(Peer-Reviewed) Terahertz active multi-channel vortices with parity symmetry breaking and near/far field multiplexing based on a dielectric-liquid crystal-plasmonic metadevice
Yiming Wang 王一茗 ¹, Fei Fan 范飞 ¹ ², Huijun Zhao 赵慧君 ¹, Yunyun Ji 冀允允 ², Jing Liu 刘静 ¹, Shengjiang Chang 常胜江 ²
¹ Institute of Modern Optics, Nankai University, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Micro-scale Optical Information Science and Technology, Tianjin 300350, China
中国 天津 南开大学现代光学研究所 天津市微尺度光学信息技术科学重点实验室
² Tianjin Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Sensor and Sensing Network Technology, Tianjin 300350, China
中国 天津 天津市光电传感器与传感网络技术重点实验室
Opto-Electronic Advances
, 2025-03-06
Abstract
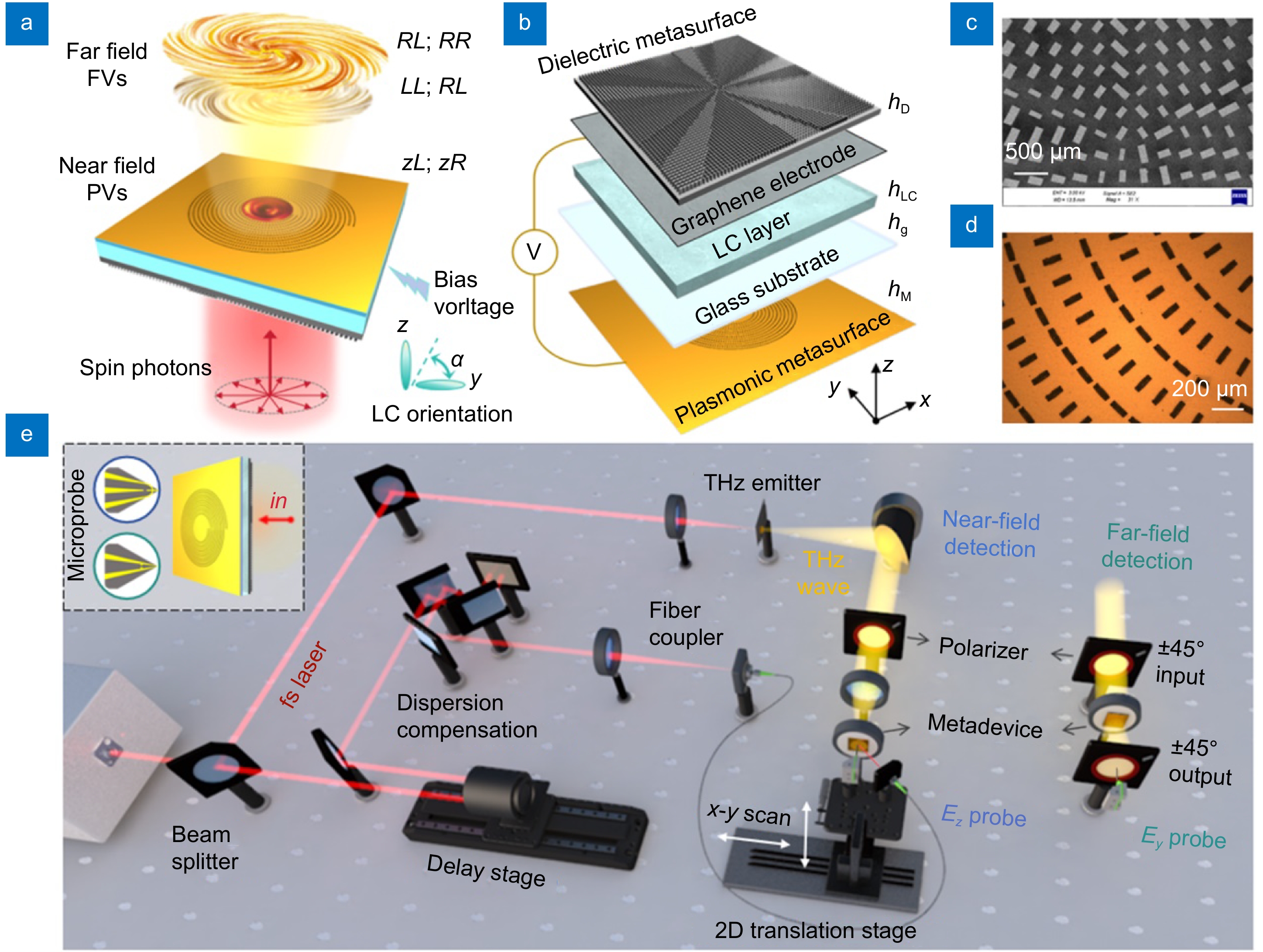
Vortex beams carrying orbital angular momentum (OAM) are of great significance for high-capacity communication and super-resolution imaging. However, there is a huge gap between the free-space vortices (FVs) and plasmonic vortices (PVs) on chips, and active manipulation as well as multiplexing in more channels have become a pressing demand.
