(Peer-Reviewed) Highly sensitive and stable probe refractometer based on configurable plasmonic resonance with nano-modified fiber core
Jianying Jing 井建迎 ¹ ² ³, Kun Liu 刘琨 ¹ ² ³, Junfeng Jiang 江俊峰 ¹ ² ³, Tianhua Xu 徐天华 ¹ ² ³, Shuang Wang 王双 ¹ ² ³, Tiegen Liu 刘铁根 ¹ ² ³
¹ School of Precision Instruments and Opto-Electronics Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
中国 天津 天津大学精密仪器与光电子工程学院
² Key Laboratory of Opto-Electronics Information Technology, Ministry of Education, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
中国 天津 光电信息技术教育部重点实验室(天津大学)
³ Tianjin Optical Fiber Sensing Engineering Center, Institute of Optical Fiber Sensing, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
中国 天津 天津大学光纤传感研究所 天津市光纤传感工程中心
Opto-Electronic Advances
, 2023-06-25
Abstract
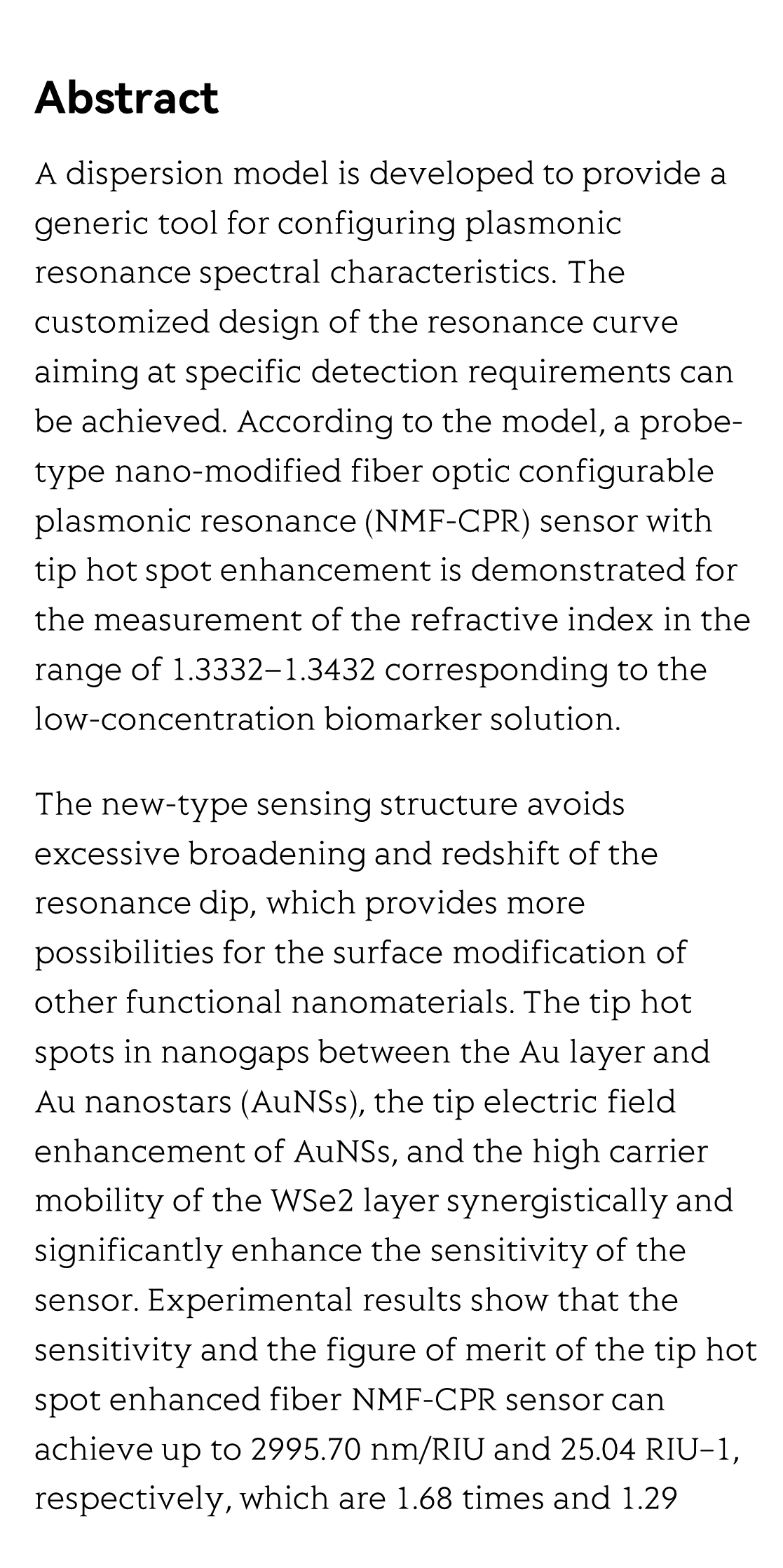
A dispersion model is developed to provide a generic tool for configuring plasmonic resonance spectral characteristics. The customized design of the resonance curve aiming at specific detection requirements can be achieved. According to the model, a probe-type nano-modified fiber optic configurable plasmonic resonance (NMF-CPR) sensor with tip hot spot enhancement is demonstrated for the measurement of the refractive index in the range of 1.3332–1.3432 corresponding to the low-concentration biomarker solution.
The new-type sensing structure avoids excessive broadening and redshift of the resonance dip, which provides more possibilities for the surface modification of other functional nanomaterials. The tip hot spots in nanogaps between the Au layer and Au nanostars (AuNSs), the tip electric field enhancement of AuNSs, and the high carrier mobility of the WSe2 layer synergistically and significantly enhance the sensitivity of the sensor. Experimental results show that the sensitivity and the figure of merit of the tip hot spot enhanced fiber NMF-CPR sensor can achieve up to 2995.70 nm/RIU and 25.04 RIU−1, respectively, which are 1.68 times and 1.29 times higher than those of the conventional fiber plasmonic resonance sensor.
The results achieve good agreements with numerical simulations, demonstrate a better level compared to similar reported studies, and verify the correctness of the dispersion model. The detection resolution of the sensor reaches up to 2.00×10−5 RIU, which is obviously higher than that of the conventional side-polished fiber plasmonic resonance sensor. This indicates a high detection accuracy of the sensor.
The dense Au layer effectively prevents the intermediate nanomaterials from shedding and chemical degradation, which enables the sensor with high stability. Furthermore, the terminal reflective sensing structure can be used as a practical probe and can allow a more convenient operation.
Flicker minimization in power-saving displays enabled by measurement of difference in flexoelectric coefficients and displacement-current in positive dielectric anisotropy liquid crystals
Junho Jung, HaYoung Jung, GyuRi Choi, HanByeol Park, Sun-Mi Park, Ki-Sun Kwon, Heui-Seok Jin, Dong-Jin Lee, Hoon Jeong, JeongKi Park, Byeong Koo Kim, Seung Hee Lee, MinSu Kim
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25
Dual-frequency angular-multiplexed fringe projection profilometry with deep learning: breaking hardware limits for ultra-high-speed 3D imaging
Wenwu Chen, Yifan Liu, Shijie Feng, Wei Yin, Jiaming Qian, Yixuan Li, Hang Zhang, Maciej Trusiak, Malgorzata Kujawinska, Qian Chen, Chao Zuo
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25