(Peer-Reviewed) Integrated photonic polarizers with 2D reduced graphene oxide
Junkai Hu 胡竣凯 ¹ ², Jiayang Wu 吴佳旸 ¹, Di Jin 金迪 ¹ ², Wenbo Liu 刘文博 ¹ ³ ⁴, Yuning Zhang 张宇宁 ⁵, Yunyi Yang 杨云翼 ¹, Linnan Jia 贾林楠 ³ ⁴, Yijun Wang 王一军 ², Duan Huang 黄端 ⁶ ⁷, Baohua Jia 贾宝华 ³ ⁴, David J. Moss ¹
¹ Optical Sciences Centre, Swinburne University of Technology, Melbourne 3122, Australia
² School of Automation, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
中国 长沙 中南大学自动化学院
³ School of Science, RMIT University, Melbourne 3000, Australia
⁴ The Australian Research Council (ARC) Industrial Transformation Training Centre in Surface Engineering for Advanced Materials (SEAM), RMIT University, Melbourne 3000, Australia
⁵ School of Physics, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
中国 北京 北京大学物理学院
⁶ School of Electronic Information, Central South University, Changsha 410083, China
中国 长沙 中南大学电子信息学院
⁷ Hefei National Laboratory, Hefei 230088, China
中国 合肥 合肥国家实验室
Opto-Electronic Science
, 2025-05-22
Abstract
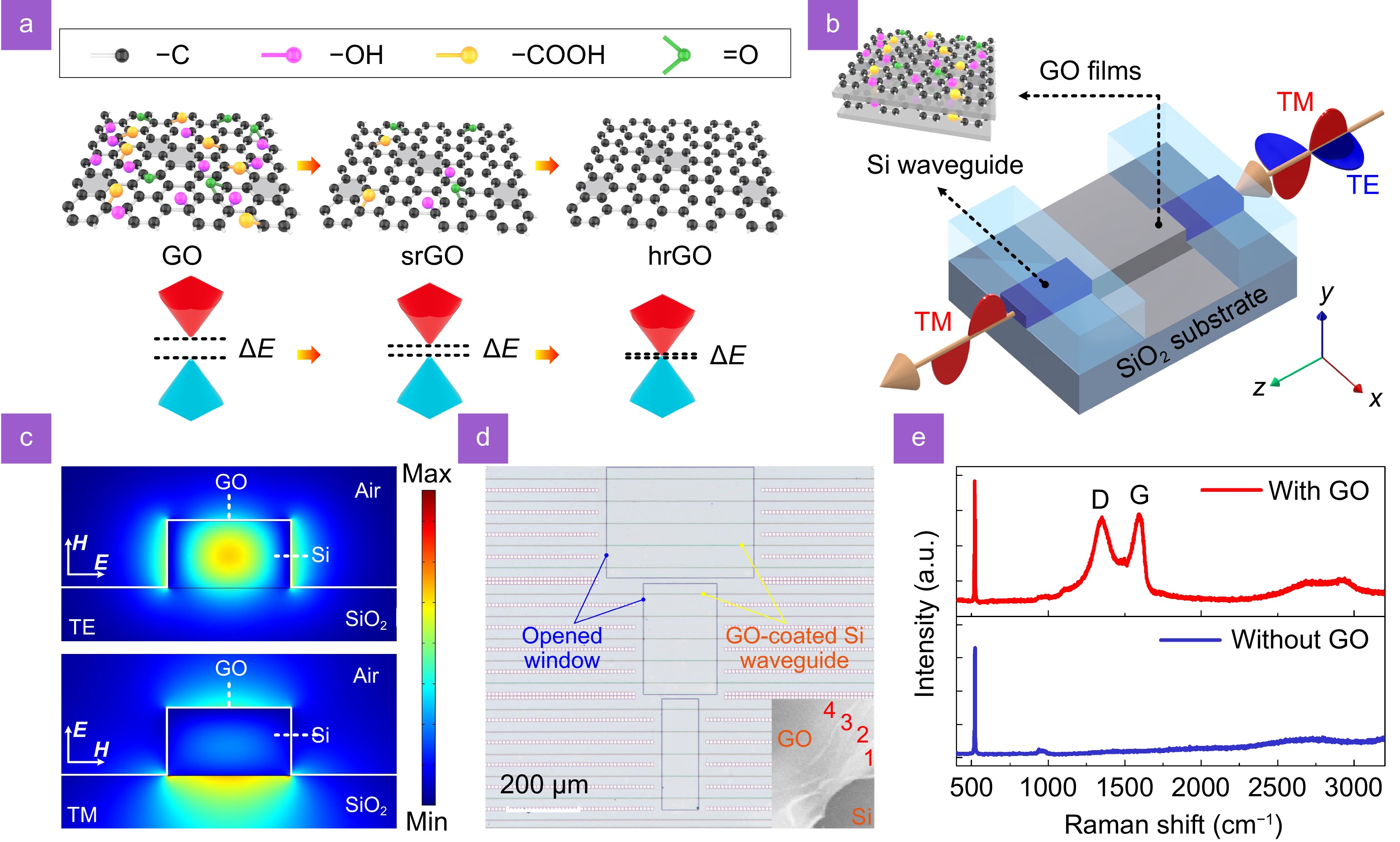
Optical polarizers, which allow the transmission of specific polarization states, are essential components in modern optical systems. Here, we experimentally demonstrate integrated photonic polarizers incorporating reduced graphene oxide (rGO) films. 2D graphene oxide (GO) films are integrated onto silicon waveguides and microring resonators (MRRs) with precise control over their thicknesses and sizes, followed by GO reduction via two different methods including uniform thermal reduction and localized photothermal reduction.
We measure devices with various lengths, thicknesses, and reduction degrees of GO films. The results show that the devices with rGO exhibit better performance than those with GO, achieving a polarization-dependent loss of ~47 dB and a polarization extinction ratio of ~16 dB for the hybrid waveguides and MRRs with rGO, respectively. By fitting the experimental results with theory, it is found that rGO exhibits more significant anisotropy in loss, with an anisotropy ratio over 4 times that of GO.
In addition, rGO shows higher thermal stability and greater robustness to photothermal reduction than GO. These results highlight the strong potential of rGO films for implementing high-performance polarization selective devices in integrated photonic platforms.
Flicker minimization in power-saving displays enabled by measurement of difference in flexoelectric coefficients and displacement-current in positive dielectric anisotropy liquid crystals
Junho Jung, HaYoung Jung, GyuRi Choi, HanByeol Park, Sun-Mi Park, Ki-Sun Kwon, Heui-Seok Jin, Dong-Jin Lee, Hoon Jeong, JeongKi Park, Byeong Koo Kim, Seung Hee Lee, MinSu Kim
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25
Dual-frequency angular-multiplexed fringe projection profilometry with deep learning: breaking hardware limits for ultra-high-speed 3D imaging
Wenwu Chen, Yifan Liu, Shijie Feng, Wei Yin, Jiaming Qian, Yixuan Li, Hang Zhang, Maciej Trusiak, Malgorzata Kujawinska, Qian Chen, Chao Zuo
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25