(Peer-Reviewed) Encoding physics to learn reaction–diffusion processes
Chengping Rao 饶成平 ¹ ², Pu Ren 任普 ³, Qi Wang 王琦 ¹, Oral Buyukozturk ⁴, Hao Sun 孙浩 ¹ ⁵, Yang Liu 刘扬 ⁶
¹ Gaoling School of Artificial Intelligence, Renmin University of China, Beijing, China
中国 北京 中国人民大学高瓴人工智能学院
² Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, Northeastern University, Boston, MA, USA
³ Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Northeastern University, Boston, MA, USA
⁴ Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, MIT, Cambridge, MA, USA
⁵ Beijing Key Laboratory of Big Data Management and Analysis Methods, Beijing, China
中国 北京 大数据管理与分析方法研究北京市重点实验室
⁶ School of Engineering Science, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
中国 北京 中国科学院大学 工程科学学院
Nature Machine Intelligence, 2023-07-17
Abstract
Modelling complex spatiotemporal dynamical systems, such as reaction–diffusion processes, which can be found in many fundamental dynamical effects in various disciplines, has largely relied on finding the underlying partial differential equations (PDEs). However, predicting the evolution of these systems remains a challenging task for many cases owing to insufficient prior knowledge and a lack of explicit PDE formulation for describing the nonlinear process of the system variables.
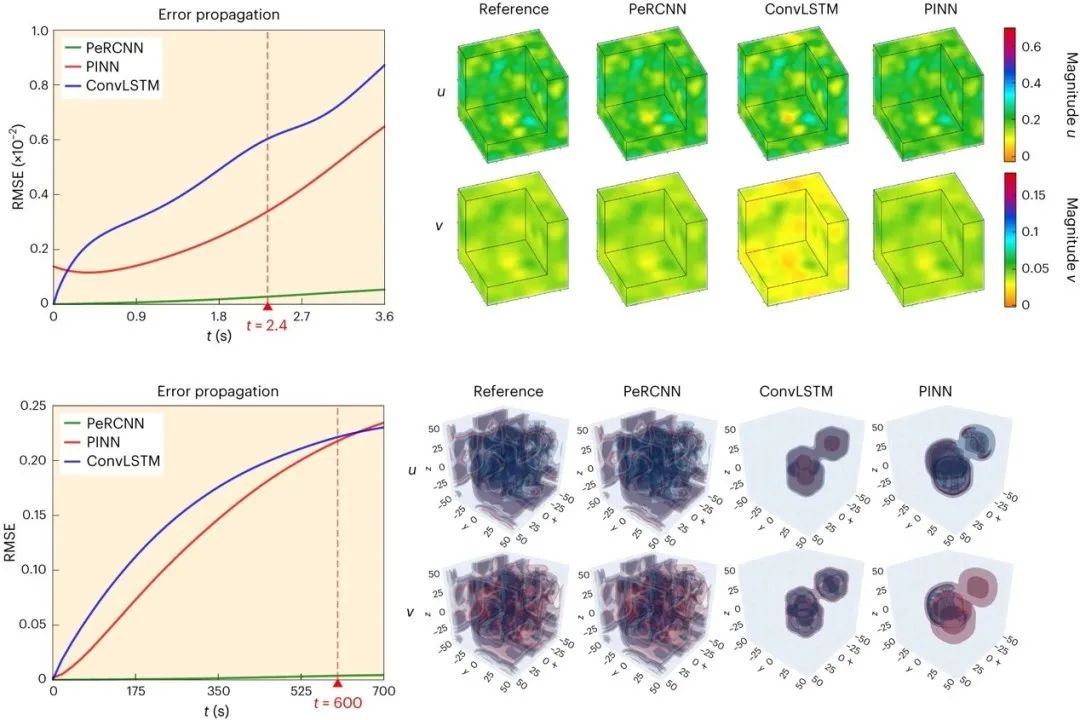
With recent data-driven approaches, it is possible to learn from measurement data while adding prior physics knowledge. However, existing physics-informed machine learning paradigms impose physics laws through soft penalty constraints, and the solution quality largely depends on a trial-and-error proper setting of hyperparameters. Here we propose a deep learning framework that forcibly encodes a given physics structure in a recurrent convolutional neural network to facilitate learning of the spatiotemporal dynamics in sparse data regimes.
We show with extensive numerical experiments how the proposed approach can be applied to a variety of problems regarding reaction–diffusion processes and other PDE systems, including forward and inverse analysis, data-driven modelling and discovery of PDEs. We find that our physics-encoding machine learning approach shows high accuracy, robustness, interpretability and generalizability.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25