(Peer-Reviewed) Cultivation of gut microorganisms of the marine ascidian Halocynthia roretzi reveals their potential roles in the environmental adaptation of their host
Yang Yang 杨阳 ¹, Yuting Zhu ¹, Haiming Liu ¹, Jiankai Wei 隗健凯 ¹, Haiyan Yu 于海燕 ¹, Bo Dong 董波 ¹ ² ³
¹ Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Marine Genetics and Breeding, College of Marine Life Sciences, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, 266003, China
中国 青岛 中国海洋大学海洋生命学院 海洋生物遗传与育种教育部重点实验室
² Laboratory for Marine Biology and Biotechnology, Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (Qingdao), Qingdao, 266237, China
中国 青岛 海洋生物学与生物技术实验室 青岛海洋科学与技术试点国家实验室
³ Institute of Evolution and Marine Biodiversity, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, 266003, China
中国 青岛 中国海洋大学海洋生物多样性与进化研究所
Abstract
It has long been known that abundant symbiotic bacteria exist in the tunic and gut of marine ascidians, and that these play crucial roles in host development, physiological metabolism, and environmental adaptation. However, the identity, roles and functions of these symbiotic bacteria are known for only a few strains.
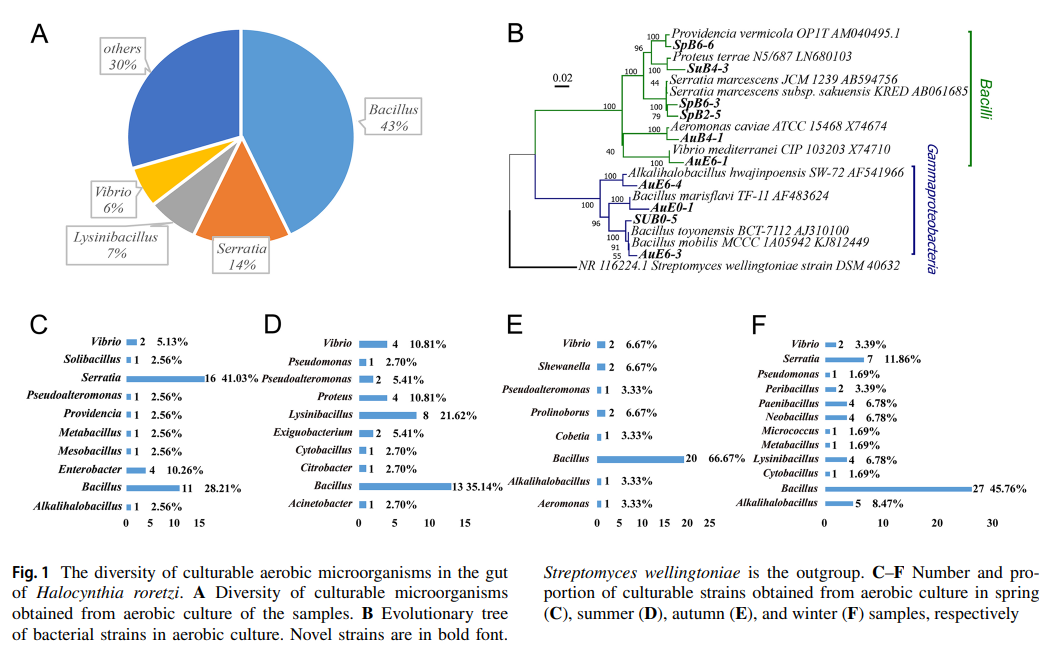
In this study, we isolated and cultivated 263 strains of microorganisms from the intestine of the marine ascidian Halocynthia roretzi through a combination of aerobic and anaerobic culture approaches. Most cultivated species, both aerobic and anaerobic, from ascidian stool samples belonged to the genus Bacillus based on 16S rDNA sequencing identification and phylogenetic assays. The distribution of cultured bacteria varied with seasonal changes in environmental conditions.
To explore the functions of cultured bacteria, we screened out a strain of Serratia sp. whose extracts showed high antibacterial activity against aquatic pathogens. These findings revealed the potential roles of gut microorganisms in ascidian defense and environmental adaptation, thus providing insights into the interaction and co-evolution between gut bacteria and their hosts.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25