(Peer-Reviewed) Ferroelectric domain engineering of lithium niobate
Jackson J. Chakkoria ¹ ², Aditya Dubey ¹ ², Arnan Mitchell ¹ ², Andreas Boes ² ³ ⁴
¹ Integrated Photonics and Applications Centre, School of Engineering, RMIT University, Melbourne, VIC 3001, Australia
² ARC Centre of Excellence in Optical Microcombs for Breakthrough Science (COMBS)
³ School of Electrical and Mechanical Engineering, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, SA 5005, Australia
⁴ Institute for Photonics and Advanced Sensing, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, SA 5005, Australia
Opto-Electronic Advances
, 2025-01-03
Abstract
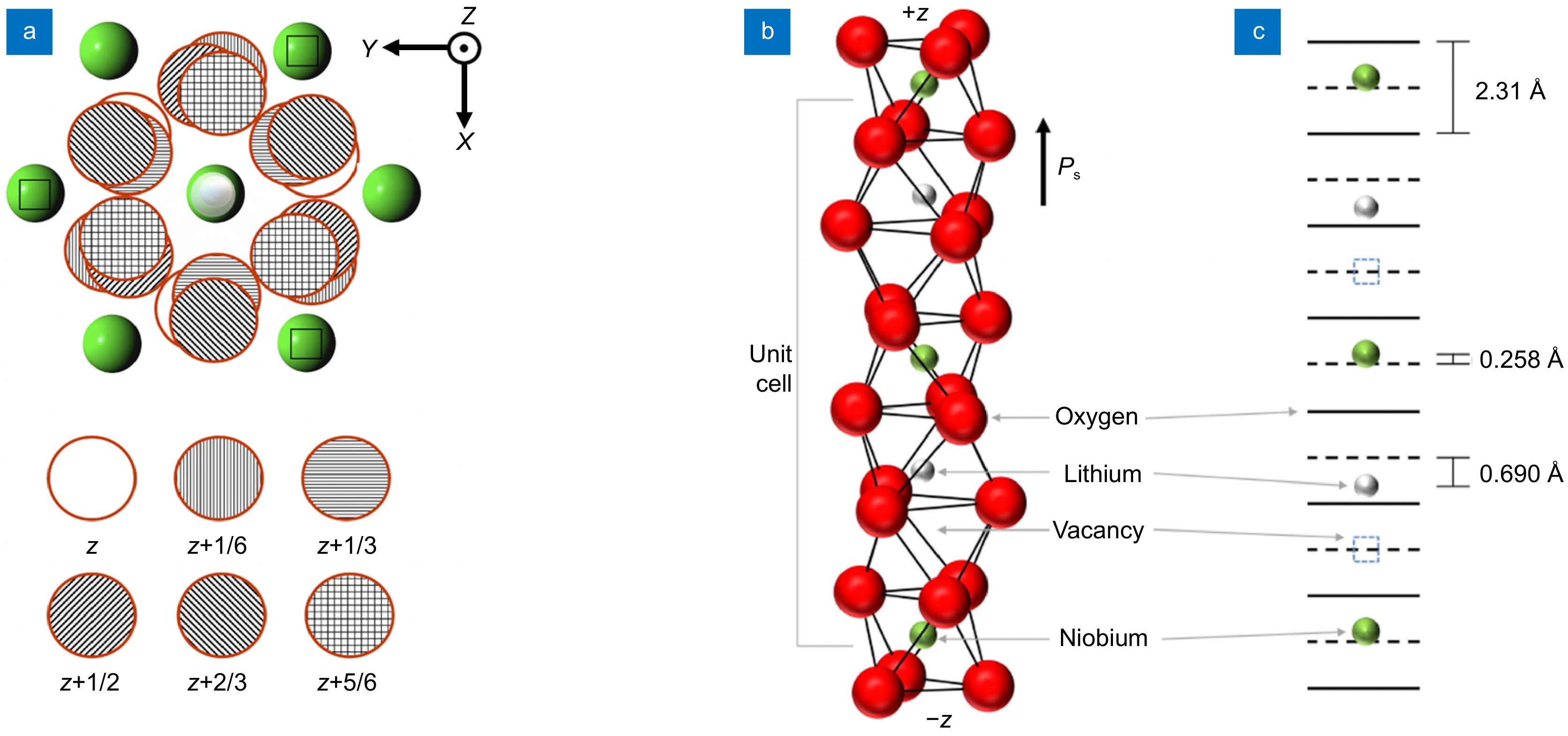
Lithium niobate (LN) has remained at the forefront of academic research and industrial applications due to its rich material properties, which include second-order nonlinear optic, electro-optic, and piezoelectric properties. A further aspect of LN’s versatility stems from the ability to engineer ferroelectric domains with micro and even nano-scale precision in LN, which provides an additional degree of freedom to design acoustic and optical devices with improved performance and is only possible in a handful of other materials.
In this review paper, we provide an overview of the domain engineering techniques developed for LN, their principles, and the typical domain size and pattern uniformity they provide, which is important for devices that require high-resolution domain patterns with good reproducibility. It also highlights each technique's benefits, limitations, and adaptability for an application, along with possible improvements and future advancement prospects.
Further, the review provides a brief overview of domain visualization methods, which is crucial to gain insights into domain quality/shape and explores the adaptability of the proposed domain engineering methodologies for the emerging thin-film lithium niobate on an insulator platform, which creates opportunities for developing the next generation of compact and scalable photonic integrated circuits and high frequency acoustic devices.
Flicker minimization in power-saving displays enabled by measurement of difference in flexoelectric coefficients and displacement-current in positive dielectric anisotropy liquid crystals
Junho Jung, HaYoung Jung, GyuRi Choi, HanByeol Park, Sun-Mi Park, Ki-Sun Kwon, Heui-Seok Jin, Dong-Jin Lee, Hoon Jeong, JeongKi Park, Byeong Koo Kim, Seung Hee Lee, MinSu Kim
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25
Dual-frequency angular-multiplexed fringe projection profilometry with deep learning: breaking hardware limits for ultra-high-speed 3D imaging
Wenwu Chen, Yifan Liu, Shijie Feng, Wei Yin, Jiaming Qian, Yixuan Li, Hang Zhang, Maciej Trusiak, Malgorzata Kujawinska, Qian Chen, Chao Zuo
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25