(Peer-Reviewed) All-optical computing based on convolutional neural networks
Kun Liao 廖琨 ¹, Ye Chen 陈烨 ¹, Zhongcheng Yu 俞钟承 ¹, Xiaoyong Hu 胡小永 ¹ ², Xingyuan Wang 王兴远 ³, Cuicui Lu 路翠翠 ⁴, Hongtao Lin 林宏焘 ⁵, Qingyang Du 杜清扬 ⁶, Juejun Hu 胡崛隽 ⁶, Qihuang Gong 龚旗煌 ¹ ²
¹ State Key Laboratory for Mesoscopic Physics & Department of Physics, Collaborative Innovation Center of Quantum Matter, Beijing Academy of Quantum Information Sciences, Nano-optoelectronics Frontier Center of Ministry of Education, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
中国 北京 北京量子科学研究院 量子物质科学协同创新中心 介观物理国家重点实验室 纳光电子前沿科学中心 北京大学物理学院
² Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
中国 太原 山西大学 极端光学协同创新中心
³ College of Mathematics and Physics, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, Beijing 100029, China
中国 北京 北京化工大学数理学院
⁴ Beijing Key Laboratory of Nanophotonics and Ultrafine Optoelectronic Systems, School of Physics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
中国 北京 北京理工大学物理学院 纳米光子学与超精密光电系统北京市重点实验室
⁵ College of Information Science & Electronic Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
中国 杭州 浙江大学 信息与电子工程学院
⁶ Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2021-11-25
Abstract
The rapid development of information technology has fueled an ever-increasing demand for ultrafast and ultralow-energy-consumption computing. Existing computing instruments are pre-dominantly electronic processors, which use electrons as information carriers and possess von Neumann architecture featured by physical separation of storage and processing. The scaling of computing speed is limited not only by data transfer between memory and processing units, but also by RC delay associated with integrated circuits.
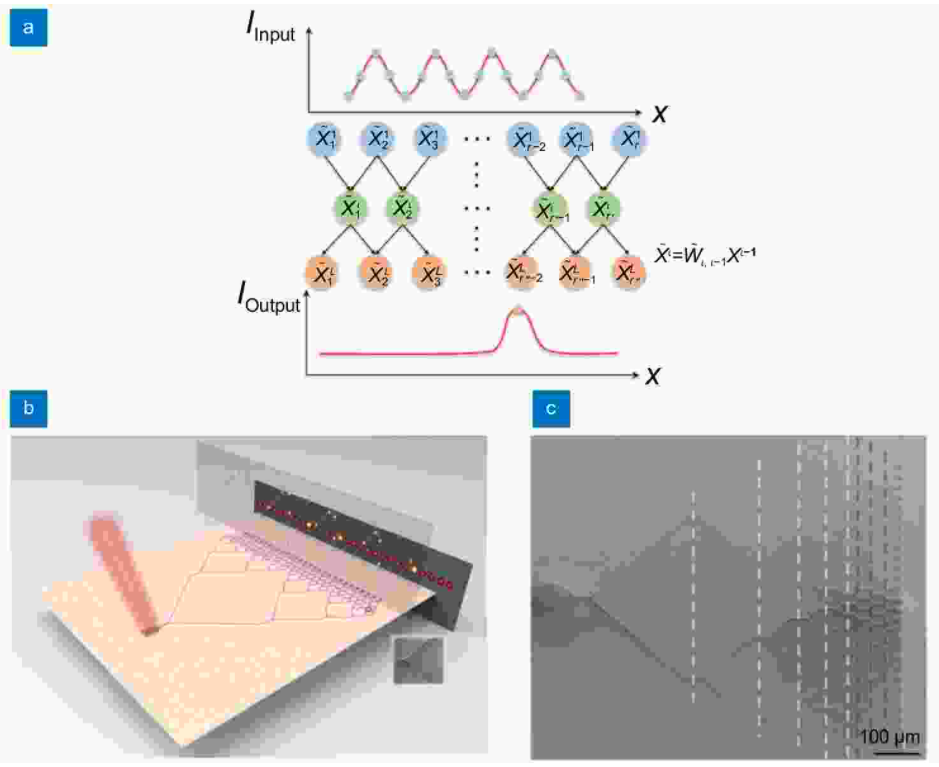
Moreover, excessive heating due to Ohmic losses is becoming a severe bottleneck for both speed and power consumption scaling. Using photons as information carriers is a promising alternative. Owing to the weak third-order optical nonlinearity of conventional materials, building integrated photonic computing chips under traditional von Neumann architecture has been a challenge. Here, we report a new all-optical computing framework to realize ultrafast and ultralow-energy-consumption all-optical computing based on convolutional neural networks. The device is constructed from cascaded silicon Y-shaped waveguides with side-coupled silicon waveguide segments which we termed “weight modulators” to enable complete phase and amplitude control in each waveguide branch. The generic device concept can be used for equation solving, multifunctional logic operations as well as many other mathematical operations.
Multiple computing functions including transcendental equation solvers, multifarious logic gate operators, and half-adders were experimentally demonstrated to validate the all-optical computing performances. The time-of-flight of light through the network structure corresponds to an ultrafast computing time of the order of several picoseconds with an ultralow energy consumption of dozens of femtojoules per bit. Our approach can be further expanded to fulfill other complex computing tasks based on non-von Neumann architectures and thus paves a new way for on-chip all-optical computing.
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25