(Peer-Reviewed) Physics-data-driven intelligent optimization for large-aperture metalenses
Yingli Ha 哈颖丽 ¹ ² ³, Yu Luo 罗宇 ¹ ² ³, Mingbo Pu 蒲明博 ¹ ² ³ ⁴, Fei Zhang 张飞 ¹ ² ³, Qiong He 何琼 ¹ ², Jinjin Jin 靳金金 ¹ ², Mingfeng Xu 徐明峰 ¹ ² ³ ⁴, Yinghui Guo 郭迎辉 ¹ ² ³ ⁴, Xiaogang Li 李小岗 ⁵, Xiong Li 李雄 ¹ ² ⁴, Xiaoliang Ma 马晓亮 ¹ ² ⁴, Xiangang Luo 罗先刚 ¹ ² ³ ⁴
¹ National Key Laboratory of Optical Field Manipulation Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
中国 成都 中国科学院光场调控科学技术全国重点实验室
² State Key Laboratory of Optical Technologies on Nano-Fabrication and Micro-Engineering, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
中国 成都 中国科学院光电技术研究所 微细加工光学技术国家重点实验室
³ Research Center on Vector Optical Fields, Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610209, China
中国 成都 中国科学院光电技术研究所 矢量光场研究中心
⁴ School of Optoelectronics, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
中国 北京 中国科学院大学光电学院
⁵ Tianfu Xinglong Lake Laboratory, Chengdu 610299, China
中国 成都 天府兴隆湖实验室
Opto-Electronic Advances
, 2023-11-15
Abstract
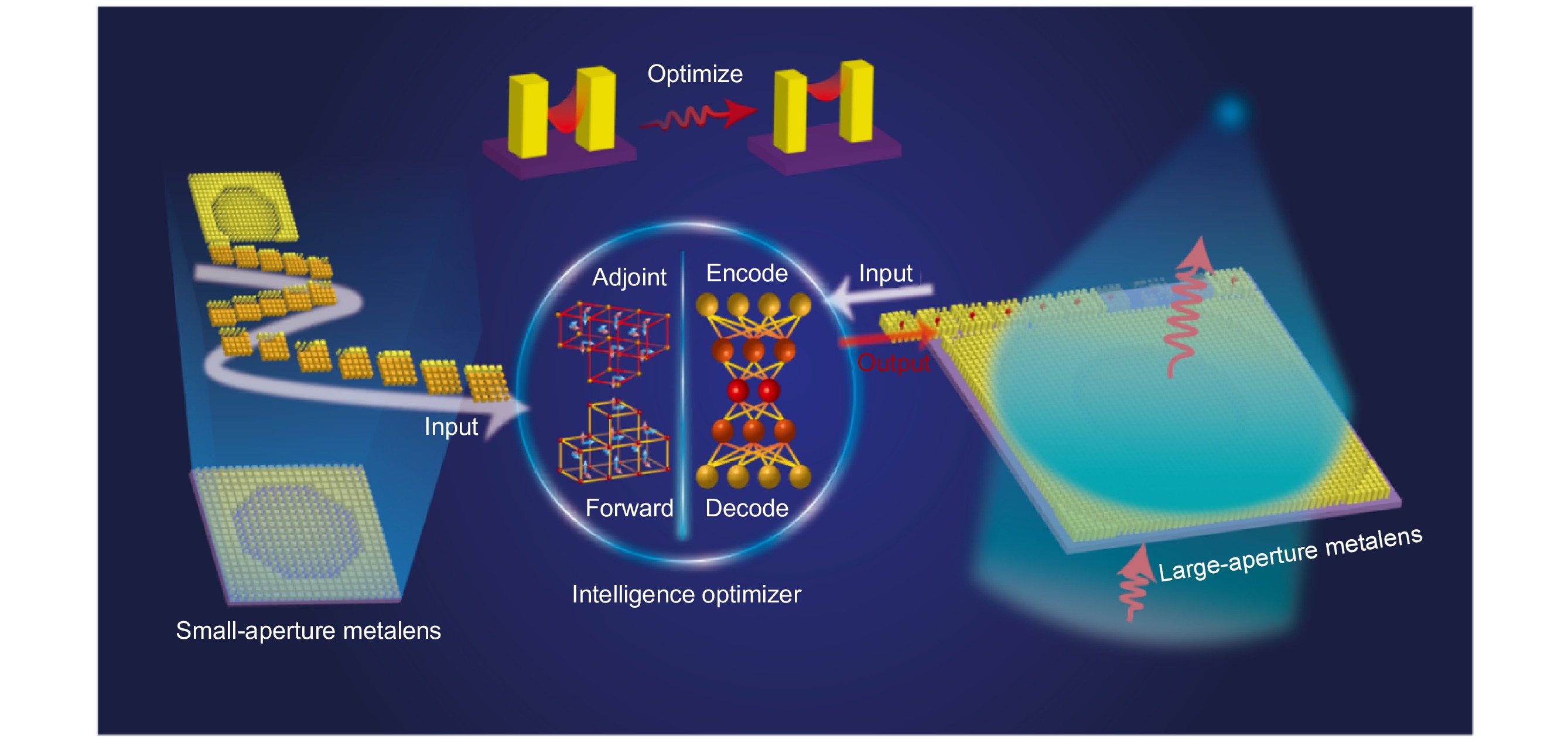
Metalenses have gained significant attention and have been widely utilized in optical systems for focusing and imaging, owing to their lightweight, high-integration, and exceptional-flexibility capabilities. Traditional design methods neglect the coupling effect between adjacent meta-atoms, thus harming the practical performance of meta-devices. The existing physical/data-driven optimization algorithms can solve the above problems, but bring significant time costs or require a large number of data-sets.
Here, we propose a physics-data-driven method employing an “intelligent optimizer” that enables us to adaptively modify the sizes of the meta-atom according to the sizes of its surrounding ones. The implementation of such a scheme effectively mitigates the undesired impact of local lattice coupling, and the proposed network model works well on thousands of data-sets with a validation loss of 3×10−3. Based on the “intelligent optimizer”, a 1-cm-diameter metalens is designed within 3 hours, and the experimental results show that the 1-mm-diameter metalens has a relative focusing efficiency of 93.4% (compared to the ideal focusing efficiency) and a Strehl ratio of 0.94.
Compared to previous inverse design method, our method significantly boosts designing efficiency with five orders of magnitude reduction in time. More generally, it may set a new paradigm for devising large-aperture meta-devices.
Flicker minimization in power-saving displays enabled by measurement of difference in flexoelectric coefficients and displacement-current in positive dielectric anisotropy liquid crystals
Junho Jung, HaYoung Jung, GyuRi Choi, HanByeol Park, Sun-Mi Park, Ki-Sun Kwon, Heui-Seok Jin, Dong-Jin Lee, Hoon Jeong, JeongKi Park, Byeong Koo Kim, Seung Hee Lee, MinSu Kim
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25
Dual-frequency angular-multiplexed fringe projection profilometry with deep learning: breaking hardware limits for ultra-high-speed 3D imaging
Wenwu Chen, Yifan Liu, Shijie Feng, Wei Yin, Jiaming Qian, Yixuan Li, Hang Zhang, Maciej Trusiak, Malgorzata Kujawinska, Qian Chen, Chao Zuo
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-09-25