(Peer-Reviewed) Functional isolation, culture and cryopreservation of adult human primary cardiomyocytes
Bingying Zhou 周冰莹 ¹ ², Xun Shi 师珣 ¹, Xiaoli Tang 唐晓丽 ¹, Quanyi Zhao ¹ ², Le Wang ¹, Fang Yao 姚芳 ¹, Yongfeng Hou 侯永凤 ¹, Xianqiang Wang 王现强 ³, Wei Feng 凤玮 ³, Liqing Wang 王立清 ³, Xiaogang Sun 孙晓刚 ³, Li Wang 王利 ¹ ², Shengshou Hu 胡盛寿 ¹ ² ³
¹ State Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Disease, Fuwai Hospital, National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China
中国 北京 中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院 阜外医院 心血管疾病国家重点实验室 国家心血管病中心
² Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Disease, Fuwai Hospital Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Shenzhen, Shenzhen, China
中国 深圳 中国医学科学院阜外医院 深圳市心血管疾病重点实验室
³ Department of Cardiac Surgery, Fuwai Hospital, National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China
中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院 国家心血管病中心 阜外医院心外科
Abstract
Cardiovascular diseases are the most common cause of death globally. Accurately modeling cardiac homeostasis, dysfunction, and drug response lies at the heart of cardiac research. Adult human primary cardiomyocytes (hPCMs) are a promising cellular model, but unstable isolation efficiency and quality, rapid cell death in culture, and unknown response to cryopreservation prevent them from becoming a reliable and flexible in vitro cardiac model.
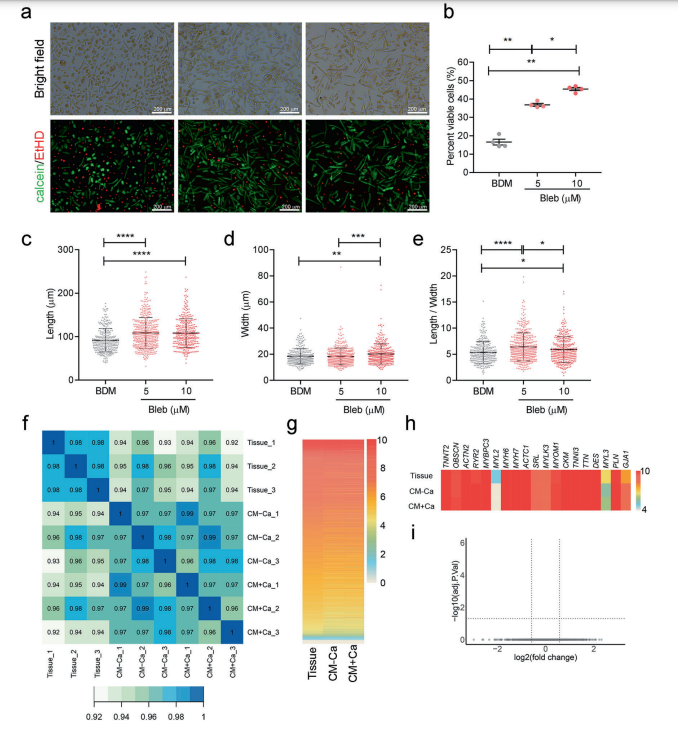
Combing the use of a reversible inhibitor of myosin II ATPase, (-)-blebbistatin (Bleb), and multiple optimization steps of the isolation procedure, we achieved a 2.74-fold increase in cell viability over traditional methods, accompanied by better cellular morphology, minimally perturbed gene expression, intact electrophysiology, and normal neurohormonal signaling. Further optimization of culture conditions established a method that was capable of maintaining optimal cell viability, morphology, and mitochondrial respiration for at least 7 days.
Most importantly, we successfully cryopreserved hPCMs, which were structurally, molecularly, and functionally intact after undergoing the freeze-thaw cycle. hPCMs demonstrated greater sensitivity towards a set of cardiotoxic drugs, compared to human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs). Further dissection of cardiomyocyte drug response at both the population and single-cell transcriptomic level revealed that hPCM responses were more pronouncedly enriched in cardiac function, whereas hiPSC-CMs responses reflected cardiac development.
Together, we established a full set of methodologies for the efficient isolation and prolonged maintenance of functional primary adult human cardiomyocytes in vitro, unlocking their potential as a cellular model for cardiovascular research, drug discovery, and safety pharmacology.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25