In this work, we demonstrate a terahertz (THz) cascaded metadevice composed of a helical plasmonic metasurface, a liquid crystal (LC) layer, and a helical dielectric metasurface. By spin-orbital angular momentum coupling and photon state superposition, PVs and FVs are generated with mode purity of over 85% on average. Due to the inversion asymmetric design of the helical metasurfaces, the parity symmetry breaking of OAM is realized (the topological charge numbers no longer occur in positive and negative pairs, but all are positive), generating 6 independent channels associated with the decoupled spin states and the near-/far- field positions.
Moreover, by the LC integration, dynamic mode switching and energy distribution can be realized, finally obtaining up to 12 modes with a modulation ratio of above 70%. This active tuning and multi-channel multiplexing metadevice establishes a bridge connection between the PVs and FVs, exhibiting promising applications in THz communication, intelligent perception, and information processing.
Review for wireless communication technology based on digital encoding metasurfaces
Haojie Zhan, Manna Gu, Ying Tian, Huizhen Feng, Mingmin Zhu, Haomiao Zhou, Yongxing Jin, Ying Tang, Chenxia Li, Bo Fang, Zhi Hong, Xufeng Jing, Le Wang
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-07-17
Multiphoton intravital microscopy in small animals of long-term mitochondrial dynamics based on super‐resolution radial fluctuations
Saeed Bohlooli Darian, Jeongmin Oh, Bjorn Paulson, Minju Cho, Globinna Kim, Eunyoung Tak, Inki Kim, Chan-Gi Pack, Jung-Man Namgoong, In-Jeoung Baek, Jun Ki Kim
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-07-17
Non-volatile tunable multispectral compatible infrared camouflage based on the infrared radiation characteristics of Rosaceae plants
Xin Li, Xinye Liao, Junxiang Zeng, Zao Yi, Xin He, Jiagui Wu, Huan Chen, Zhaojian Zhang, Yang Yu, Zhengfu Zhang, Sha Huang, Junbo Yang
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-07-09
CW laser damage of ceramics induced by air filament
Chuan Guo, Kai Li, Zelin Liu, Yuyang Chen, Junyang Xu, Zhou Li, Wenda Cui, Changqing Song, Cong Wang, Xianshi Jia, Ji'an Duan, Kai Han
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-06-27
Operando monitoring of state of health for lithium battery via fiber optic ultrasound imaging system
Chen Geng, Wang Anqi, Zhang Yi, Zhang Fujun, Xu Dongchen, Liu Yueqi, Zhang Zhi, Yan Zhijun, Li Zhen, Li Hao, Sun Qizhen
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-06-25
Observation of polaronic state assisted sub-bandgap saturable absorption
Li Zhou, Yiduo Wang, Jianlong Kang, Xin Li, Quan Long, Xianming Zhong, Zhihui Chen, Chuanjia Tong, Keqiang Chen, Zi-Lan Deng, Zhengwei Zhang, Chuan-Cun Shu, Yongbo Yuan, Xiang Ni, Si Xiao, Xiangping Li, Yingwei Wang, Jun He
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-06-19