(Peer-Reviewed) A highly sensitive LITES sensor based on a multi-pass cell with dense spot pattern and a novel quartz tuning fork with low frequency
Yahui Liu 刘亚辉 ¹ ², Shunda Qiao 乔顺达 ¹ ², Chao Fang 房超 ¹ ², Ying He 何应 ¹ ², Haiyue Sun 孙海岳 ¹ ², Jian Liu 刘俭 ³, Yufei Ma 马欲飞 ¹ ²
¹ National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Tunable Laser, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150000 China
中国 哈尔滨 哈尔滨工业大学 可调谐(气体)激光技术国家级重点实验室
² Zhengzhou Research Institute, Harbin Institute of Technology, Zhengzhou 450000, China
中国 郑州 哈尔滨工业大学 郑州研究院
³ Advanced Microscopy and Instrumentation Research Center, School of Instrumentation Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150080, China
中国 哈尔滨 哈尔滨工业大学 仪器科学与工程学院 现代显微仪器研究所
Opto-Electronic Advances, 2024-03-20
Abstract
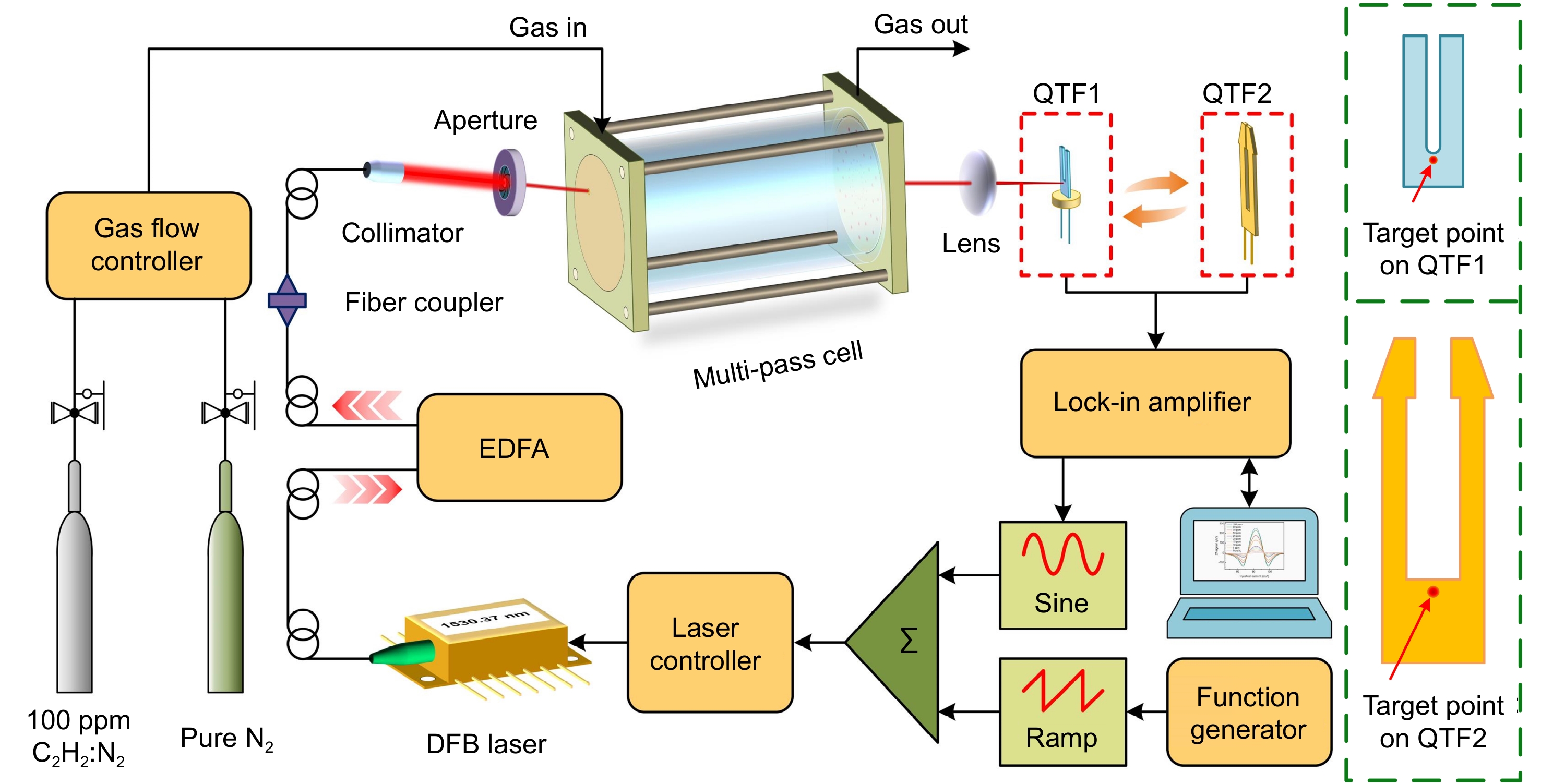
A highly sensitive light-induced thermoelectric spectroscopy (LITES) sensor based on a multi-pass cell (MPC) with dense spot pattern and a novel quartz tuning fork (QTF) with low resonance frequency is reported in this manuscript. An erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) was employed to amplify the output optical power so that the signal level was further enhanced.
The optical path length (OPL) and the ratio of optical path length to volume (RLV) of the MPC is 37.7 m and 13.8 cm⁻², respectively. A commercial QTF and a self-designed trapezoidal-tip QTF with low frequency of 9461.83 Hz were used as the detectors of the sensor, respectively. The target gas selected to test the performance of the system was acetylene (C₂H₂).
When the optical power was constant at 1000 mW, the minimum detection limit (MDL) of the C₂H₂-LITES sensor can be achieved 48.3 ppb when using the commercial QTF and 24.6 ppb when using the trapezoidal-tip QTF. An improvement of the detection performance by a factor of 1.96 was achieved after replacing the commercial QTF with the trapezoidal-tip QTF.
Separation and identification of mixed signal for distributed acoustic sensor using deep learning
Huaxin Gu, Jingming Zhang, Xingwei Chen, Feihong Yu, Deyu Xu, Shuaiqi Liu, Weihao Lin, Xiaobing Shi, Zixing Huang, Xiongji Yang, Qingchang Hu, Liyang Shao
Opto-Electronic Advances
2025-11-25
A review on optical torques: from engineered light fields to objects
Tao He, Jingyao Zhang, Din Ping Tsai, Junxiao Zhou, Haiyang Huang, Weicheng Yi, Zeyong Wei Yan Zu, Qinghua Song, Zhanshan Wang, Cheng-Wei Qiu, Yuzhi Shi, Xinbin Cheng
Opto-Electronic Science
2025-11-25