(Peer-Reviewed) High-intensity spatial-mode steerable frequency up-converter toward on-chip integration
Haizhou Huang 黄海洲 ², Huaixi Chen 陈怀熹 ², Huagang Liu 刘华刚 ¹ ³, Zhi Zhang 张志 ¹, Xinkai Feng 冯新凯 ⁴, Jiaying Chen 陈家颖 ¹ ⁵, Hongchun Wu 吴鸿春 ¹ ⁵, Jing Deng 邓晶 ¹ ⁵, Wanguo Liang 梁万国 ¹, Wenxiong Lin 林文雄 ¹ ³
¹ Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials Chemistry and Physics, Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Science, Fuzhou 350002, China
中国 福州 中国科学院 福建物质结构研究所 光电材料化学与物理院重点实验室
² Key Laboratory of Opto-Electronic Science and Technology for Medicine of Ministry of Education, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Photonics Technology, College of Photonic and Electronic Engineering, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350117, China
中国 福州 福建省光子技术重点实验室 医学光电科学与技术教育部重点实验室
³ Fujian Science & Technology Innovation Laboratory for Optoelectronic Information of China, Fuzhou 350108, China
中国 福州 福建光电信息科学与技术创新实验室
⁴ College of Digital Economy, Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou 350002, China
中国 福州 福建农林大学 数字经济学院
⁵ University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
中国 北京 中国科学院大学
Opto-Electronic Science, 2024-04-24
Abstract
Integrated photonic devices are essential for on-chip optical communication, optical-electronic systems, and quantum information sciences. To develop a high-fidelity interface between photonics in various frequency domains without disturbing their quantum properties, nonlinear frequency conversion, typically steered with the quadratic (χ2) process, should be considered.
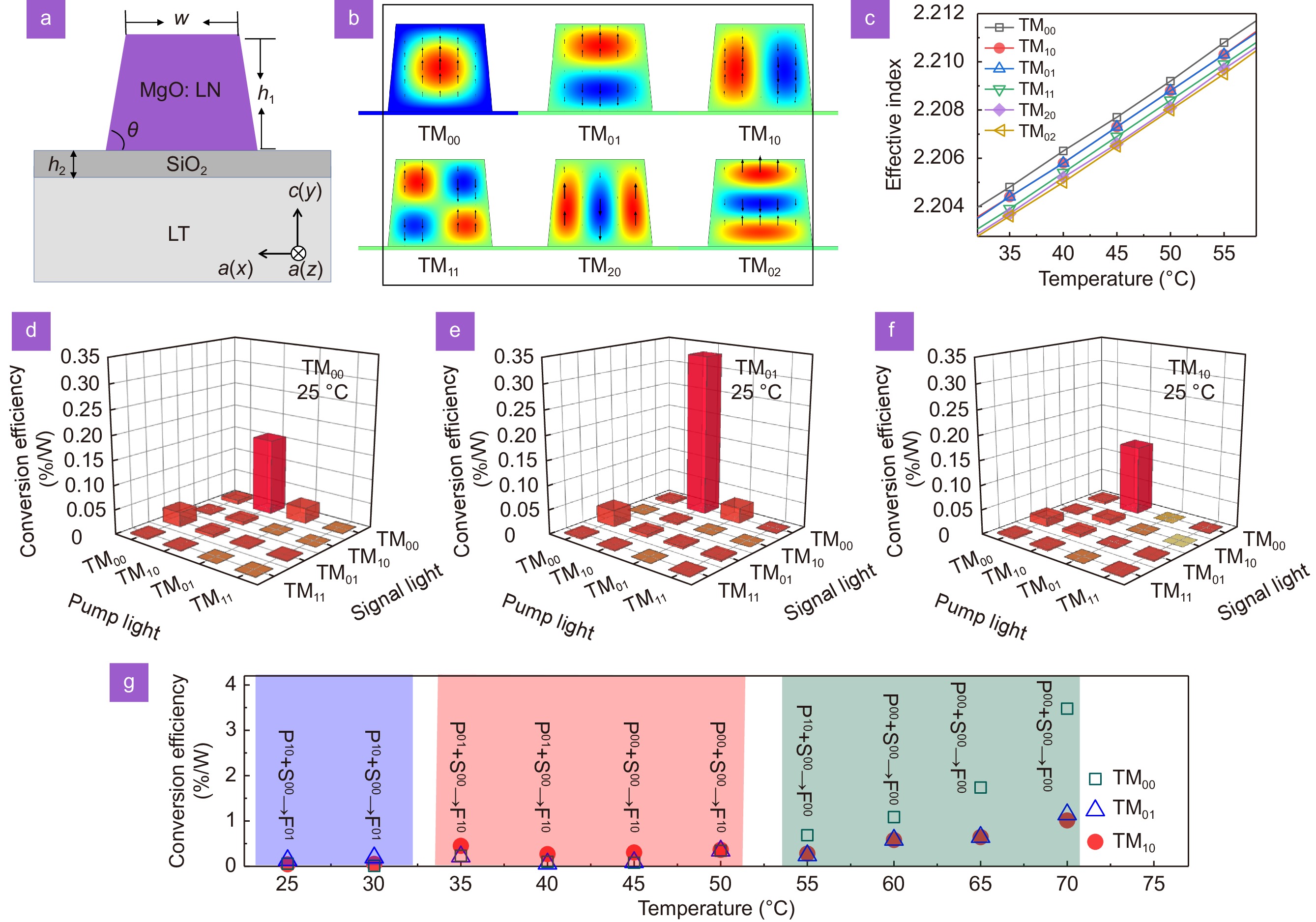
Furthermore, another degree of freedom in steering the spatial modes during the χ2 process, with unprecedent mode intensity is proposed here by modulating the lithium niobate (LN) waveguide-based inter-mode quasi-phase-matching conditions with both temperature and wavelength parameters. Under high incident light intensities (25 and 27.8 dBm for the pump and the signal lights, respectively), mode conversion at the sum-frequency wavelength with sufficient high output power (−7 – 8 dBm) among the TM01, TM10, and TM00 modes is realized automatically with characterized broad temperature (ΔT ≥ 8 °C) and wavelength windows (Δλ ≥ 1 nm), avoiding the previous efforts in carefully preparing the signal or pump modes.
The results prove that high-intensity spatial modes can be prepared at arbitrary transparent wavelength of the χ2 media toward on-chip integration, which facilitates the development of chip-based communication and quantum information systems because spatial correlations can be applied to generate hyperentangled states and provide additional robustness in quantum error correction with the extended Hilbert space.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25