(Peer-Reviewed) Eco-friendly quantum-dot light-emitting diode display technologies: prospects and challenges
Gao Peili 高佩丽 ¹, Li Chan 李婵 ², Zhou Hao 周浩 ², He Songhua 何颂华 ², Yin Zhen 殷震 ², Ng Kar Wei 吴嘉伟 ¹, Wang Shuangpeng 王双鹏 ¹
¹ Institute of Applied Physics and Materials Engineering, University of Macau, Taipa, Macau SAR 999078, China
中国 澳门 澳门大学应用物理及材料工程研究院
² School of Digital Media, Shenzhen Polytechnic University, Shenzhen 518055, China
中国 深圳 深圳信息职业技术学院 数字媒体学院
Opto-Electronic Science
, 2025-06-25
Abstract
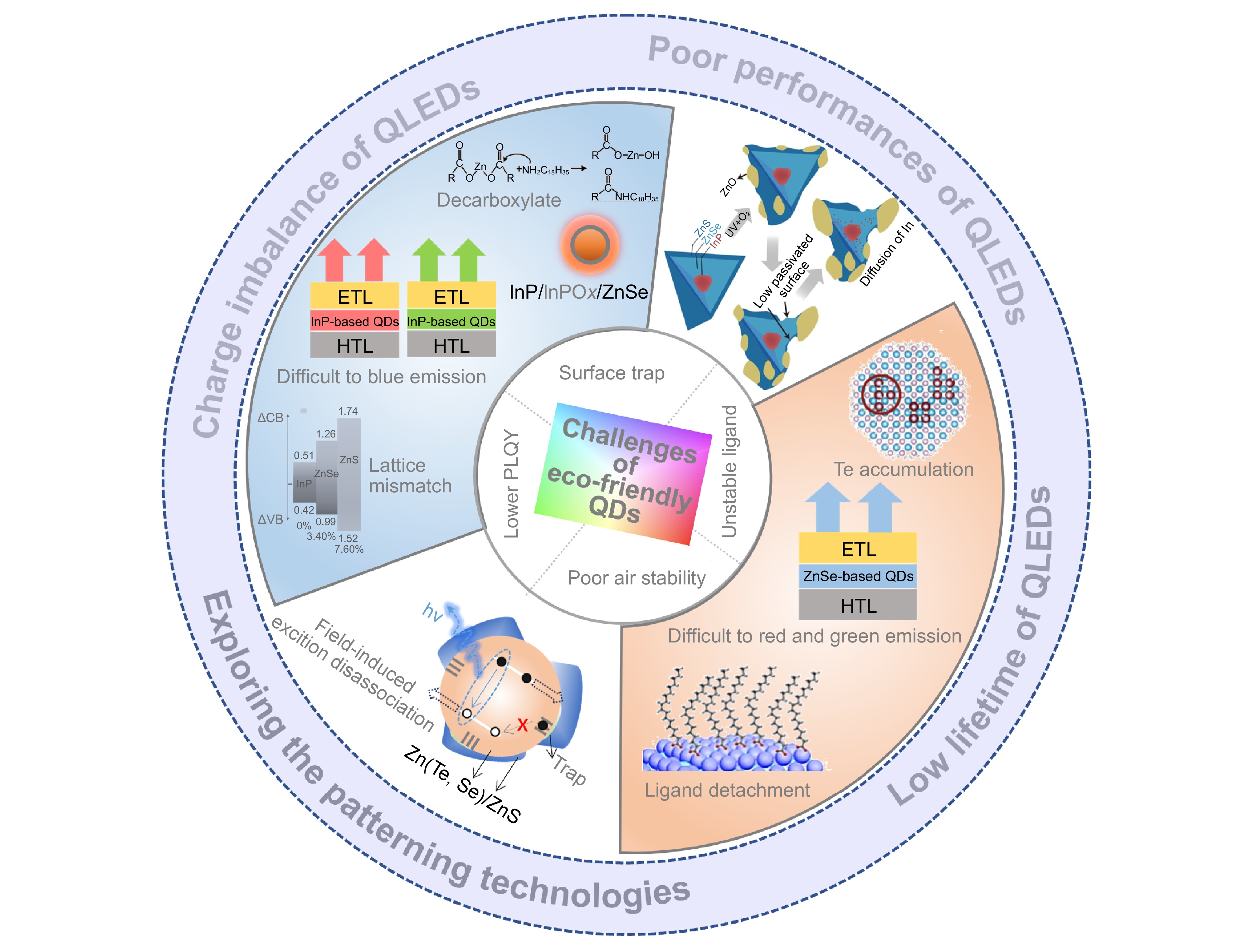
Eco-friendly quantum-dot light-emitting diodes (QLEDs), which employ colloidal quantum dots (QDs) such as InP, and ZnSe, stand out due to their low toxicity, color purity, and high efficiency. Currently, significant advancements have been made in the performance of cadmium-free QLEDs. However, several challenges persist in the industrialization of eco-friendly QLED displays.
For instance, (1) the poor performance, characterized by low photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY), unstable ligand, and charge imbalance, cannot be effectively addressed with a solitary strategy; (2) the degradation mechanism, involving emission quenching, morphological inhomogeneity, and field-enhanced electron delocalization remains unclear; (3) the lack of techniques for color patterning, such as optical lithography and transfer printing.
Herein, we undertake a specific review of all technological breakthroughs that endeavor to tackle the above challenges associated with cadmium-free QLED displays. We begin by reviewing the evolution, architecture, and operational characteristics of eco-friendly QLEDs, highlighting the photoelectric properties of QDs, carrier transport layer stability, and device lifetime.
Subsequently, we focus our attention not only on the latest insights into device degradation mechanisms, particularly, but also on the remarkable technological progress in color patterning techniques. To conclude, we provide a synthesis of the promising prospects, current challenges, potential solutions, and emerging research trends for QLED displays.
Flicker minimization in power-saving displays enabled by measurement of difference in flexoelectric coefficients and displacement-current in positive dielectric anisotropy liquid crystals
Junho Jung, HaYoung Jung, GyuRi Choi, HanByeol Park, Sun-Mi Park, Ki-Sun Kwon, Heui-Seok Jin, Dong-Jin Lee, Hoon Jeong, JeongKi Park, Byeong Koo Kim, Seung Hee Lee, MinSu Kim
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25
Dual-frequency angular-multiplexed fringe projection profilometry with deep learning: breaking hardware limits for ultra-high-speed 3D imaging
Wenwu Chen, Yifan Liu, Shijie Feng, Wei Yin, Jiaming Qian, Yixuan Li, Hang Zhang, Maciej Trusiak, Malgorzata Kujawinska, Qian Chen, Chao Zuo
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25