(Preprint) Fluidic Endogenous Magnetism and Magnetic Monopole Clues from Liquid Metal Droplet Machine
Yingxin Zhou ¹ ², Jiasheng Zu ¹ ², Jing Liu 刘静 ¹ ² ³
¹ Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
中国 北京 中国科学院理化技术研究所
² School of Future Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
中国 北京 中国科学院大学未来技术学院
³ Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
中国 北京 清华大学医学院生物医学工程系
ChinaXiv, 2021-09-27
Abstract
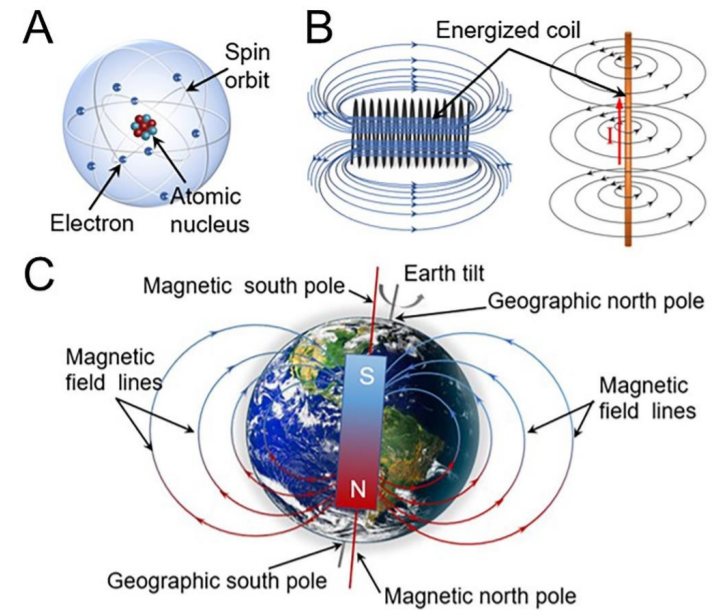
Magnetism and magnetic monopole are classical issues in physics. Conventional magnets are generally composed of rigid materials which may face challenges in extreme situations. Here, from an alternative other than rigid magnet, we proposed for the first time to generate fluidic endogenous magnetism and construct magnetic monopole through tuning liquid metal machine. Based on theoretical interpretation and conceptual experimental evidences, we illustrated that when gallium base liquid metal in solution rotates under electrical actuation, it forms an endogenous magnetic field inside which well explains the phenomenon that two such discrete metal droplets could easily fuse together, indicating their reciprocal attraction via N and S poles.
Further, we clarified that the self-fueled liquid metal motor also runs as an endogenous fluidic magnet owning electromagnetic homology. When liquid gallium in solution swallowed aluminum inside, it formed a spin motor and dynamically variable charge distribution which produced endogenous magnetism inside. This explains the phenomena that there often happened reflection collision and attraction fusion between running liquid metal motors which were just caused by the dynamic adjustment of their N and S polarities, respectively.
Finally, we conceived that such endogenous magnet could lead to magnetic monopole and four technical routes to realize this object were thus suggested as: 1. Matching interior flow of liquid metal machines; 2. Superposition between external electric effect and magnetic field; 3. Composite construction between magnetic particles and liquid metal motor; 4. Chemical ways such as via galvanic cell reaction. Overall, the present theory and revealed experimental evidences disclosed the role of liquid metal machine as a fluidic endogenous magnet and pointed out some promising ways to realize magnetic monopole. A group of unconventional magnetoelectric devices and applications can be possible in the near future.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25