(Peer-Reviewed) High-frequency enhanced ultrafast compressed active photography
Yizhao Meng 孟毅钊 ¹, Yu Lu 陆宇 ¹, Pengfei Zhang 张鹏飞 ¹, Yi Liu 刘毅 ¹, Fei Yin 尹飞 ², Lin Kai 凯林 ¹, Qing Yang 杨青 ², Feng Chen 陈烽 ¹
¹ State Key Laboratory for Manufacturing System Engineering and Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Photonics Technology for Information, School of Electronic Science and Engineering, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an 710049, China
中国 西安 西安交通大学电子与信息学部电子科学与工程学院 机械制造系统工程国家重点实验室 陕西省信息光子技术重点实验室
² School of Mechanical Engineering, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China
中国 西安 西安交通大学机械工程学院
Opto-Electronic Advances
, 2025-01-15
Abstract
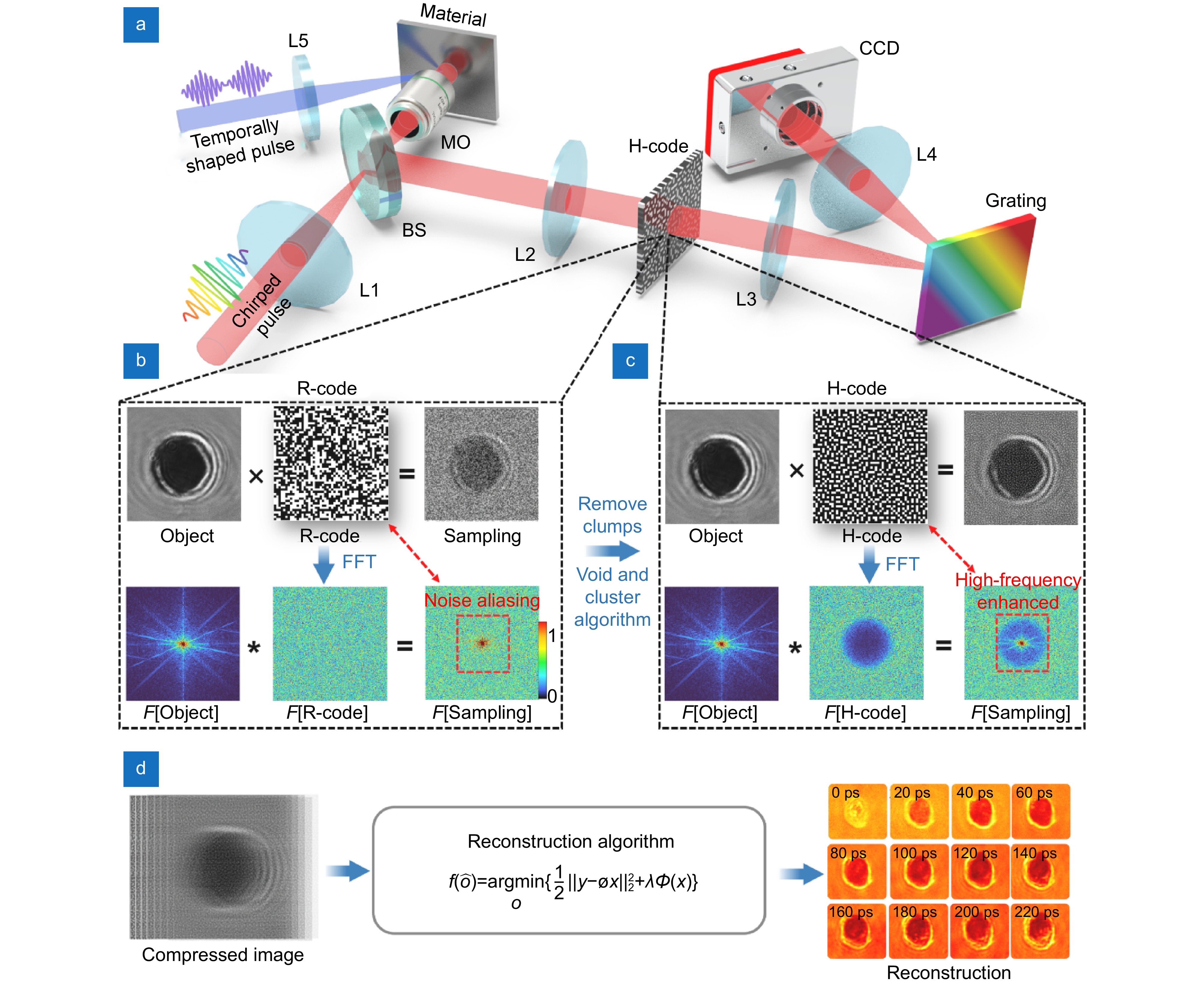
Single-shot ultrafast compressed imaging (UCI) is an effective tool for studying ultrafast dynamics in physics, chemistry, or material science because of its excellent high frame rate and large frame number. However, the random code (R-code) used in traditional UCI will lead to low-frequency noise covering high-frequency information due to its uneven sampling interval, which is a great challenge in the fidelity of large-frame reconstruction.
Here, a high-frequency enhanced compressed active photography (H-CAP) is proposed. By uniformizing the sampling interval of R-code, H-CAP capture the ultrafast process with a random uniform sampling mode. This sampling mode makes the high-frequency sampling energy dominant, which greatly suppresses the low-frequency noise blurring caused by R-code and achieves high-frequency information of image enhanced.
The superior dynamic performance and large-frame reconstruction ability of H-CAP are verified by imaging optical self-focusing effect and static object, respectively. We applied H-CAP to the spatial-temporal characterization of double-pulse induced silicon surface ablation dynamics, which is performed within 220 frames in a single-shot of 300 ps. H-CAP provides a high-fidelity imaging method for observing ultrafast unrepeatable dynamic processes with large frames.
Flicker minimization in power-saving displays enabled by measurement of difference in flexoelectric coefficients and displacement-current in positive dielectric anisotropy liquid crystals
Junho Jung, HaYoung Jung, GyuRi Choi, HanByeol Park, Sun-Mi Park, Ki-Sun Kwon, Heui-Seok Jin, Dong-Jin Lee, Hoon Jeong, JeongKi Park, Byeong Koo Kim, Seung Hee Lee, MinSu Kim
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25
Dual-frequency angular-multiplexed fringe projection profilometry with deep learning: breaking hardware limits for ultra-high-speed 3D imaging
Wenwu Chen, Yifan Liu, Shijie Feng, Wei Yin, Jiaming Qian, Yixuan Li, Hang Zhang, Maciej Trusiak, Malgorzata Kujawinska, Qian Chen, Chao Zuo
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25