(Peer-Reviewed) Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response
Mingrui Shao 邵明瑞 ¹, Chang Ji 纪昌 ¹, Jibing Tan 谭吉兵 ¹, Baoqiang Du 杜宝强 ¹, Xiaofei Zhao 赵晓菲 ¹, Jing Yu 郁菁 ¹, Baoyuan Man 满宝元 ¹, Kaichen Xu 徐凯臣 ², Chao Zhang 张超 ¹, Zhen Li 李振 ¹
¹ Institute of Materials and Clean Energy, School of Physics and Electronics, Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China
中国 济南 山东师范大学物理与电子科学学院 材料与清洁能源研究院
² State Key Laboratory of Fluid Power and Mechatronic Systems, School of Mechanical Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310030, China
中国 杭州 浙江大学机械工程学院 流体动力与机电系统国家重点实验室
Opto-Electronic Advances
, 2023-11-15
Abstract
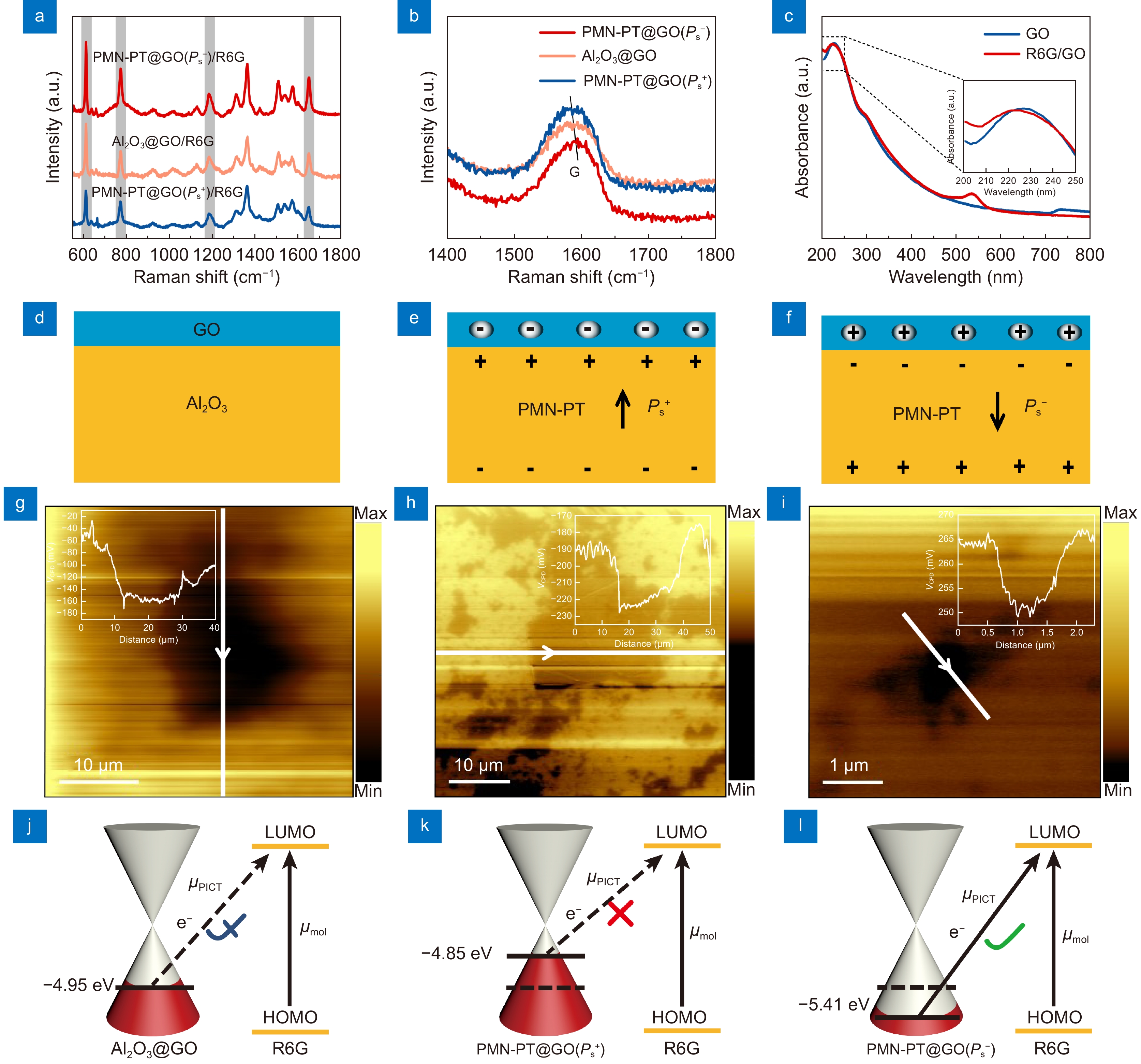
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrates based on chemical mechanism (CM) have received widespread attentions for the stable and repeatable signal output due to their excellent chemical stability, uniform molecular adsorption and controllable molecular orientation. However, it remains huge challenges to achieve the optimal SERS signal for diverse molecules with different band structures on the same substrate.
Herein, we demonstrate a graphene oxide (GO) energy band regulation strategy through ferroelectric polarization to facilitate the charge transfer process for improving SERS activity. The Fermi level (Ef) of GO can be flexibly manipulated by adjusting the ferroelectric polarization direction or the temperature of the ferroelectric substrate. Experimentally, kelvin probe force microscopy (KPFM) is employed to quantitatively analyze theEf of GO.
Theoretically, the density functional theory calculations are also performed to verify the proposed modulation mechanism. Consequently, the SERS response of probe molecules with different band structures (R6G, CV, MB, PNTP) can be improved through polarization direction or temperature changes without the necessity to redesign the SERS substrate.
This work provides a novel insight into the SERS substrate design based on CM and is expected to be applied to other two-dimensional materials.
Flicker minimization in power-saving displays enabled by measurement of difference in flexoelectric coefficients and displacement-current in positive dielectric anisotropy liquid crystals
Junho Jung, HaYoung Jung, GyuRi Choi, HanByeol Park, Sun-Mi Park, Ki-Sun Kwon, Heui-Seok Jin, Dong-Jin Lee, Hoon Jeong, JeongKi Park, Byeong Koo Kim, Seung Hee Lee, MinSu Kim
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25
Dual-frequency angular-multiplexed fringe projection profilometry with deep learning: breaking hardware limits for ultra-high-speed 3D imaging
Wenwu Chen, Yifan Liu, Shijie Feng, Wei Yin, Jiaming Qian, Yixuan Li, Hang Zhang, Maciej Trusiak, Malgorzata Kujawinska, Qian Chen, Chao Zuo
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25