(Peer-Reviewed) Smart palm-size optofluidic hematology analyzer for automated imaging-based leukocyte concentration detection
Deer Su 苏德尔 ¹, Xiangyu Li 李翔宇 ², Weida Gao 高伟达 ³, Qiuhua Wei 韦秋华 ⁴, Haoyu Li 李浩宇 ¹, Changliang Guo 郭长亮 ⁵ ⁶, Weisong Zhao 赵唯淞 ¹
¹ Innovation Photonics and Imaging Center, School of Instrumentation Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150080, China
中国 哈尔滨 哈尔滨工业大学仪器科学与工程学院 先进光电成像技术研究室
² Department of Control Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150081, China
中国 哈尔滨 哈尔滨工业大学控制科学与工程系
³ Department of neurosurgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150086, China
中国 哈尔滨 哈尔滨医科大学附属第二医院神经外科
⁴ Institute of Optical Measurement and Intellectualization, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150080, China
中国 哈尔滨 哈尔滨工业大学 光电测控与智能化研究所
⁵ Beijing Institute of Collaborative Innovation, Beijing 100094, China
中国 北京 北京协同创新研究院
⁶ State Key Laboratory of Membrane Biology, Beijing Key Laboratory of Cardiometabolic Molecular Medicine, Institute of Molecular Medicine, National Biomedical Imaging Center, School of Future Technology, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
中国 北京 北京大学未来技术学院 分子医学研究所 国家生物医学成像科学中心 代谢及心血管分子医学北京市重点实验室 膜生物学国家重点实验室
Opto-Electronic Science, 2023-12-28
Abstract
A critical function of flow cytometry is to count the concentration of blood cells, which helps in the diagnosis of certain diseases. However, the bulky nature of commercial flow cytometers makes such tests only available in hospitals or laboratories, hindering the spread of point-of-care testing (POCT), especially in underdeveloped areas.
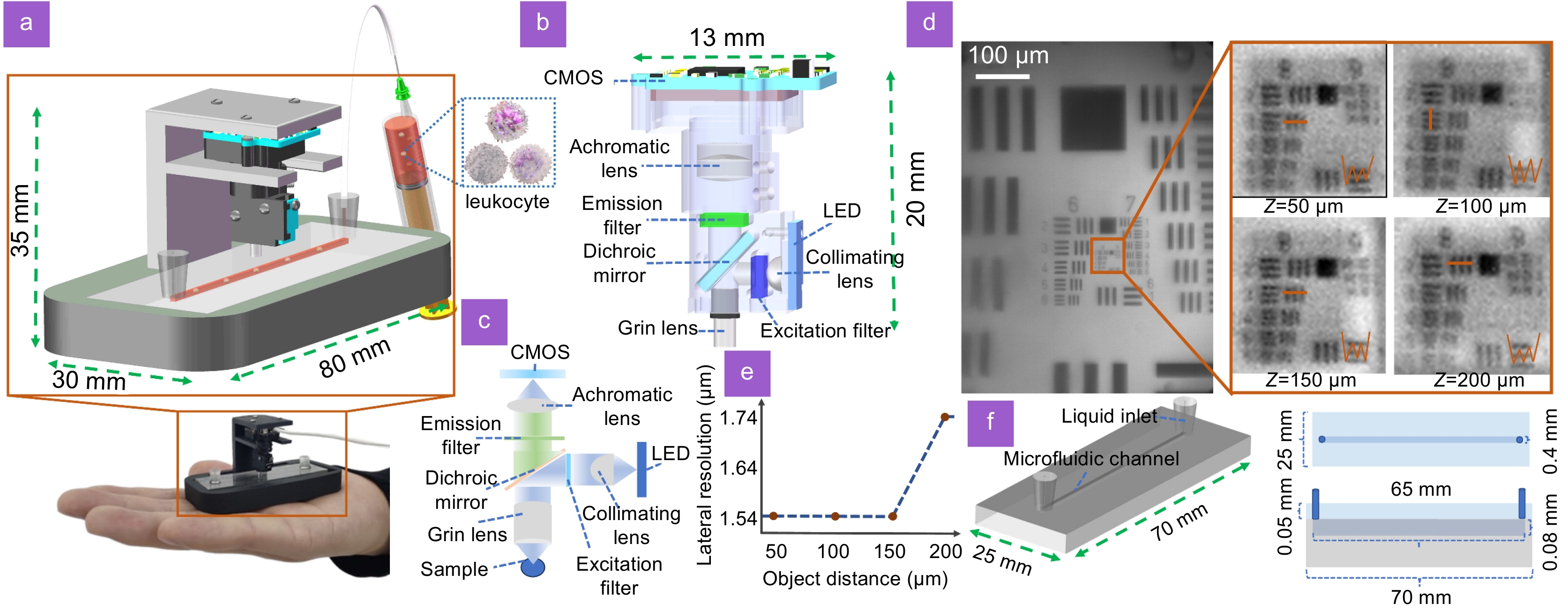
Here, we propose a smart Palm-size Optofluidic Hematology Analyzer based on a miniature fluorescence microscope and a microfluidic platform to lighten the device to improve its portability. This gadget has a dimension of 35 × 30 × 80 mm and a mass of 39 g, less than 5% of the weight of commercially available flow cytometers.
Additionally, automatic leukocyte concentration detection has been realized through the integration of image processing and leukocyte counting algorithms. We compared the leukocyte concentration measurement between our approach and a hemocytometer using the Passing-Bablok analysis and achieved a correlation coefficient of 0.979. Through Bland-Altman analysis, we obtained the relationship between their differences and mean measurement values and established 95% limits of agreement, ranging from −0.93×10³ to 0.94×10³ cells/μL.
We anticipate that this device can be used widely for monitoring and treating diseases such as HIV and tumors beyond hospitals.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25