(Peer-Reviewed) Performance evaluation of ultra-long lithium heat pipe using an improved lumped parameter model
Chong-Ju Hu ¹ ² ³, Da-Li Yu 余大利 ¹, Mei-Sheng He 何梅生 ¹, Hua-Ping Mei 梅华平 ¹, Jie Yu 郁杰 ¹, Tao-Sheng Li 李桃生 ¹
¹ Institute of Nuclear Energy Safety Technology, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hefei, 230031, China
中国 合肥 中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院 核能安全技术研究所
² University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, 230026, China
中国 合肥 中国科学技术大学
³ Suzhou University, Suzhou, 234000, China
中国 苏州 苏州大学
Abstract
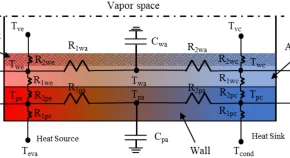
Lithium heat pipes have broad applications in heat pipe cooling reactors and hypersonic vehicles owing to their ultra-high working temperature. In particular, when the length of the lithium heat pipe is ultra-long, the flow and heat transfer characteristics are more complex.
In this study, an improved lumped parameter model that considers the Marangoni effect, bending effect, and different vapor flow patterns and Mach numbers was developed. Thereafter, the proposed model was verified using the University of New Mexico’s Heat Pipe and HTPIPE models. Finally, the verified model was applied to simulate the steady-state operation of an ultra-long lithium heat pipe in a Heat Pipe-Segmented Thermoelectric Module Converters space reactor.
Based on the results:
(1) Vapor thermal resistance was dominant at low heating power and decreased with increasing heating power. The vapor flow inside the heat pipe developed from the laminar to the turbulent phase, whereas the liquid phase in the heat pipe was always laminar.
(2) The vapor pressure drop caused by bending was approximately 22–23% of the total, and the bending effect on the liquid pressure drop could be ignored.
(3) The Marangoni effect reduced the capillary limit by hindering the liquid reflux, especially at low vapor temperatures. Without considering the Marangoni effect, the capillary limit of the lithium heat pipe was overestimated by 9% when the vapor temperature was 1400 K.
(4) The total thermal resistance of the heat pipe significantly increased with increasing adiabatic length when the vapor temperature was low.
Further, the wick dryness increased with increasing adiabatic length at any vapor temperature. Such findings improve on current knowledge for the optimal design and safety analysis of a heat pipe reactor, which adopts ultra-long lithium heat pipes.
Embedded solar adaptive optics telescope: achieving compact integration for high-efficiency solar observations
Naiting Gu, Hao Chen, Ao Tang, Xinlong Fan, Carlos Quintero Noda, Yawei Xiao, Libo Zhong, Xiaosong Wu, Zhenyu Zhang, Yanrong Yang, Zao Yi, Xiaohu Wu, Linhai Huang, Changhui Rao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-05-27
Wearable photonic smart wristband for cardiorespiratory function assessment and biometric identification
Wenbo Li, Yukun Long, Yingyin Yan, Kun Xiao, Zhuo Wang, Di Zheng, Arnaldo Leal-Junior, Santosh Kumar, Beatriz Ortega, Carlos Marques, Xiaoli Li, Rui Min
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-05-27
Integrated photonic polarizers with 2D reduced graphene oxide
Junkai Hu, Jiayang Wu, Di Jin, Wenbo Liu, Yuning Zhang, Yunyi Yang, Linnan Jia, Yijun Wang, Duan Huang, Baohua Jia, David J. Moss
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-05-22
Structural color: an emerging nanophotonic strategy for multicolor and functionalized applications
Wenhao Wang, Long Wang, Qianqian Fu, Wang Zhang, Liuying Wang, Gu Liu, Youju Huang, Jie Huang, Haoyuan Zhang, Fuqiang Guo, Xiaohu Wu
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-04-25