(Peer-Reviewed) Low-loss chip-scale programmable silicon photonic processor
Yiwei Xie 谢意维 ¹, Shihan Hong 洪仕瀚 ¹, Hao Yan 闫昊 ¹, Changping Zhang 张昌平 ¹, Long Zhang 张龙 ¹, Leimeng Zhuang 庄磊勐 ², Daoxin Dai 戴道锌 ¹ ³
¹ Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, State Key Laboratory for Modern Optical Instrumentation, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory for Sensing Technologies, Zhejiang University, Zijingang Campus, Hangzhou 310058, China
中国 杭州 浙江大学紫金港校区 现代光学仪器国家重点实验室 浙江省光电磁传感技术研究重点实验室 光及电磁波研究中心
² Imec USA, Nanoelectronics Design Center, Inc., 194 Neocity Way, Kissimmee, FL34744, USA
³ Ningbo Research Institute, Zhejiang University, Ningbo 315100, China
中国 宁波 浙江大学宁波研究院
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2022-10-28
Abstract
Chip-scale programmable optical signal processors are often used to flexibly manipulate the optical signals for satisfying the demands in various applications, such as lidar, radar, and artificial intelligence. Silicon photonics has unique advantages of ultra-high integration density as well as CMOS compatibility, and thus makes it possible to develop large-scale programmable optical signal processors. The challenge is the high silicon waveguides propagation losses and the high calibration complexity for all tuning elements due to the random phase errors.
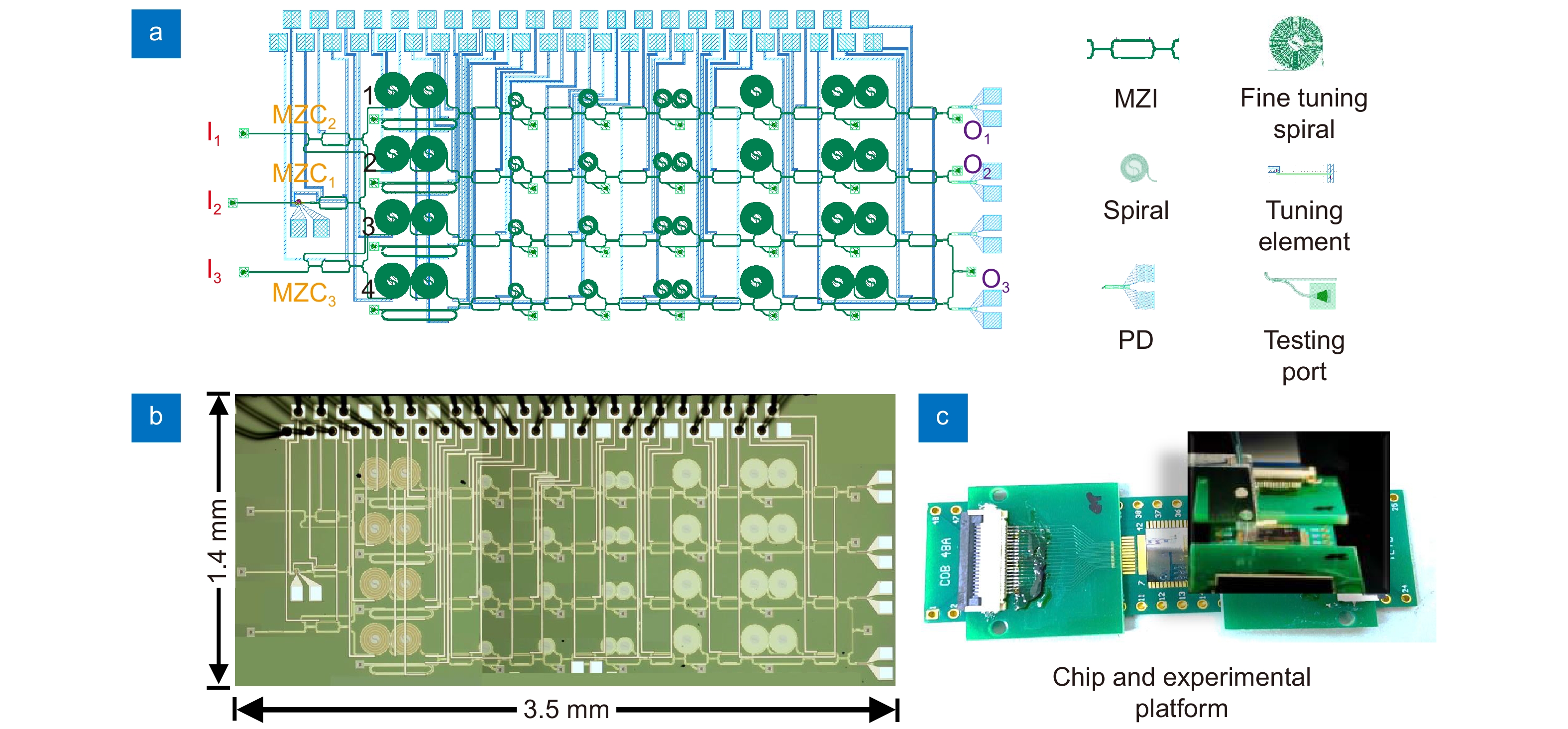
In this paper, we propose and demonstrate a programmable silicon photonic processor for the first time by introducing low-loss multimode photonic waveguide spirals and low-random-phase-error Mach-Zehnder switches. The present chip-scale programmable silicon photonic processor comprises a 1×4 variable power splitter based on cascaded Mach-Zehnder couplers (MZCs), four Ge/Si photodetectors, four channels of thermally-tunable optical delaylines. Each channel consists of a continuously-tuning phase shifter based on a waveguide spiral with a micro-heater and a digitally-tuning delayline realized with cascaded waveguide-spiral delaylines and MZSs for 5.68 ps time-delay step.
Particularly, these waveguide spirals used here are designed to be as wide as 2 µm, enabling an ultralow propagation loss of 0.28 dB/cm. Meanwhile, these MZCs and MZSs are designed with 2-µm-wide arm waveguides, and thus the random phase errors in the MZC/MZS arms are negligible, in which case the calibration for these MZSs/MZCs becomes easy and furthermore the power consumption for compensating the phase errors can be reduced greatly.
Finally, this programmable silicon photonic processor is demonstrated successfully to verify a number of distinctively different functionalities, including tunable time-delay, microwave photonic beamforming, arbitrary optical signal filtering, and arbitrary waveform generation.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25