(Peer-Reviewed) Finely regulated luminescent Ag-In-Ga-S quantum dots with green-red dual emission toward white light-emitting diodes
Zhi Wu 吴智, Leimeng Xu 许蕾梦, Jindi Wang 王金迪, Jizhong Song 宋继中
Key Laboratory of Materials Physics of Ministry of Education, Laboratory of Zhongyuan Light, School of Physics, Zhengzhou University, Daxue Road 75, Zhengzhou 450052, China
中国 郑州 郑州大学物理学院 中原之光实验室 材料物理教育部重点实验室
Opto-Electronic Advances
, 2024-09-18
Abstract
Ag-In-Ga-S (AIGS) quantum dots (QDs) have recently attracted great interests due to the outstanding optical properties and eco-friendly components, which are considered as an alternative replacement for toxic Pb- and Cd-based QDs. However, enormous attention has been paid to how to narrow their broadband spectra, ignoring the application advantages of the broadband emission.
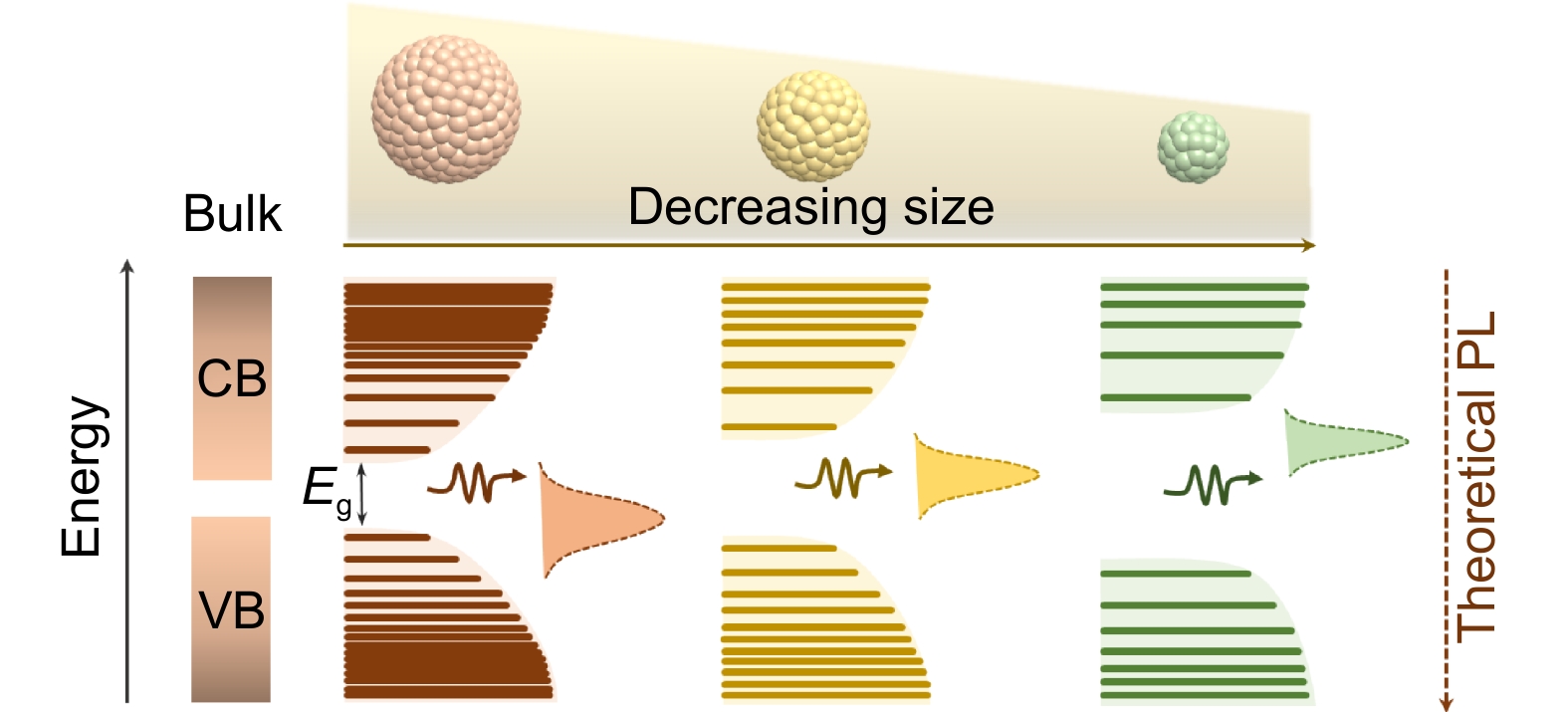
In this work, the AIGS QDs with controllable broad green-red dual-emission are first reported, which is achieved through adjusting the size distribution of QDs by controlling the nucleation and growth of AIGS crystals. Resultantly, the AIGS QDs exhibit broad dual-emission at green- and red- band evidenced by photoluminescence (PL) spectra, and the PL relative intensity and peak position can be finely adjusted.
Furthermore, the dual-emission is the intrinsic characteristics from the difference in confinement effect of large particles and tiny particles confirmed by temperature-dependent PL spectra. Accordingly, the AIGS QDs (the size consists of 17 nm and 3.7 nm) with 530 nm and 630 nm emission could successfully be synthesized at 220 °C.
By combining the blue light-emitting diode (LED) chips and dual-emission AIGS QDs, the constructed white light-emitting devices (WLEDs) exhibit a continuous and broad spectrum like natural sunlight with the Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage (CIE) chromaticity coordinates of (0.33, 0.31), a correlated color temperature (CCT) of 5425 K, color rendering index (CRI) of 90, and luminous efficacy of radiation (LER) of 129 lm/W, which indicates that the AIGS QDs have huge potential for lighting applications.
Flicker minimization in power-saving displays enabled by measurement of difference in flexoelectric coefficients and displacement-current in positive dielectric anisotropy liquid crystals
Junho Jung, HaYoung Jung, GyuRi Choi, HanByeol Park, Sun-Mi Park, Ki-Sun Kwon, Heui-Seok Jin, Dong-Jin Lee, Hoon Jeong, JeongKi Park, Byeong Koo Kim, Seung Hee Lee, MinSu Kim
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25
Dual-frequency angular-multiplexed fringe projection profilometry with deep learning: breaking hardware limits for ultra-high-speed 3D imaging
Wenwu Chen, Yifan Liu, Shijie Feng, Wei Yin, Jiaming Qian, Yixuan Li, Hang Zhang, Maciej Trusiak, Malgorzata Kujawinska, Qian Chen, Chao Zuo
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25