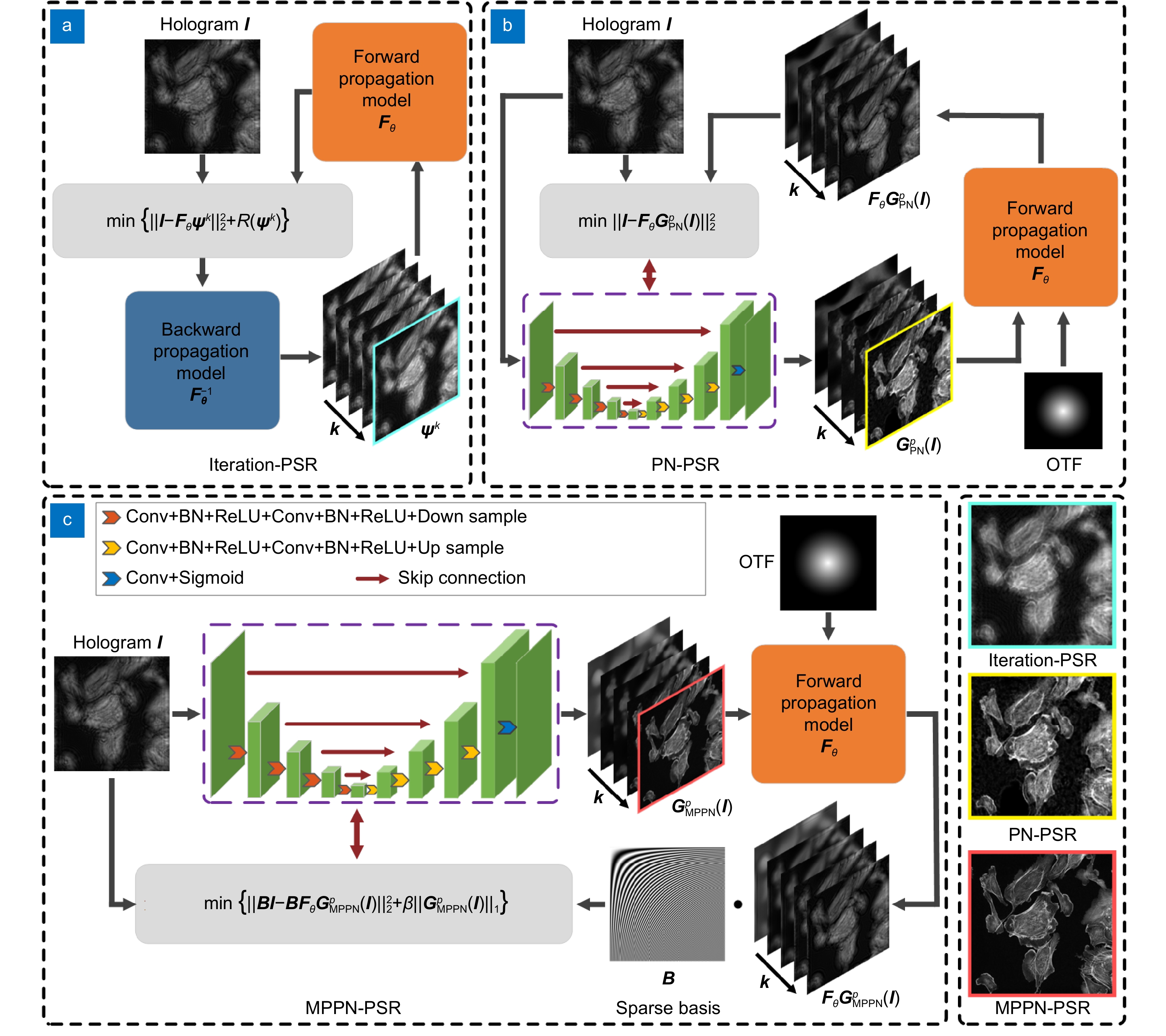
Digital in-line holographic microscopy (DIHM) is a widely used interference technique for real-time reconstruction of living cells’ morphological information with large space-bandwidth product and compact setup. However, the need for a larger pixel size of detector to improve imaging photosensitivity, field-of-view, and signal-to-noise ratio often leads to the loss of sub-pixel information and limited pixel resolution.
Additionally, the twin-image appearing in the reconstruction severely degrades the quality of the reconstructed image. The deep learning (DL) approach has emerged as a powerful tool for phase retrieval in DIHM, effectively addressing these challenges. However, most DL-based strategies are data-driven or end-to-end net approaches, suffering from excessive data dependency and limited generalization ability. Herein, a novel multi-prior physics-enhanced neural network with pixel super-resolution (MPPN-PSR) for phase retrieval of DIHM is proposed. It encapsulates the physical model prior, sparsity prior and deep image prior in an untrained deep neural network.
The effectiveness and feasibility of MPPN-PSR are demonstrated by comparing it with other traditional and learning-based phase retrieval methods. With the capabilities of pixel super-resolution, twin-image elimination and high-throughput jointly from a single-shot intensity measurement, the proposed DIHM approach is expected to be widely adopted in biomedical workflow and industrial measurement.
Review for wireless communication technology based on digital encoding metasurfaces
Haojie Zhan, Manna Gu, Ying Tian, Huizhen Feng, Mingmin Zhu, Haomiao Zhou, Yongxing Jin, Ying Tang, Chenxia Li, Bo Fang, Zhi Hong, Xufeng Jing, Le Wang
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-07-17
Multiphoton intravital microscopy in small animals of long-term mitochondrial dynamics based on super‐resolution radial fluctuations
Saeed Bohlooli Darian, Jeongmin Oh, Bjorn Paulson, Minju Cho, Globinna Kim, Eunyoung Tak, Inki Kim, Chan-Gi Pack, Jung-Man Namgoong, In-Jeoung Baek, Jun Ki Kim
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-07-17
Non-volatile tunable multispectral compatible infrared camouflage based on the infrared radiation characteristics of Rosaceae plants
Xin Li, Xinye Liao, Junxiang Zeng, Zao Yi, Xin He, Jiagui Wu, Huan Chen, Zhaojian Zhang, Yang Yu, Zhengfu Zhang, Sha Huang, Junbo Yang
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-07-09
CW laser damage of ceramics induced by air filament
Chuan Guo, Kai Li, Zelin Liu, Yuyang Chen, Junyang Xu, Zhou Li, Wenda Cui, Changqing Song, Cong Wang, Xianshi Jia, Ji'an Duan, Kai Han
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-06-27
Operando monitoring of state of health for lithium battery via fiber optic ultrasound imaging system
Chen Geng, Wang Anqi, Zhang Yi, Zhang Fujun, Xu Dongchen, Liu Yueqi, Zhang Zhi, Yan Zhijun, Li Zhen, Li Hao, Sun Qizhen
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-06-25
Observation of polaronic state assisted sub-bandgap saturable absorption
Li Zhou, Yiduo Wang, Jianlong Kang, Xin Li, Quan Long, Xianming Zhong, Zhihui Chen, Chuanjia Tong, Keqiang Chen, Zi-Lan Deng, Zhengwei Zhang, Chuan-Cun Shu, Yongbo Yuan, Xiang Ni, Si Xiao, Xiangping Li, Yingwei Wang, Jun He
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-06-19