(Peer-Reviewed) Variability of Antarctic sea ice extent over the past 200 years
Jiao Yang 杨佼 ¹, Cunde Xiao 效存德 ¹ ², Jiping Liu 刘骥平 ³, Shutong Li 李姝彤 ¹ ⁴, Dahe Qin 秦大河 ¹
¹ State Key Laboratory of Cryospheric Science, Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou 730000, China 中国科学院 西北生态环境资源研究院 冰冻圈科学国家重点实验室
² State Key Laboratory of Earth Surface Processes and Resource Ecology, Beijing Normal University, Beijing 100875, China 北京师范大学 地表过程与资源生态国家重点实验室
³ Department of Atmospheric and Environmental Sciences, University at Albany, State University of New York, Albany, NY 12222, USA
⁴ College of Resources and Environment, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China 中国科学院大学 资源与环境学院
Science Bulletin
, 2021-07-21
Abstract
While Arctic sea ice has been decreasing in recent decades that is largely due to anthropogenic forcing, the extent of Antarctic sea ice showed a positive trend during 1979–2015, followed by an abrupt decrease. The shortness of the satellite record limits our ability to quantify the possible contribution of anthropogenic forcing and internal variability to the observed Antarctic sea ice variability.
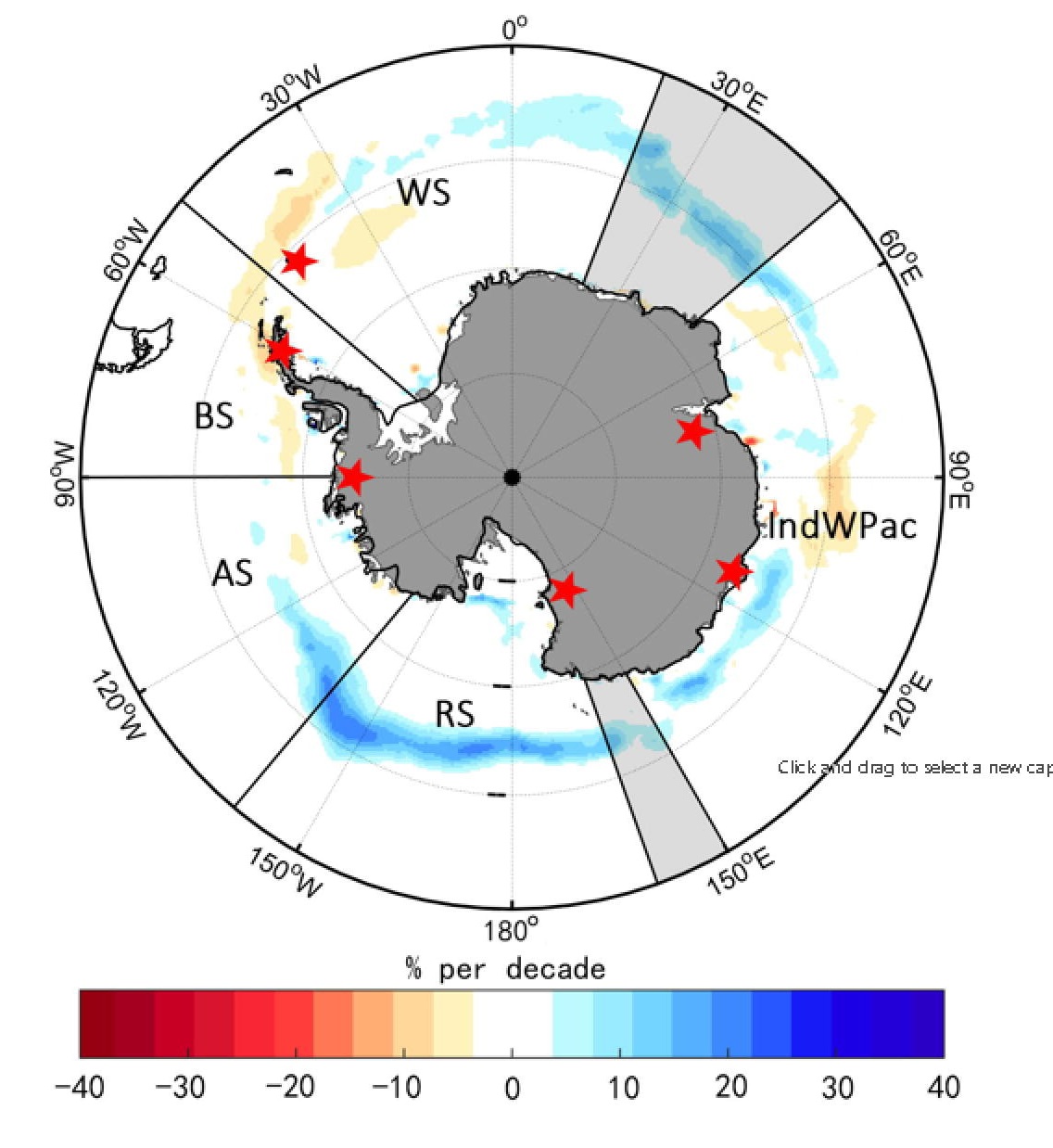
In this study, ice core and fast ice records with annual resolution from six sites are used to reconstruct the annual-resolved northernmost latitude of sea ice edge (NLSIE) for different sectors of the Southern Ocean, including the Weddell Sea (WS), Bellingshausen Sea (BS), Amundsen Sea (AS), Ross Sea (RS), and the Indian and western Pacific Ocean (IndWPac). The linear trends of the NLSIE are analyzed for each sector for the past 100–200 years and found to be −0.08°, −0.17°, +0.07°, +0.02°, and −0.03° per decade (≥95% confidence level) for the WS, BS, AS, RS, and IndWPac, respectively.
For the entire Antarctic, our composite NLSIE shows a decreasing trend (−0.03° per decade, 99% confidence level) during the 20th century, with a rapid decline in the mid-1950s. It was not until the early 1980s that the observed increasing trend occurred.
