(Peer-Reviewed) Broad-band spatial light modulation with dual epsilon-near-zero modes
Long Wen 文龙 ¹, Xianghong Nan 南向红 ¹, Jiaxiang Li 李家祥 ¹, David R. S. Cumming ³, Xin Hu 胡鑫 ², Qin Chen 陈沁 ¹
¹ Institute of Nanophotonics, Jinan University, Guangzhou 511443, China
中国 广州 暨南大学纳米光子学研究院
² Hangzhou Dianzi University, Hangzhou 310018, China
中国 杭州 杭州电子科技大学
³ James Watt School of Engineering, University of Glasgow, Glasgow G12 8QQ, UK
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2022-05-27
Abstract
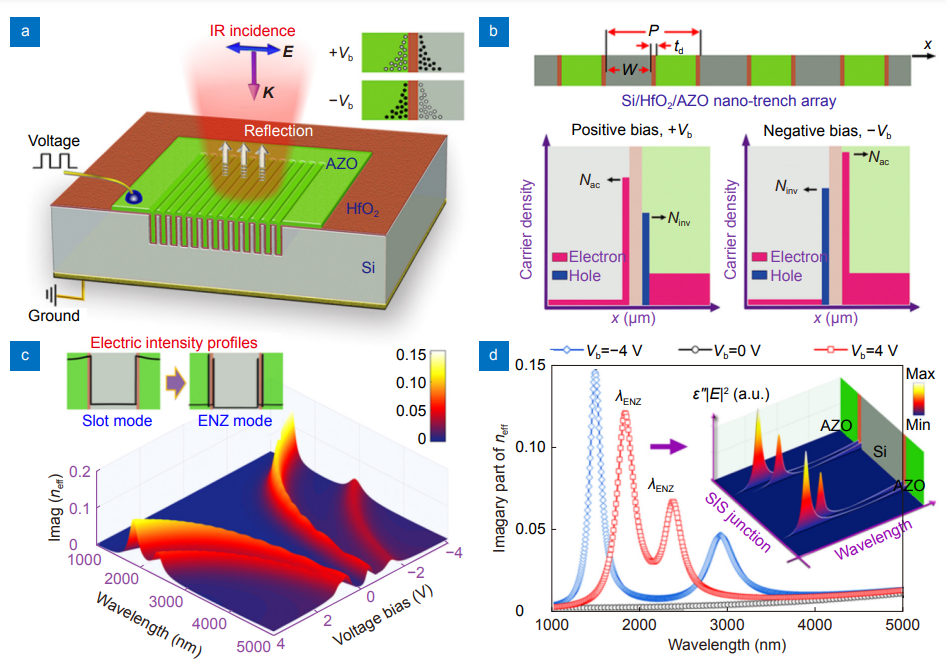
Epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) modes have attracted extensive interests due to its ultrasmall mode volume resulting in extremely strong light-matter interaction (LMI) for active optoelectronic devices. The ENZ modes can be electrically toggled between on and off states with a classic metal-insulator-semiconductor (MIS) configuration and therefore allow access to electro-absorption (E-A) modulation.
Relying on the quantum confinement of charge-carriers in the doped semiconductor, the fundamental limitation of achieving high modulation efficiency with MIS junction is that only a nanometer-thin ENZ confinement layer can contribute to the strength of E-A. Further, for the ENZ based spatial light modulation, the requirement of resonant coupling inevitably leads to small absolute modulation depth and limited spectral bandwidth as restricted by the properties of the plasmonic or high-Q resonance systems.
In this paper, we proposed and demonstrated a dual-ENZ mode scheme for spatial light modulation with a TCOs/dielectric/silicon nanotrench configuration for the first time. Such a SIS junction can build up two distinct ENZ layers arising from the induced charge-carriers of opposite polarities adjacent to both faces of the dielectric layer. The non-resonant and low-loss deep nanotrench framework allows the free space light to be modulated efficiently via interaction of dual ENZ modes in an elongated manner.
Our theoretical and experimental studies reveal that the dual ENZ mode scheme in the SIS configuration leverages the large modulation depth, extended spectral bandwidth together with high speed switching, thus holding great promise for achieving electrically addressed spatial light modulation in near- to mid-infrared regions.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25