(Peer-Reviewed) Self-energy dynamics and mode-specific phonon threshold effect in a Kekulé-ordered graphene
Hongyun Zhang 张红云 ¹, Changhua Bao 鲍昌华 ¹, Michael Schüler ², Shaohua Zhou 周绍华 ¹, Qian Li 李骞 ¹, Laipeng Luo 罗来鹏 ¹, Wei Yao 姚维 ¹, Zhong Wang ³, Thomas P Devereaux ² ⁴, Shuyun Zhou 周树云 ¹ ⁵
¹ State Key Laboratory of Low Dimensional Quantum Physics and Department of Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, P.R. China
中国 北京 清华大学物理系 低维量子物理国家重点实验室
² Stanford Institute for Materials and Energy Sciences (SIMES), SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Menlo Park, California 94025, USA
³ Institute for Advanced Study, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084, P. R. China
中国 北京 清华大学高等研究院
⁴ Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94035, USA
⁵ Frontier Science Center for Quantum Information, Beijing 100084, P. R. China
中国 北京 清华大学量子信息前沿科学中心
National Science Review, 2021-09-16
Abstract
Electron-phonon interaction and related self-energy are fundamental to both the equilibrium properties and non-equilibrium relaxation dynamics of solids. Although electron-phonon interaction has been suggested by various time-resolved measurements to be important for the relaxation dynamics of graphene, the lack of energy- and momentum-resolved self-energy dynamics prohibits direct identification of the role of specific phonon modes in the relaxation dynamics.
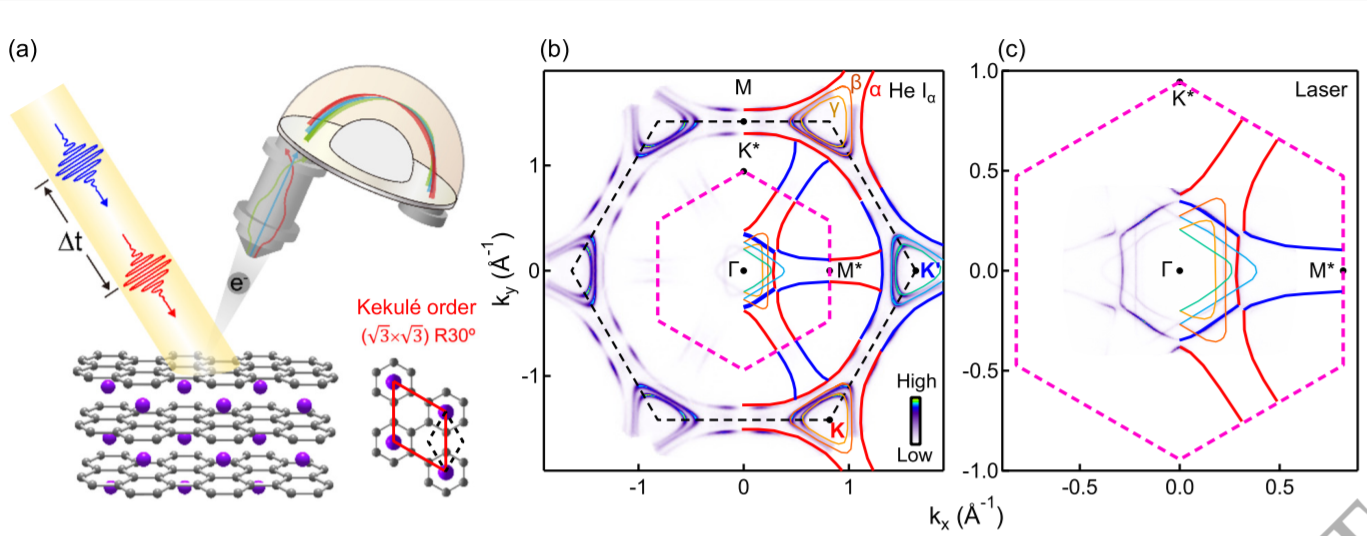
Here by performing time- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy measurements on a Kekulé-ordered graphene with folded Dirac cones at the Γ point, we have succeeded in resolving the self-energy effect induced by coupling of electrons to two phonons at Ω1 = 177 meV and Ω2 = 54 meV and revealing its dynamical change in the time domain. Moreover, these strongly coupled phonons define energy thresholds, which separate the hierarchical relaxation dynamics from ultrafast, fast to slow, thereby providing direct experimental evidence for the dominant role of mode-specific phonons in the relaxation dynamics.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25