A comparison with major climate indices shows that the long-term linear trends in all five sectors are largely dominated by the changes in the Southern Annular Mode (SAM). The multi-decadal variability in WS, BS, and AS is dominated by the Interdecadal Pacific Oscillation, whereas that in the IndWPac and RS is dominated by the SAM.
Review for wireless communication technology based on digital encoding metasurfaces
Haojie Zhan, Manna Gu, Ying Tian, Huizhen Feng, Mingmin Zhu, Haomiao Zhou, Yongxing Jin, Ying Tang, Chenxia Li, Bo Fang, Zhi Hong, Xufeng Jing, Le Wang
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-07-17
Multiphoton intravital microscopy in small animals of long-term mitochondrial dynamics based on super‐resolution radial fluctuations
Saeed Bohlooli Darian, Jeongmin Oh, Bjorn Paulson, Minju Cho, Globinna Kim, Eunyoung Tak, Inki Kim, Chan-Gi Pack, Jung-Man Namgoong, In-Jeoung Baek, Jun Ki Kim
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-07-17
Non-volatile tunable multispectral compatible infrared camouflage based on the infrared radiation characteristics of Rosaceae plants
Xin Li, Xinye Liao, Junxiang Zeng, Zao Yi, Xin He, Jiagui Wu, Huan Chen, Zhaojian Zhang, Yang Yu, Zhengfu Zhang, Sha Huang, Junbo Yang
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-07-09
CW laser damage of ceramics induced by air filament
Chuan Guo, Kai Li, Zelin Liu, Yuyang Chen, Junyang Xu, Zhou Li, Wenda Cui, Changqing Song, Cong Wang, Xianshi Jia, Ji'an Duan, Kai Han
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-06-27
Operando monitoring of state of health for lithium battery via fiber optic ultrasound imaging system
Chen Geng, Wang Anqi, Zhang Yi, Zhang Fujun, Xu Dongchen, Liu Yueqi, Zhang Zhi, Yan Zhijun, Li Zhen, Li Hao, Sun Qizhen
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-06-25
Observation of polaronic state assisted sub-bandgap saturable absorption
Li Zhou, Yiduo Wang, Jianlong Kang, Xin Li, Quan Long, Xianming Zhong, Zhihui Chen, Chuanjia Tong, Keqiang Chen, Zi-Lan Deng, Zhengwei Zhang, Chuan-Cun Shu, Yongbo Yuan, Xiang Ni, Si Xiao, Xiangping Li, Yingwei Wang, Jun He
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-06-19