(Peer-Reviewed) Comparative analysis of NovaSeq 6000 and MGISEQ 2000 single-cell RNA sequencing data
Weiran Chen ¹, Md Wahiduzzaman ¹, Quan Li ¹ , Yixue Li 李亦学 ¹ ², Guangyong Zheng 郑广勇 ¹, Tao Huang 黄涛 ¹
¹ Bio-Med Big Data Center, Key Laboratory of Computational Biology, Shanghai Institute of Nutrition and Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200031, China
中国 上海 中国科学院上海营养与健康研究所 计算生物学重点实验室 生物医学大数据中心
² School of Life Science, Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, China
中国 杭州 中国科学院大学 杭州高等研究院 生命与健康科学学院
Abstract
Background
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) technology is now becoming a widely applied method of transcriptome exploration that helps to reveal cell-type composition as well as cell-state heterogeneity for specific biological processes. Distinct sequencing platforms and processing pipelines may contribute to various results even for the same sequencing samples. Therefore, benchmarking sequencing platforms and processing pipelines was considered as a necessary step to interpret scRNA-seq data. However, recent comparing efforts were constrained in sequencing platforms or analyzing pipelines. There is still a lack of knowledge of analyzing pipelines matched with specific sequencing platforms in aspects of sensitivity, precision, and so on.
Methods
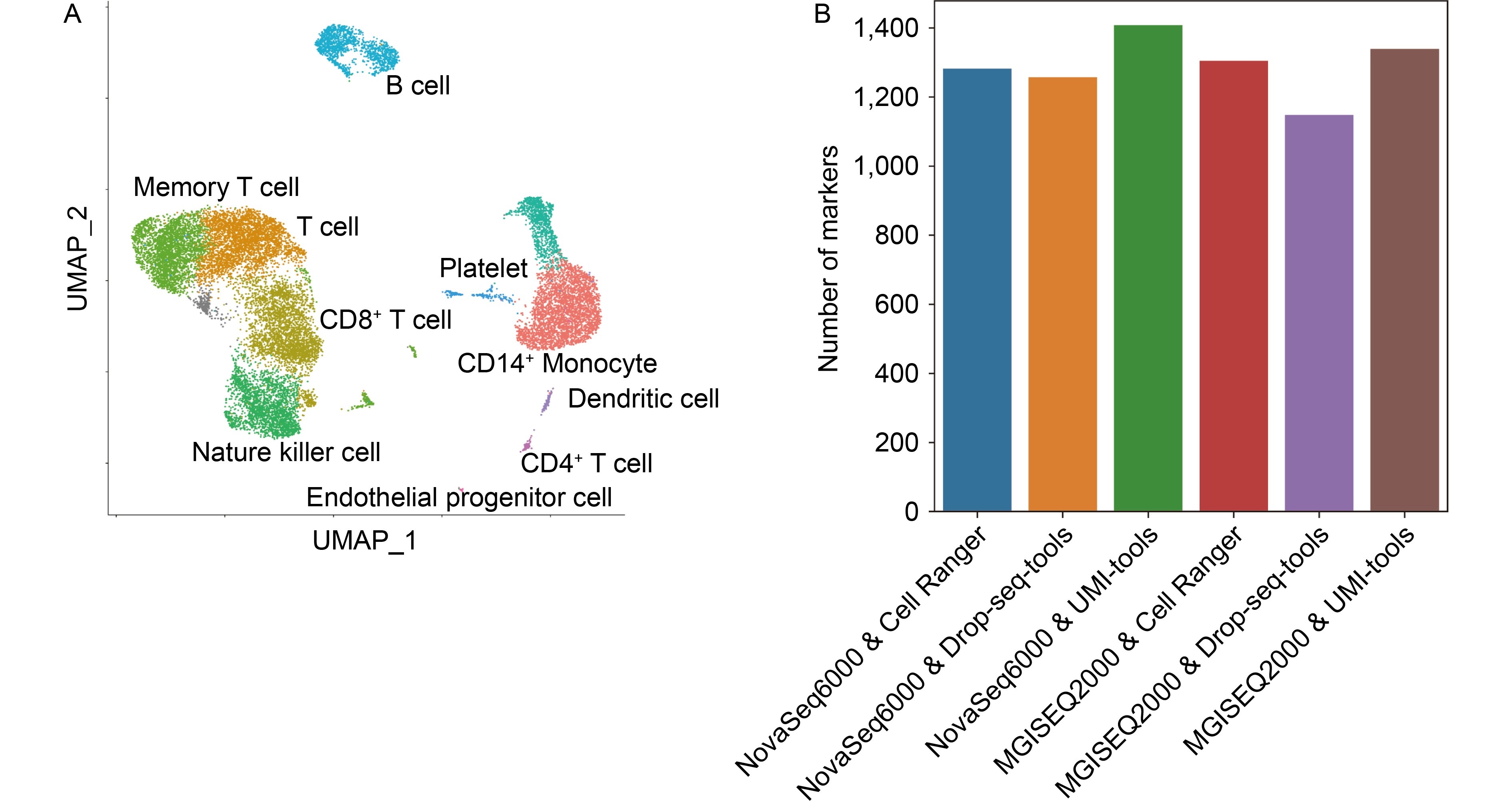
We downloaded public scRNA-seq data that was generated by two distinct sequencers, NovaSeq 6000 and MGISEQ 2000. Then data was processed through the Drop-seq-tools, UMI-tools and Cell Ranger pipeline respectively. We calculated multiple measurements based on the expression profiles of the six platform-pipeline combinations.
Results
We found that all three pipelines had comparable performance, the Cell Ranger pipeline achieved the best performance in precision while UMI-tools prevailed in terms of sensitivity and marker calling.
Conclusions
Our work provided an insight into the selection of scRNA-seq data processing tools for two sequencing platforms as well as a framework to evaluate platform-pipeline combinations.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25