(Peer-Reviewed) Deep learning assisted variational Hilbert quantitative phase imaging
Zhuoshi Li 李卓识 ¹ ² ³, Jiasong Sun 孙佳嵩 ¹ ² ³, Yao Fan 范瑶 ¹ ² ³, Yanbo Jin 金彦伯 ¹ ² ³, Qian Shen 沈茜 ¹ ² ³, Maciej Trusiak ⁴, Maria Cywińska ⁴, Peng Gao 郜鹏 ⁵, Qian Chen 陈钱 ³, Chao Zuo 左超 ¹ ² ³
¹ Smart Computational Imaging Laboratory (SCILab), School of Electronic and Optical Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China
中国 南京 南京理工大学智能计算成像实验室
² Smart Computational Imaging Research Institute (SCIRI) of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China
中国 南京 南京理工大学智能计算成像研究院
³ Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Spectral Imaging and Intelligent Sense, Nanjing 210094, China
中国 南京 江苏省光谱成像与智能感知重点实验室
⁴ Institute of Micromechanics and Photonics, Warsaw University of Technology, 8 Sw. A. Boboli St., Warsaw 02-525, Poland
⁵ School of Physics, Xidian University, Xi'an 710126, China
中国 西安 西安电子科技大学物理学院
Opto-Electronic Science, 2023-05-18
Abstract
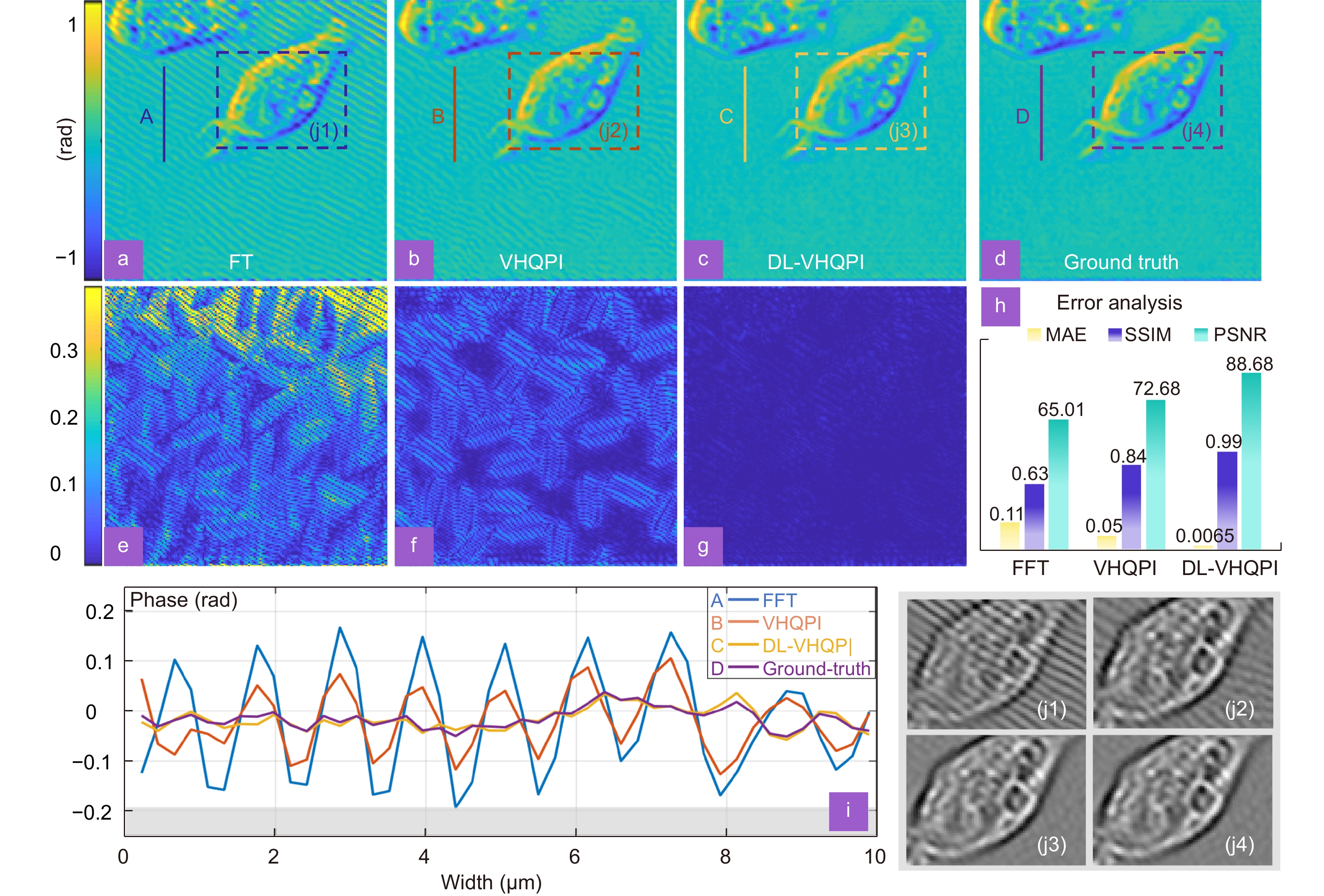
We propose a high-accuracy artifacts-free single-frame digital holographic phase demodulation scheme for relatively low-carrier frequency holograms—deep learning assisted variational Hilbert quantitative phase imaging (DL-VHQPI). The method, incorporating a conventional deep neural network into a complete physical model utilizing the idea of residual compensation, reliably and robustly recovers the quantitative phase information of the test objects.
It can significantly alleviate spectrum-overlapping-caused phase artifacts under the slightly off-axis digital holographic system. Compared to the conventional end-to-end networks (without a physical model), the proposed method can reduce the dataset size dramatically while maintaining the imaging quality and model generalization.
The DL-VHQPI is quantitatively studied by numerical simulation. The live-cell experiment is designed to demonstrate the method's practicality in biological research. The proposed idea of the deep learning-assisted physical model might be extended to diverse computational imaging techniques.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25